Azorult Trojan steals user passwords while running in the background like Google Update
AZORult Trojan is a malware released to steal user information on a large scale.Of course, this malicious code was unable to bypass the security experts of the Minerva Labs team.Accordingly, this malicious code will act as a signed Google Update installer and spread on the victim's system by replacing the legitimate Google Updater program on these systems.
AZORult is a Trojan that specializes in data theft and is constantly being improved and developed in recent years.In addition, they are also known as downloaders for other malware in attack campaigns divided into several stages.In fact, AZORult has been involved in complex and large-scale malicious campaigns, spreading malware, data theft and global electronic money.

In essence, AZORult is designed to filter out as much sensitive information as possible on the system, from files, passwords, cookies and browser history to bank information and e-wallets.Once successfully entered into the targeted computer, the Trojan will crawl every corner of the computer and retrieve all the information it deems necessary.
- Android apps contain malicious code that uses motion sensors to avoid detection
Stolen certificate is used to sign fake Google Update binary
According to security experts Asaf Aprozper and Gal Bitensky of Minerva Labs, they received the GoogleUpdate.exe binary signed with a valid certificate from a strange source, and the source was blocked by the Anti-Evasion Platform of Minerva.
The problem is that everything about this GoogleUpdate.exe program shows that it is a legitimate update from Google, has the appropriate icon and is signed with an undocumented certificate.
However, as usual, when examined more closely, the researchers found that the binary was actually signed with a certificate issued to "Singh Agile Content Design Limited" instead of Google.
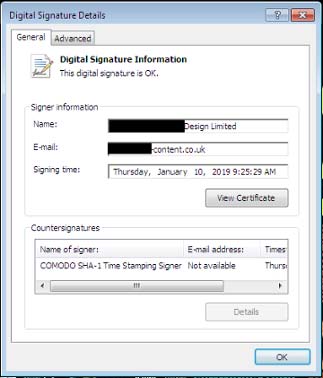
The information shows that this certificate was issued on November 19 and since then, it has been used to sign more than one hundred binary, all of which are disguised as a GoogleUpdate executable file.
- New malware uses Google Drive as a command-and-control server
AZORult Trojan transmits and receives system access privileges through perfect camouflage ability

After further analysis, two experts Asaf Aprozper and Gal Bitensky found that the malware was in a fake GoogleUpdate binary file that was identified as an Azorult Trojan based on many patterns, including an HTTP POST required for / index.php that it created, using .bit domain names (for DNS via blockchain), and Mozilla / 4.0 User-Agent typical.
Researchers were then able to validate their conclusions with malware analysis results obtained through Intezer and VirusTotal, based on the uploaded malware samples for more in-depth testing.
Besides the common data theft habit, the malicious GoogleUpdate.exe program found on one of the client's computers saves the help of Minerva Labs and has an additional ability: It can run Perfect hiding by disguising as a Google Updater program in C: Program FilesGoogleUpdateGoogleUpdate.exe file.
This will allow malware to run with administrative privileges on the system, and become more difficult to detect and eliminate by using this superior stealth mechanism.Researchers have also stated the following:
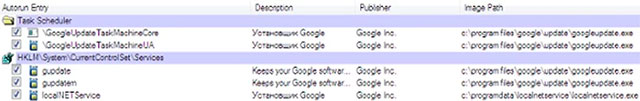
Google usually identifies two tasks to update its products on a schedule, that is:
- GoogleUpdateTaskMachineCore - runs when a user logs in to the system and once a day.
- GoogleUpdateTaskMachineUA - run once a day.
In addition, there are two Google update services that also run this binary, as defined in the following registry values:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesgupdatemImagePath
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesgupdateImagePath
Thanks to the ability to effectively replace Google's update program, this Azorult series is able to operate persistently in the system without bothering users to change the Windows registry or add any tasks. follow your own schedule.
It does this by hijacking Google's created control on the system.In addition, this feature also contributed significantly to improving the efficiency of user infection and anti-malware solutions will be more difficult to determine if something suspicious happens with system.
- Warning: New extortion code GandCrab is attacking Vietnamese Internet users
According to the information that the research team of Minerva Labs pointed out, although this malware is disguised as legitimate programs is not something new, but this is the first time that Azorult linked to this technique, making it a more dangerous and difficult to control Trojan.
To prove its effectiveness, Azorult was recently distributed as a payload for Fallout Exploit Kit, and was popularized as part of a blackmail threat campaign with ransomware GandCrab.In addition, the Trojan has been used in a high-level phishing attack and is very successful against dozens of government services from around the world, and has stolen more than 40,000 information. log in.
See more:
- Malware and user security bugs are found in top free VPN applications
- MySQL vulnerabilities allow malicious servers to steal data from customers
- Microsoft shook hands with VirusTotal in resolving malicious code issues that affected MSI files
- The Internet is experiencing a huge problem with C / C ++, causing developers to "sweat"