Understanding Network Operating System Network Operating System (NOS)
You have heard a lot about the network operating system (NOS) but not fully understand it. Therefore, this article will explain the concept as well as mention the features of this operating system.
- Networking basics - Part 16: Connecting to the Windows operating system network
- Understanding the OSI Model (Network Knowledge Part 17)
- Network basics: Part 18 - Sharing resources
What is the network operating system Network Operating System?
A network operating system is a specialized operating system for a network device such as a router, switch or firewall.
The network operating system is designed for the sole purpose of supporting workstations, sharing databases, sharing applications and files, accessing printers with multiple computers on a network. Some operating systems are independent, such as Microsoft Windows NT and Digital OpenVMS, which can function as network operating systems. Some of the most famous network operating systems include Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows Server 2008, Linux and Mac OS X.
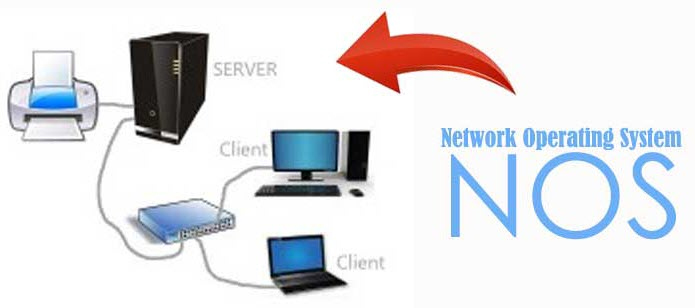
Previously, the network-connected operating system was called the network operating system because it allowed the personal computer (PC) to join the computer network and share the file, accessing the printer in the local network. (LAN). Today's popular operating systems include a network stack to support the client-server model.
Early computer operating systems such as CP / M, DOS and Mac OS were designed for one user on one computer. Packet switching network was developed to share hardware resources such as large and expensive computers, printers or hard drives. When local area network technology appears, there are two ways to share resources on the network.
Previously, a network operating system was the operating system for a computer, implementing network capabilities. Operating systems with stacked protocols allow personal computers to participate in the client-server architecture, in which the server allows multiple clients to share resources such as printers.
Peer-to-peer operating systems use network connectivity to share resources and files on personal computers. This system is not based on file servers or centralized management resources. Peer networks establish all the same connected computers, all of which share the same ability to use available resources on the network. For example, a peer-to-peer peer-to-peer operating system like AppleShare is used to connect Apple devices, LANtastic supports DOS, Microsoft Windows and OS / 2 computers.
Today distributed computing and groupware applications become the norm. In the 1980s, the demand for computers was network capable and the number of network devices increased rapidly. Partly because it allows interaction with the TCP / IP protocol suite that is commonly used in network architectures. Therefore, the computer operating system and firmware of the network device should support the TCP / IP protocol.
Network operating system features
The outstanding features of the network operating system are:
- Basic features such as protocol support, processor support, hardware detection and multi-processor support for applications.
- Security features such as authentication, limit, authorization and access control.
- Features for files, web services, printing and copying.
- Manage directory services and names.
- User management features along with rules for remote access and system management.
- Network connectivity features such as routing and WAN ports.
- Clustering capability.
Common tasks related to network operating systems include:
- User management.
- Operating system maintenance as backup.
- Task related to file management.
- Security monitoring on all resources in the network.
- Set the priority to print jobs in the network.
Network device operating system
Network operating systems can be embedded in routers or hardware firewalls that operate functions in the network layer (layer 3).
Exclusive network operating system
- Cisco IOS, a group of network operating systems, is used on most Cisco Systems and Cisco's existing network switches. Previous switches have run the CatOS Catalyst OS.
- pfSense, a branch of M0n0wall using PF.
- IPOS, used in Ericsson routers.
- FortiOS, used in Fortigates from Fortinet.
- TiMOS, used in Alcatel-Lucent routers.
- The platform Versatile Routing Platform (VRP), used in Huawei's routers.
- RouterOS, the software turns the PC or MikroTik hardware into a router.
- ZyNOS, used in ZyXEL network devices.
- Extended operating systems are used in switches from Arista.
- Network operating system Drivenets (DNOS) is their cloud-based separation router software.
Operating system based on NetBSD or Linux
- DD-WRT, Linux based DD-WRT kernel is a Linux-based firmware for wireless routers and access points as well as low-cost networking devices such as Linksys WRT54G.
- DNOS (Open Network Installation Environment), DNOS 9 is based on NetBSD, while DNOS 6 runs Linux kernel.
- EOS (Extended operating system), running on all Arista Networks products.
- The FTOS or Force10 operating system, which is the firmware used on Force10 Ethernet switches.
- ExtremeXOS (EXOS) is used in network equipment manufactured by Extreme Networks.
- Openwrt is used to route IP packets on embedded devices.
Open source network operating system
- The Cumulus Linux distribution uses the entire Linux TCP / IP stack.
- Open Linux network (ONL).
- OPX (OpenSwitch), a Linux Foundation operating system project of the Linux Foundation, for switches compliant with Open Compute Project organization and using ONIE boot loader. The project is supported by Dell EMC, Cavium and Metaswitch.