The best science pictures of the past year
Get into the finals of the Wellcome Image 2017 Award, pictures of science but equally this art gives viewers a lot of interesting surprises. Photos taken from glowing ink, high-tech contact lenses to a tiny brain on a chip . are highly regarded in terms of technique, quality, visual level, and attractiveness. , connect ability.
The results of this award will be announced on March 15 at the Wellcome Trust in London. Here are some very popular impressive scientific photos.
Blood vessels in pig eyes
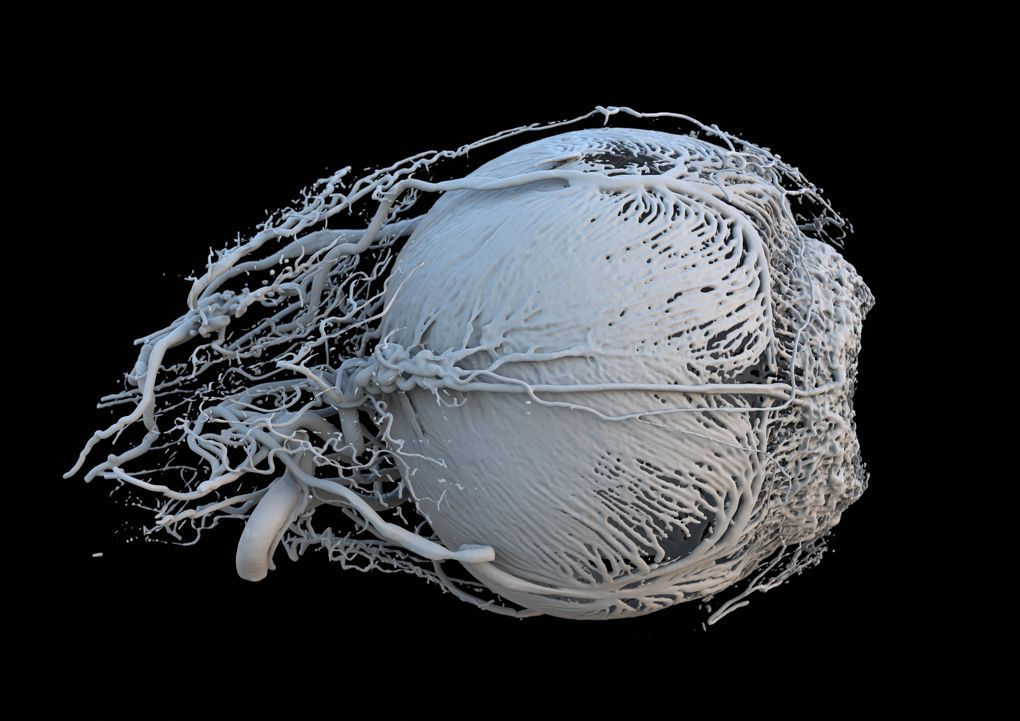
Impressive images of blood vessels in pig eyes are used by researchers from Switzerland using computerized tomography (CT) and 3D printing. These blood vessels carry nutrients and energy to the muscles around the iris, controlling the amount of light entering the eye. The rightmost is the pupil.
The retina surface of the mouse

To create an image of the retina of the mouse, scientists must use more than 400 microscopic images to put together.
- The blue lines are the blood vessels.
- Red and green lines are astrocytes, specialized cells of the nervous system.
Scientists hope, by studying the changing function of astrocytes in retinal degeneration, they will find new treatments for vision-related diseases.
