Top 12 hottest things in the universe
Fever is 115 degrees Celsius, the hottest place on Earth reaches 70.5 degrees Celsius, sunspots on the Sun have a temperature of nearly 4 million degrees Celsius, . are the hottest things in the universe when considering each their hot side.
- Gravitational waves can be the key to revealing the existence of another dimension in the universe
- Scientists have found evidence to prove the existence of the parallel universe
1. The most spicy chili

The most spicy chilli currently known as "Dragon's breath" measures up to 2.48 million units of heat on the Scovilles scale (a measure of capsaicin levels, chemicals that release spicy feeling when we bite peppers).
2. The highest fever
The record holder for the highest number of fever was Willie Jones, his body heated up to 115 degrees while the normal human body temperature ranged from 36.1 to 37.2 degrees Celsius. When he had a fever to this temperature, Willie Jones' body experienced a lot of serious complications like hallucinations, epilepsy, . Fortunately, after 24 days of treatment in the hospital he survived.
3. The highest temperature created in a laboratory
In an experiment by the European Nuclear Research Organization - CERN, scientists created the highest artificial temperature at a large particle accelerator, reaching 9.9 trillion degrees Fahrenheit, this heat level. 366,000 times higher than the Sun.
The scientists carried out this experiment aimed at creating a frictionless liquid, a primitive particle called a quark – gluon plasma.
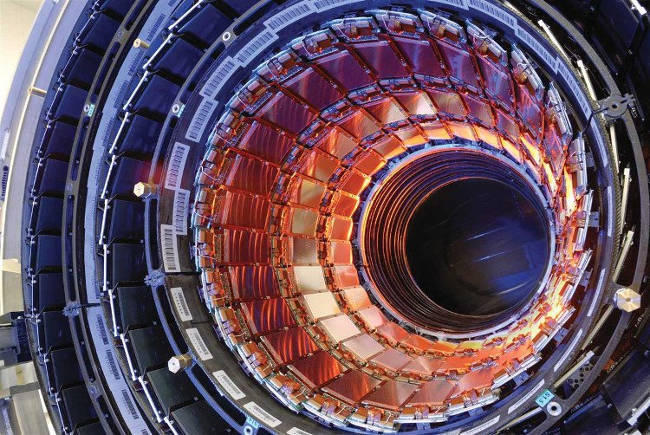
Large particle accelerator.(Photo: CERN.)
4. The hottest steam
On the ocean floor there are cracks in the Earth's crust, where magmatic mixes into the water and boil seawater to the highest limit under the tremendous pressure of the ocean, called hot spots. The average temperature here is about 407 degrees Celsius, but at some point there are often explosions and temperatures up to 464 degrees Celsius.
The highest temperature hot spot is at Two Boats (Two boats) and Sisters Peak (Sisters Peak).
 A crack in the Earth's crust lies deep beneath the ocean floor.(Photo: NOAA.)
A crack in the Earth's crust lies deep beneath the ocean floor.(Photo: NOAA.)
5. The highest temperature in America
On July 10, 1913, in California's Death Valley area, a temperature of 56.6 degrees C was measured, making the valley's low-lying area as a high-temperature autoclave.
Usually in July every year, it also recorded a record high heat but only an average of 51.6 degrees Celsius.
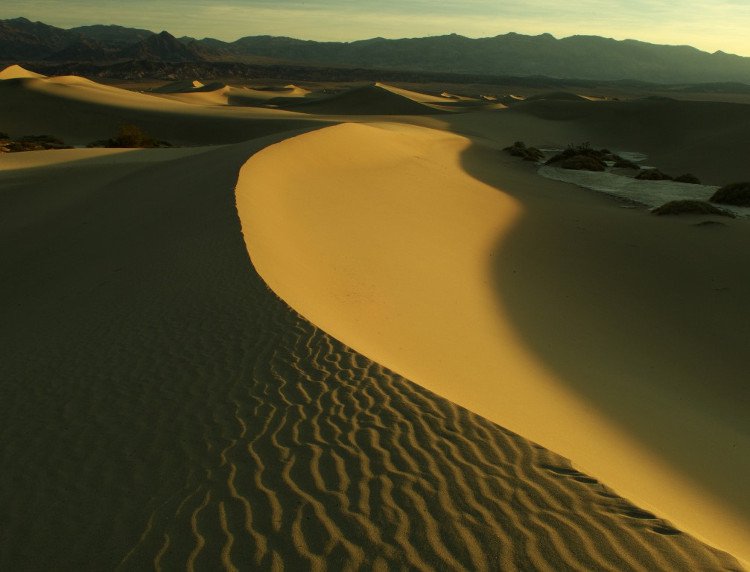

