Will Huawei be able to produce smartphones without foreign technology?
After the US government's ban, Chinese technology company was hit by a number of US technology companies.
- Google stopped working with Huawei, the phone will not be updated Android, YouTube and Gmail cannot be accessed
- Intel, Qualcomm and Broadcom both cut chip supply contracts for Huawei
- ARM in turn stopped cooperating with Huawei, could Huawei make its own chips?
- Huawei was removed from the SD memory card association, will the future of SD memory card slot disappear on Huawei phones?
- Microsoft also parted with Huawei, following a US government ban
- Huawei was "crossed out" by the Wi-Fi association, voluntarily withdrawing from the JEDEC semiconductor association

This threatens the most important device for Huawei as a smartphone. To find out what difficulties Huawei will face, let's find out what technologies are inside their phones that belong to Americans and other non-Chinese companies through their supply chain picture. Huawei demonstrates the latest flagship model, the P30 Pro.
Script architecture
ARM architecture is present on all chips on mobile devices today.
The "brain" of Huawei P30 Pro is located in Kirin 980, the integrated processor system (System-on-Chip) designed by HiSilicon - Huawei's semiconductor branch. This tiny chip is made up of many components from many technology companies around the world. One of them is the architecture license of CPU and GPU bought by Huawei from ARM to use armv8 script and build its 64-bit CPU. There is also another bus standard that is licensed from ARM as AMBA.
Memory
Huawei buys license from Samsung to design the logic circuit of memory controller and SRAM system. NAND flash memory chip on Huawei smartphone
Toshiba is the manufacturer of NAND flash memory chips for Huawei smartphones and Micron produces DRAM memory.
CPU and GPU

Detailed CPU and GPU in SoC Kirin 980.
In order to have CPU, Huawei must resort to electronic design automation software (EDA - Electronic design automation) of Synopsis, Cadence, and Xilinx, all of which are American companies.
Based on ARM core, Huawei designed Cortex-A76, high-performance cores and Cortex-A55, energy-saving cores. These cores are designed in Austin, Texas (big core) and in Cambridge, England (small core).
Huawei bought Mali-G76 GPU intellectual property rights from ARM designed at ARM headquarters in the UK to create its GPU.
Image processing chip (DSP) and camera
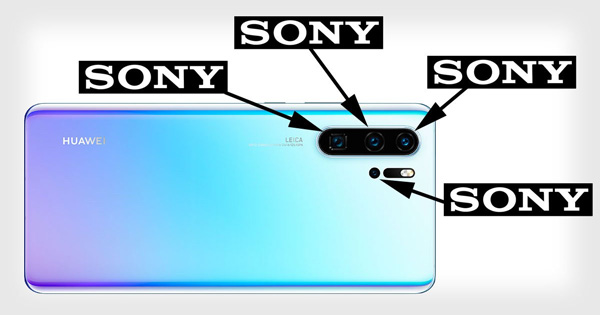
The P30 Pro's camera cluster is largely contributed by Japanese and Chinese companies.
The lens and control system were purchased by Huawei from the German optical company Leica. The lenses are manufactured by Largan Precision in Taiwan and Sunny Optical Technology (licensed by Samsung's subsidiary) in China.
All image sensors, HD video processing chips on Huawei smartphones are supplied by Sony, electric motors to focus on Mitsumi's production. Both companies are from Japan.
Hardware solution for optical image stabilization, autofocus purchased from ON Semiconductors in Phoenix, Arizona, USA.
Image signal processing chip (ISP) by HiSilicon buys copyright from CEVA, California, USA and Cambricon Technologies, Beijing, China.
Screen
The P30 version uses Samsung's hard OLED panels. And the P30 Pro has a curved screen that uses flexible OLED base panels from BOE and LG Display.
Radio frequency chip (RF)
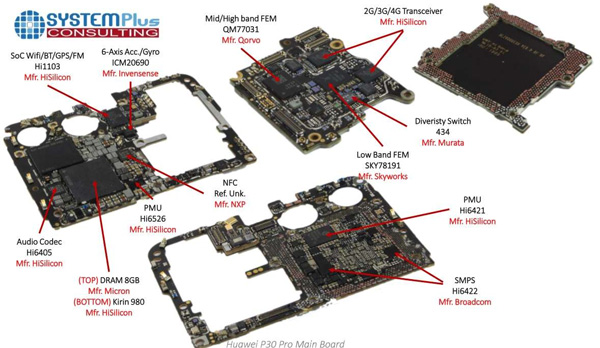
Internal components of Huawei P30 Pro are produced by Japan, Taiwan, China and the US.
Most of the radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) patents are now owned by RF Micro Devices (now becoming Qorvo), USA.
High-quality signal amplifiers and capacitors in RFIC chips are purchased from Murata, Japan.
SAW sensors (surface acoustic wave) are designed and manufactured by TST (Taiwan) and Microgate (China).
The silicon-on-insulator switches are designed by Skyworks Solutions and manufactured by Skyworks in China.
Antenna components for wave reception are designed and manufactured by Sunway in Shenzhen, China-based factories of Rosenberger (USA).
Huawei still has to rely on Japanese, Chinese and American technology firms in the upcoming 5G era.
Baseband chip (baseband)
WIFI, GPS and Bluetooth on Huawei smartphones purchased licenses from Broadcom, USA.
3G network, Huawei bought copyright from Qualcomm, USA. With 4G LTE and 5G, Huawei owns its own technology and designed the Balong wave-catching chip itself. The North Pole Global Positioning System was purchased by the Chinese company from the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
NFC connection and touch
NXP Semiconductors of the Netherlands provides NFC solutions, while Infineon of Germany produces chips. Fingerprint sensors and USB-C solutions are supplied and produced by Chinese companies.
Make
Huawei (and Apple) are both dependent on TSMC's 7nm line (Taiwan).
Taiwan's TSMC, the world's largest chipmaker, is the Kirin 980 "brain" manufacturer for Huawei. To do this, TSMC must import irreplaceable key ingredients from the Netherlands, Japan and Germany.
Assembled
Foxconn, the world's largest assembly company, is responsible for completing products for Huawei, at their Zhengzhou factory, Henan, China.

Before the US ban, not only US partners and many Japanese companies, Europe also have to think about continuing cooperation with Huawei. Under this situation, Huawei will have to find another unit to replace or handle it on its own. However, this is not easy because there are very difficult or irreplaceable companies.
It is hard to predict, can Huawei's supply chain stand and sustain?
You should read it
- ★ Huawei P30, Huawei's most popular flagship of 2019, has set its launch date
- ★ Huawei has an additional 90 days to continue updating software on smartphones
- ★ US officials reportedly agree to cut off Huawei from global chip suppliers
- ★ Huawei P40 series launch: A lot of cutting edge technology but most importantly Google still doesn't have
- ★ Huawei P40 Pro configuration leak, Kirin 990 5G chipset, 5,500mAh graphene battery, 50W fast charging