The language pathways of the brain
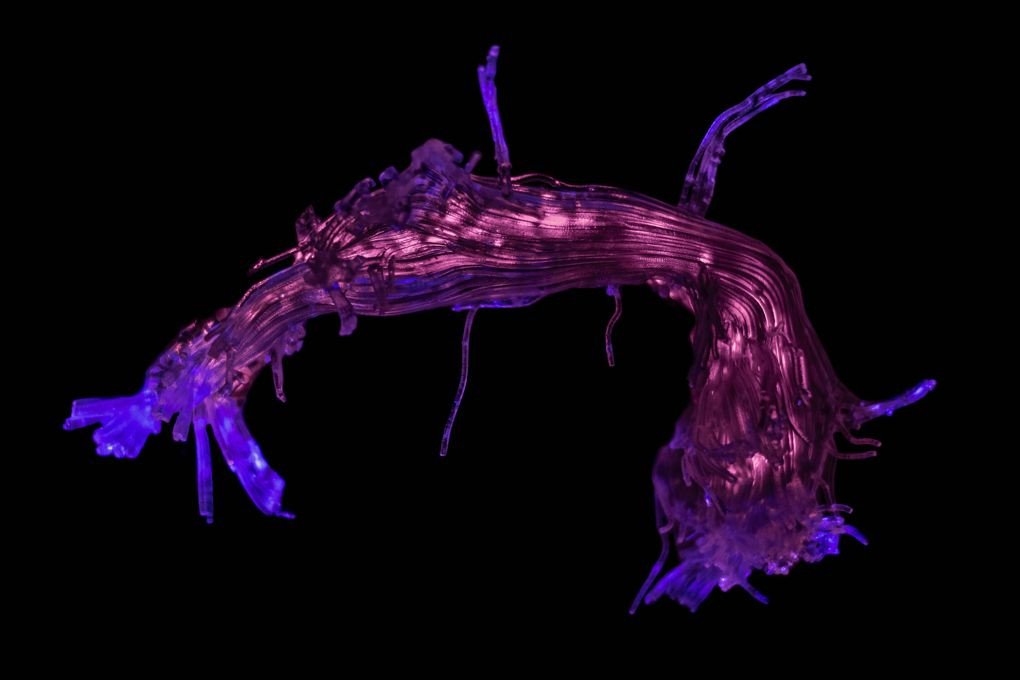
3D printing model recreates the regional connection of speech and language. Scientists used a scanner to track the movement of water molecules inside the brain, this technique called an axon map.
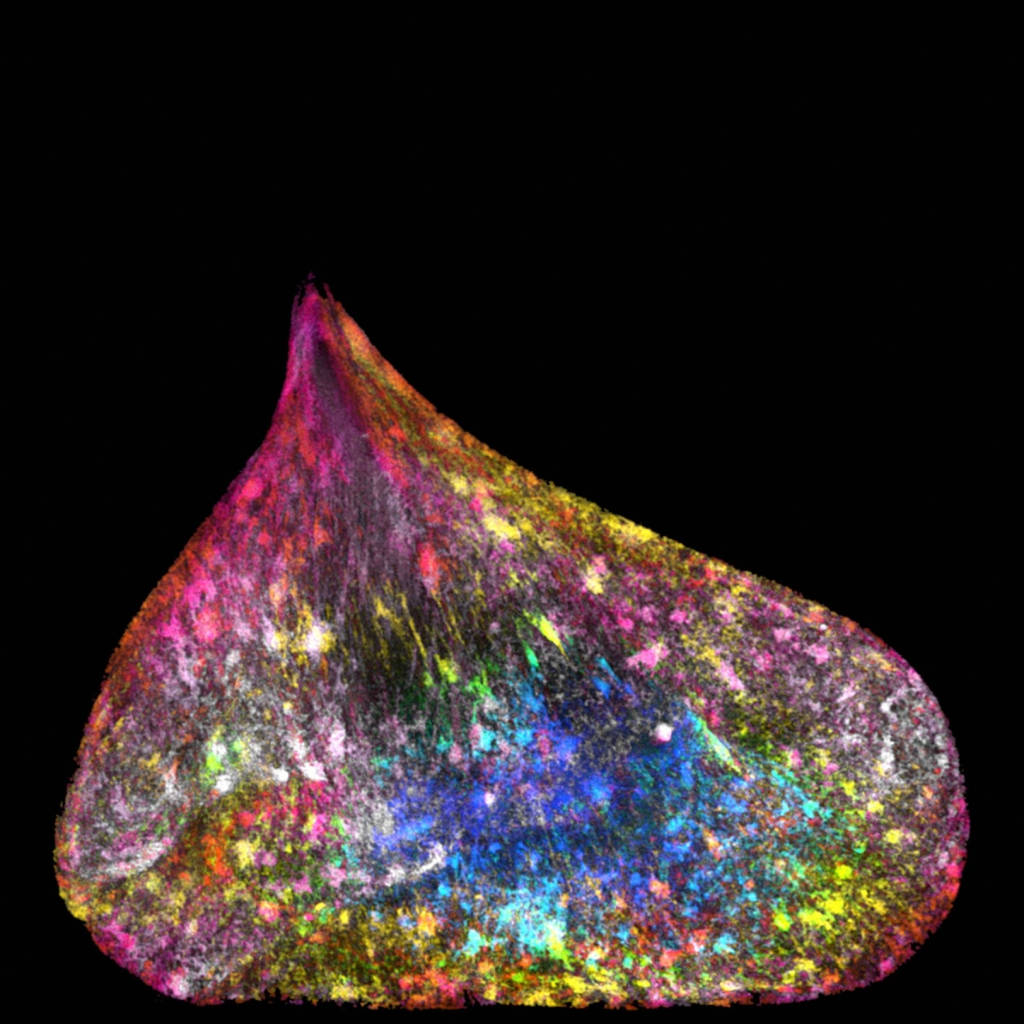
Rainbow placenta
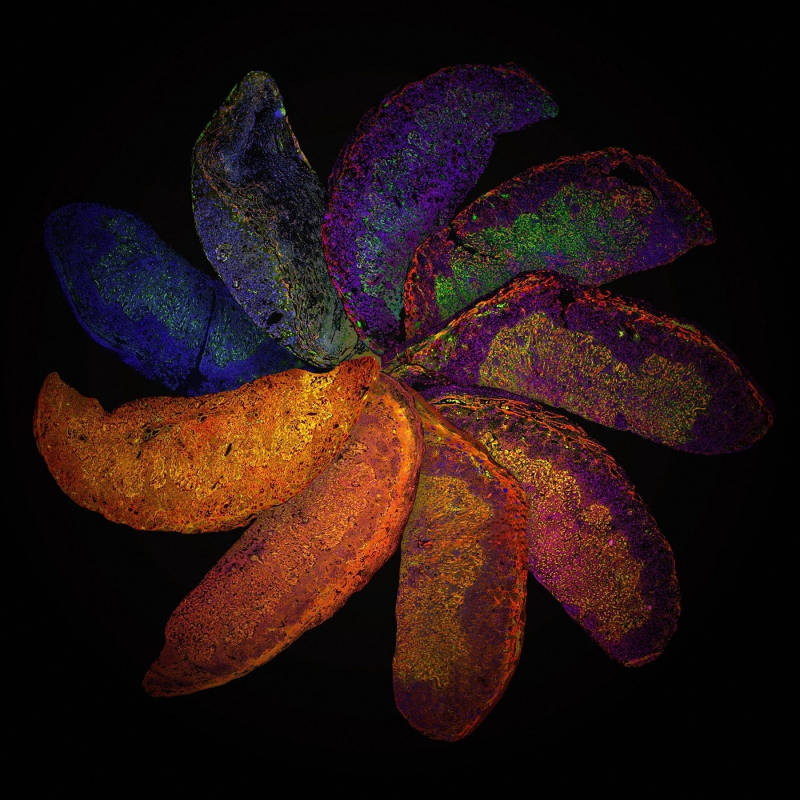

These are the placenta of genetically modified mice, each with a different immune system. This picture helps researchers to see that differences in placental development