Death Valley, United States.(Photo: NPS.)
6. The hottest place on Earth
Iranian Lut Desert has surpassed the brightest candidates such as Mars Diem Son in China and the desert regions of Queensland, Australia to become the hottest place in the world. In 2005, people measured temperatures as high as 70.5 degrees Celsius in Lut desert.
When the air temperature reaches such a high level, the surface temperature will certainly be hotter, possibly even lethal.
7. The hottest planet in the Solar System
460 degrees Celsius is the highest temperature on Venus, strangely, the temperature is even higher than Mercury (426 degrees C), which is the closest to the Sun. Our probe can only walk on this planet for as long as two hours.
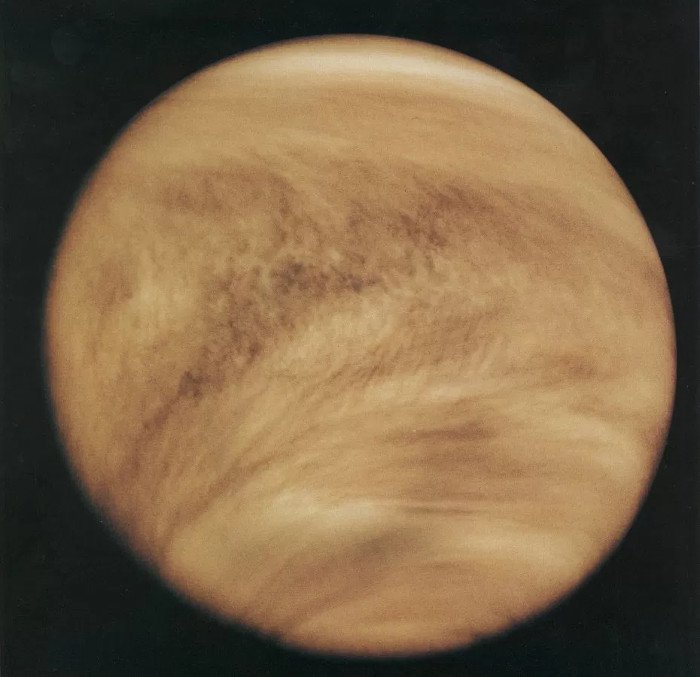

