What is NFC? How does NFC work?
NFC is a mainstream wireless technology, thanks to the development of online payment systems like Samsung Pay and Google Pay, especially when it comes to high-end devices and even more mid-range options. You may have heard this term before, but what exactly is NFC? Let's find out through the following article
What is NFC?
NFC stands for 'Near Field Communication'. It allows short-range communication between compatible devices. This requires at least one transmitting device and another device to receive signals. A range of devices can use the NFC standard and will be considered passive or active.
Passive NFC devices include things that can send information to other NFC devices without requiring their own power source. However, they cannot process any information sent from other sources and cannot connect to other passive components. They are usually in the form of interactive signs on walls or advertisements.
Active devices can send and receive data, and can communicate with each other as well as other passive devices. Smartphones are the most common form of active NFC device. Card readers on public transport and payment terminals are also good examples of this technology.
How does NFC work?
Now you know what NFC is. Next let's find out how it works. Like Bluetooth, WiFi or all other types of wireless signals, NFC operates on the principle of sending information via radio waves. NFC is a wireless data conversion standard.
This means that devices must adhere to certain specifications in order to communicate with each other properly. The technology used in NFC is based on older RFID (Radio-frequency identification) ideas, which use electromagnetic sensors to transmit information.
This marks a big difference between NFC and Bluetooth / WiFi. NFC can be used to generate current in passive components as well as send data, meaning that passive devices do not require a separate power source. Instead, they can be powered by the electromagnetic field generated by an active NFC component when it is within range. Unfortunately, NFC technology doesn't have enough inductance to charge smartphones, but the QI wireless charging feature is based on the same principle.
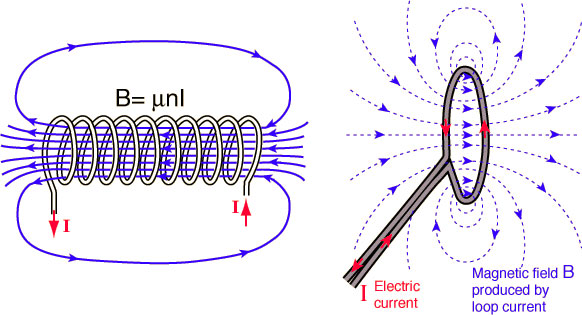
Electromagnetic fields can be used to transmit data or generate current in a receiving device. Passive NFC devices draw energy from fields created by active devices, but within a short range.
The data transmission frequency on NFC is 13.56Mghz. You can send data at 106, 212 or 424 kilobits per second. That speed is fast enough to perform a range of data transfer actions - from contact details to photos and music.
To determine what kind of information will be exchanged between devices, the NFC standard now has 3 separate operating modes. Perhaps the most common use in smartphones is peer-to-peer mode. This allows two NFC-enabled devices to exchange various information. In this mode, both devices switch back and forth between the active state when sending data and the passive when receiving.
On the other hand, read / write mode is one-way data transmission. The active device, maybe a smartphone, connects to another device to read information from that device. NFC ad tag uses this mode.
The final operating mode is card simulation. The NFC device can act as a contactless or smart credit card and make payments or access public transportation systems.
Compare with Bluetooth
For the difference between NFC and Bluetooth, refer to the article: Differences between NFC and Bluetooth.