may be a result of the immune system from the mother. From there they can better understand and find ways to treat complications that arise in human pregnancy.
The development of the spinal cord
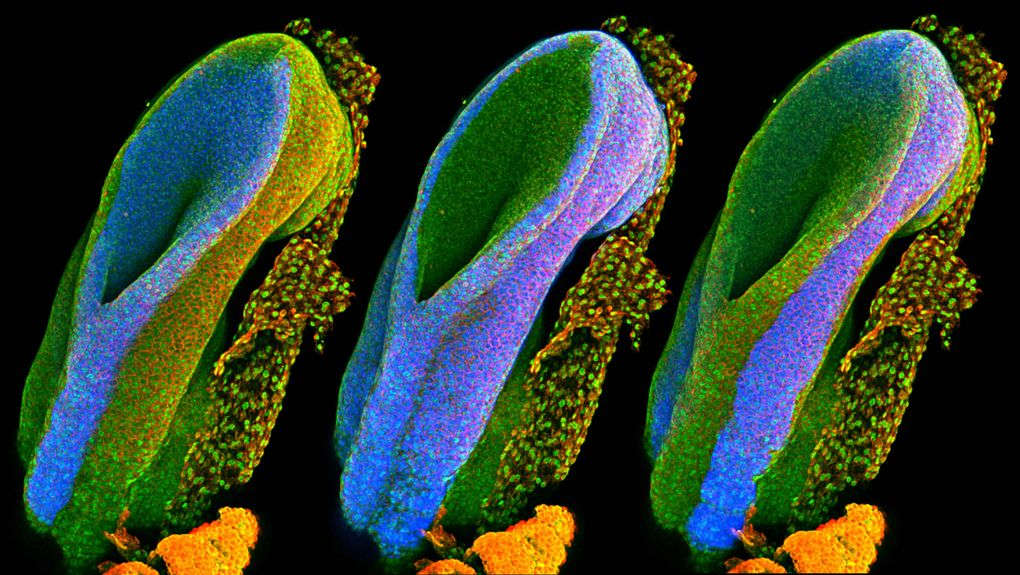
In the image is the beginning and end points of the neural tube (the part that forms the spinal cord in the first month of pregnancy) of the rat. The first image on the left will develop into the brain, spine, and nerves, in the middle will form organs and images will eventually form teeth, hair and skin.