Venus is the solar system's hottest planet.(Photo: NASA.)
In the past, Venus was once a planet that could survive life until it was trapped in carbon dioxide. Gradually this gas increased so high that it turned it into an autoclave that could melt lead.
- The surface of Venus: Why is Venus the hottest planet in the solar system?
8. The highest temperature on the Sun.
The surface of the Sun has an average temperature of about 5,540 degrees Celsius, but inside its core, the temperature soars to millions of degrees Celsius.
In addition, its coronary belt (outer atmosphere) also has a high temperature of nearly 1 million degrees Celsius. This is the hottest place in the Sun's atmosphere.
The dark areas on the Sun's surface are called Sunspots, the temperatures in these areas reach nearly 4 million degrees Celsius.
NASA's Parker probe with a carbon shield can only approach and ring the Japan 6.440 million km to get a close-up view of the star's surface.
9. The hottest star ever known
Eta Carinae is a super-giant blue-green star who is at an explosive stage and becomes a supernova at any time. It is 7,500 light-years from Earth, has 100 times the mass of the Sun but its size is only about 50 to 80 times that of the Sun. The temperature of this star's surface is up to 40,000 degrees Celsius.
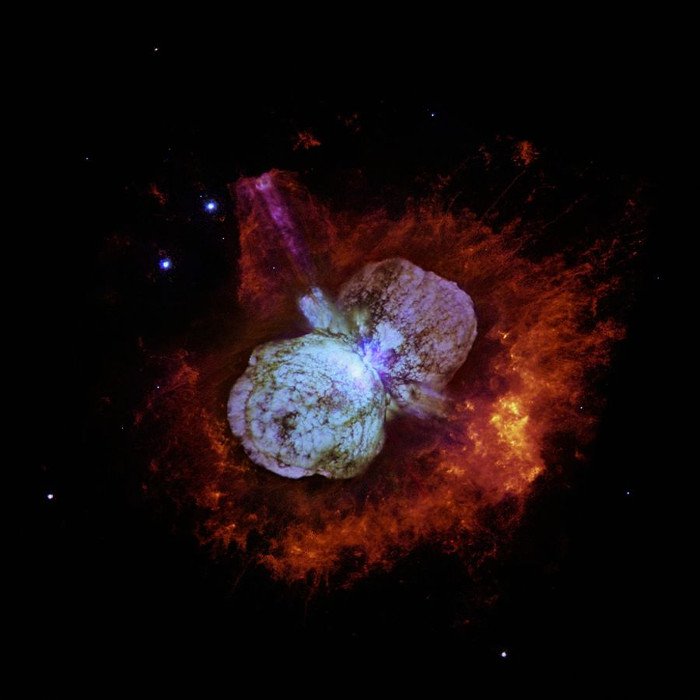

Eta Carinae is the hottest star ever known in the universe.(Photo: NASA.)
10. The hottest planet ever known
The KELT-9b planet is a young planet (only 300 million years), located outside the Solar System 650 light years away.
Due to being too close to the parent star, the temperature reached nearly 10,000 degrees Celsius and the age was relatively young, so the KELT-9b received a lot of energy to make this planet with temperatures of more than 4,000 degrees Celsius, less than the temperature. of the Sun surface about 1,200 degrees Celsius.
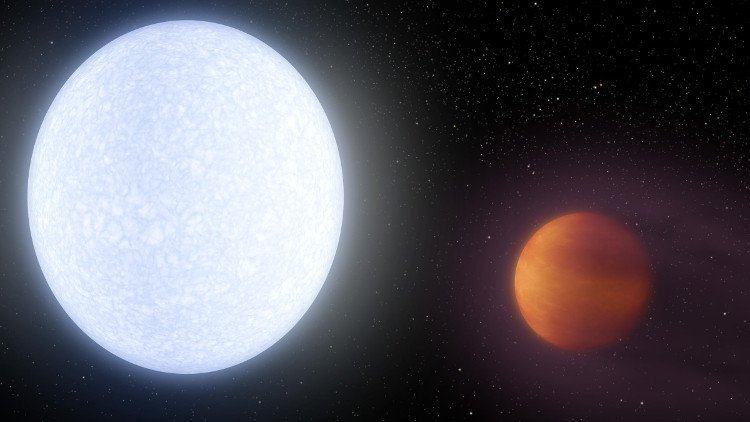