Uncoded DNA in human lung cells
The nucleus of new lung cells comes with DNA. Cell deformation is the result of prolonged stress, caused by strands of DNA being pulled between two cells.
Seahorse eyes
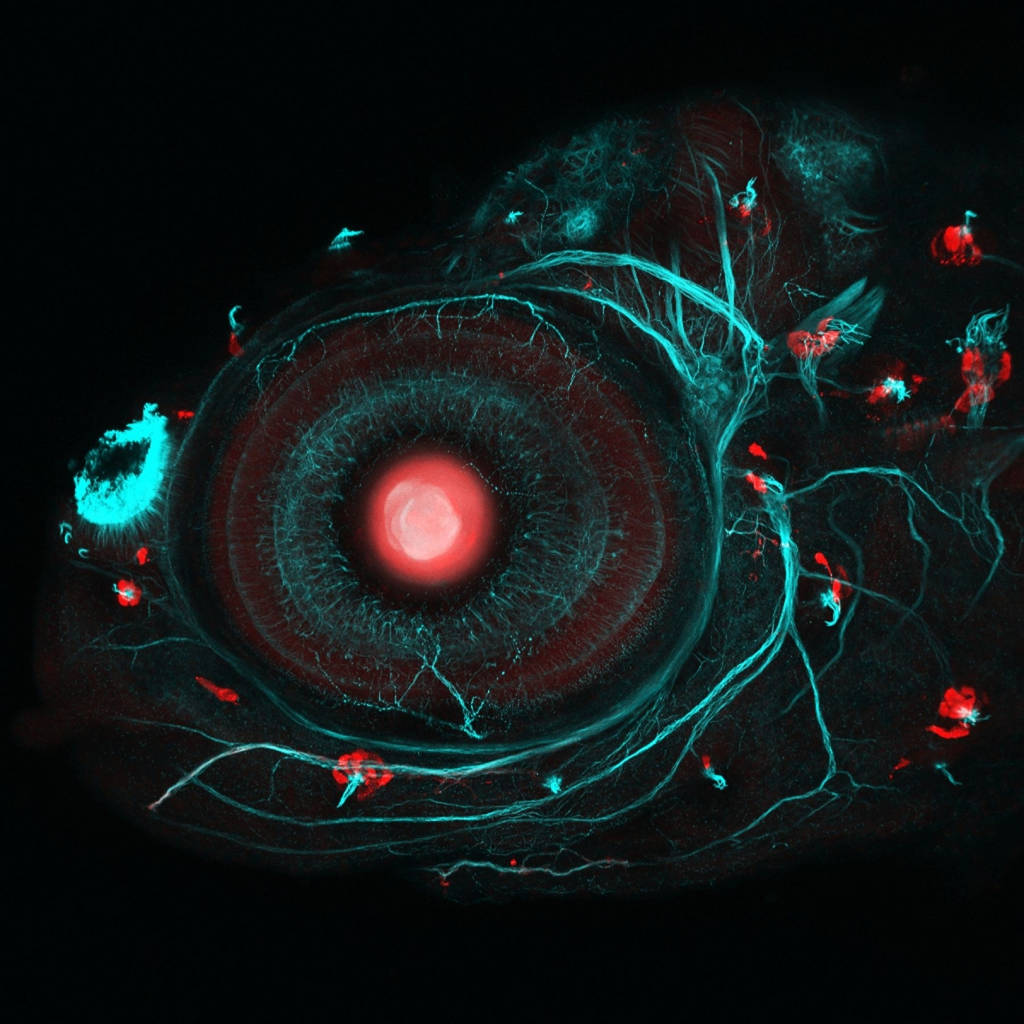
Scientists from the University of London used the CRISPR-Cas9 transgenic system and intentional insemination to create a seahorse that glows fluorescent red.
Above is an eye photo of a four-day-old four-year-old seahorse.
- Big red dot: retina of the eye.
- Small red dots: cells called sensory nerves, help fish react to water movement.
- The road is green: the nervous system of fish.
Iris clip
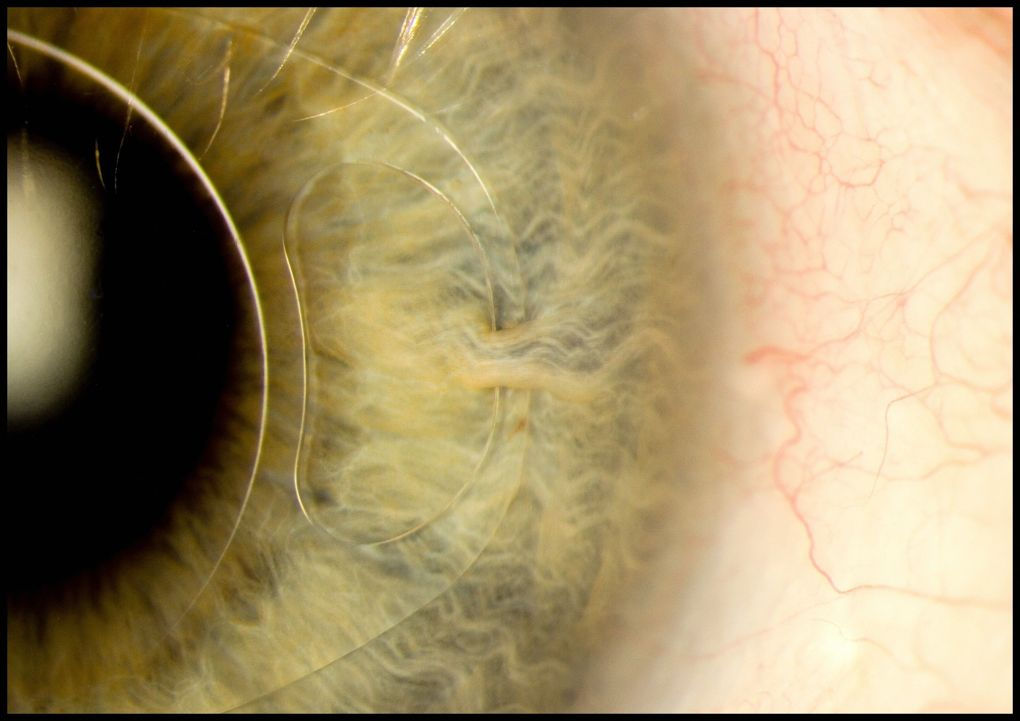
In the image is the iris clip, the artificial intraocular lens (IOL) fixed with the iris through a small incision. This device is used to treat myopia and cataracts.
Cat's skin
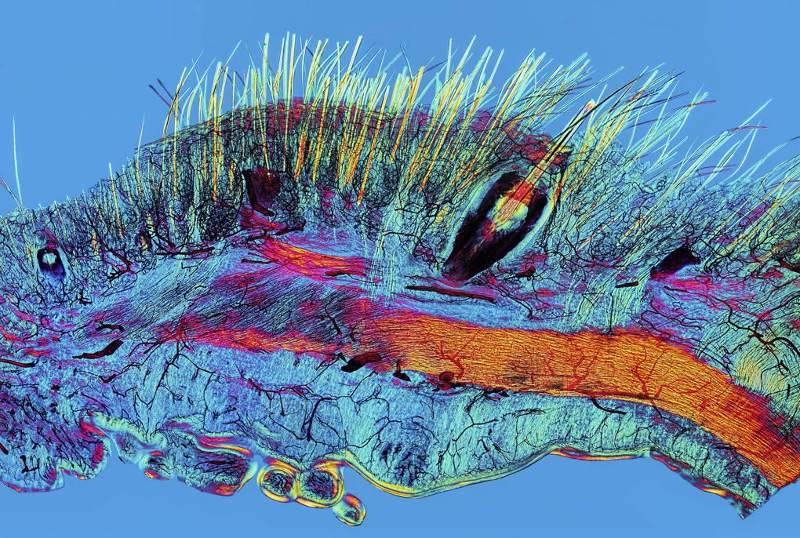

Scientists used polarizing microscopy, a type of microscope, in which the filter only allows light to travel in a specific direction to penetrate the cat's skin. In the photo, fur (yellow), beard (yellow) and blood vessels (black).