Exotic planet KELT-9b moves around the host KELT-9.(Photo: ESA.)
11. The hottest nebula ever known
At the center of the Red Spider Nebula there is a dead star with a surface temperature of 140,000 degrees Celsius, 25 times the temperature of the Sun.
This white dwarf is the hottest object in the universe. It is as small as Earth but the core of a star has lost its atmosphere after an event.
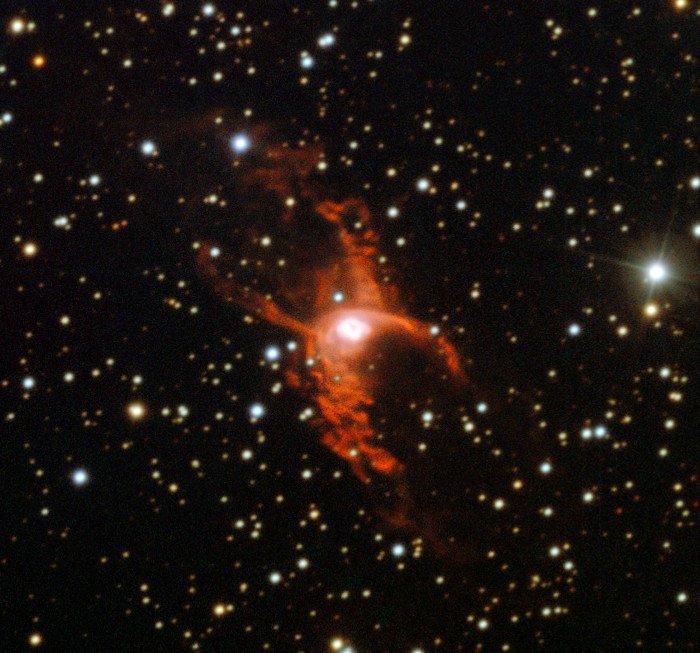

The Red Spider Nebula is the hottest known nebula due to its star inside.(Photo: NASA.)
Due to the influence of the high temperature of the dead star inside it, the Red Spider Nebula becomes the hottest nebula in the universe ever known.
12. The hottest crystal standard ever known
From 2 trillion to 22 thousand billion degrees Celsius, it is the temperature in the surrounding area of 3C 273 crystal standard. This temperature is so high that the material cannot form plasma.
Standard quasar (English name is Quasar - a star-like object) is an extremely distant and extremely bright object, with a huge redshift characteristic. In the visible light, the quasar looks like a normal star, the source of light. In fact, it is the light emitted from solid matter halo, located around the nucleus of active galaxies (young galaxies), often super-massive black holes.
The first Quasar was discovered in 1963 by the American astronomer of the Netherlands Maarten Schmidt in the constellation Virgo, from Palomar observatory, denoted by 3C 273. By 2005 more than 100,000 quasars were discovered.
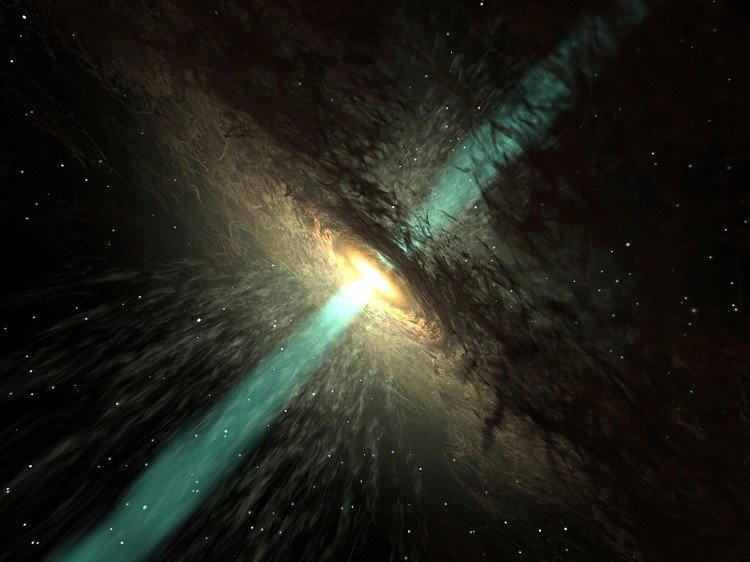

Standard 3C 273. (Artwork.)
You should read it
- ★ 12 interesting records of planets in the universe
- ★ The Earth has just recorded the hottest January in history
- ★ Do you know the 15 hottest programming languages on this GitHub?
- ★ 2017 may be the hottest year in the record breaking history of 2016
- ★ The interesting fact about the universe is not quite the same as what we thought