Connection of breast cancer via twitter
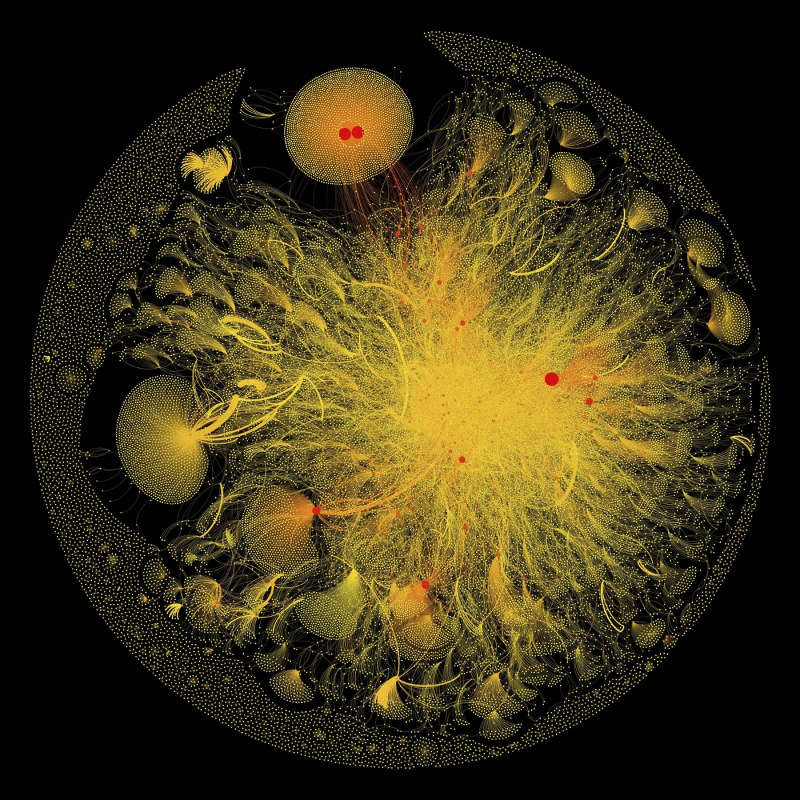
Visual graphics data collected from small items with hashtag # cancer.
- The dots represent the twitter users.
- The connecting lines represent the relationships between users.
- The buttons have different sizes according to the number and importance of the nodes they are connected to.
- The thickness of each connection is determined by the number of times that the two use interact or mention each other.
- The "double yolk in egg" structure in the upper part of the picture shows the general interests of the two accounts.
MicroRNA - Cancer remedy
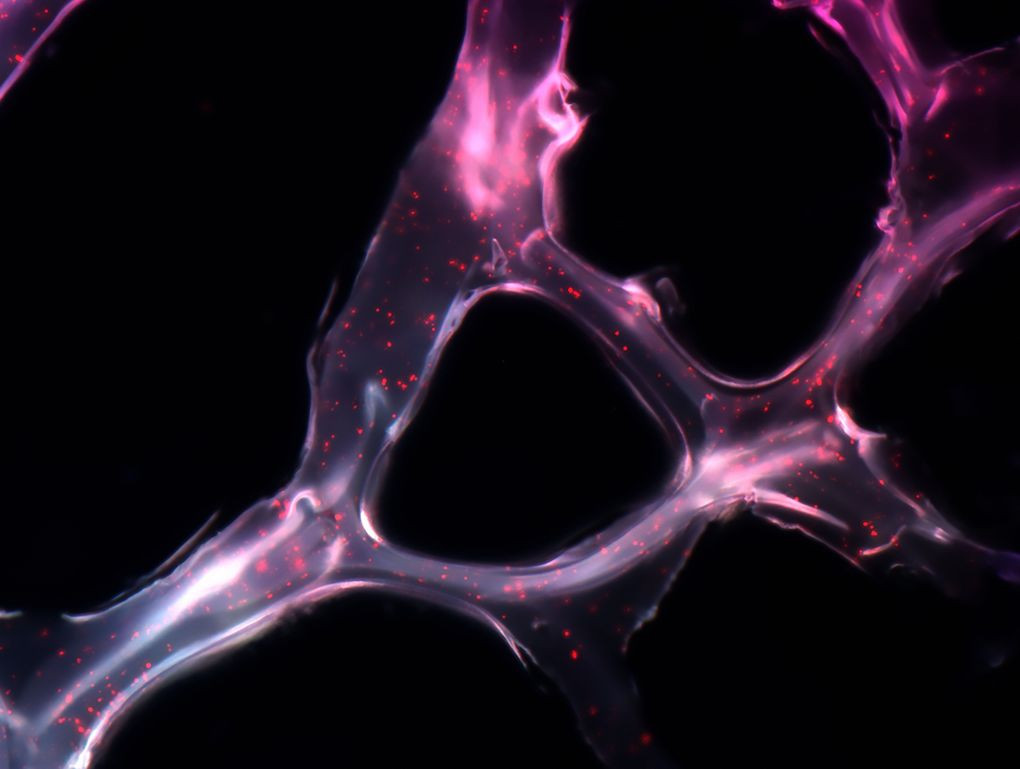
This synthetic network is called microRNA, which can cover a tumor and carry short genetic sequences to cancer cells.
This cancer treatment has been tested on mice. The results were very positive, within two weeks the tumor had shrunk to 90%.
The thermostat of pigeons
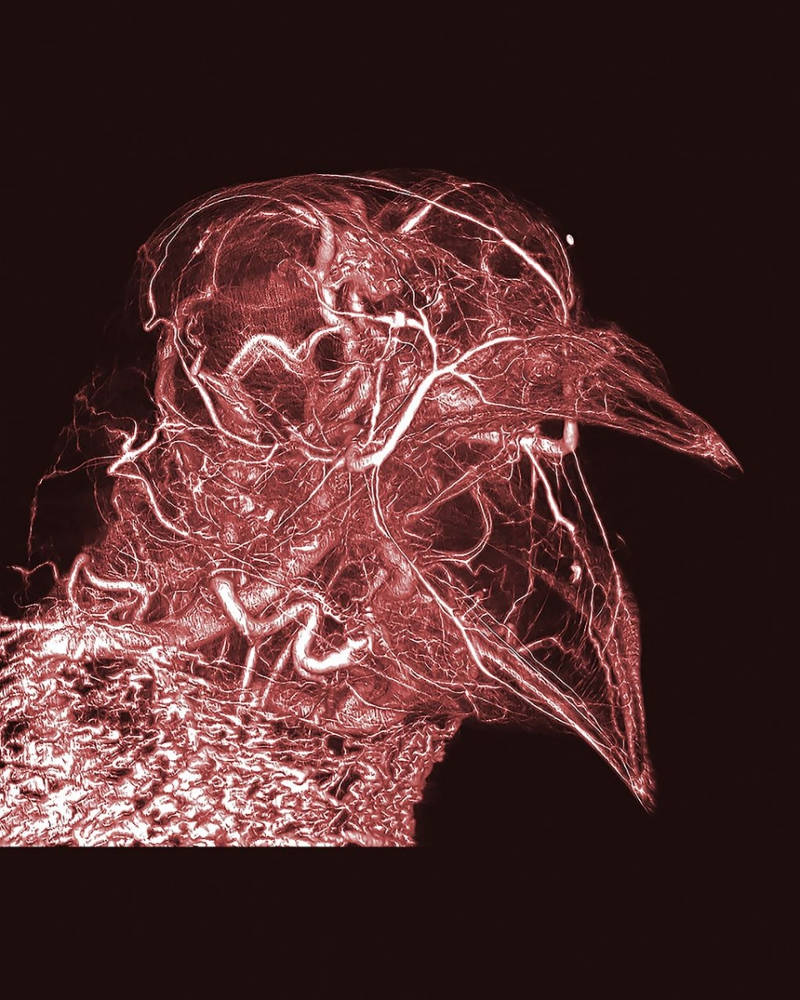
In the picture is the whole network of blood vessels, even capillaries, in a dove. At the bottom of the picture is a complex network of blood vessels in the pigeon neck. Located just under the skin is an abundant supply of blood that helps the pigeon adjust its body temperature through the process of thermostats. To get this detailed image, researchers used CT scanners and modern digital images.
Bobtail Hawaiian squid
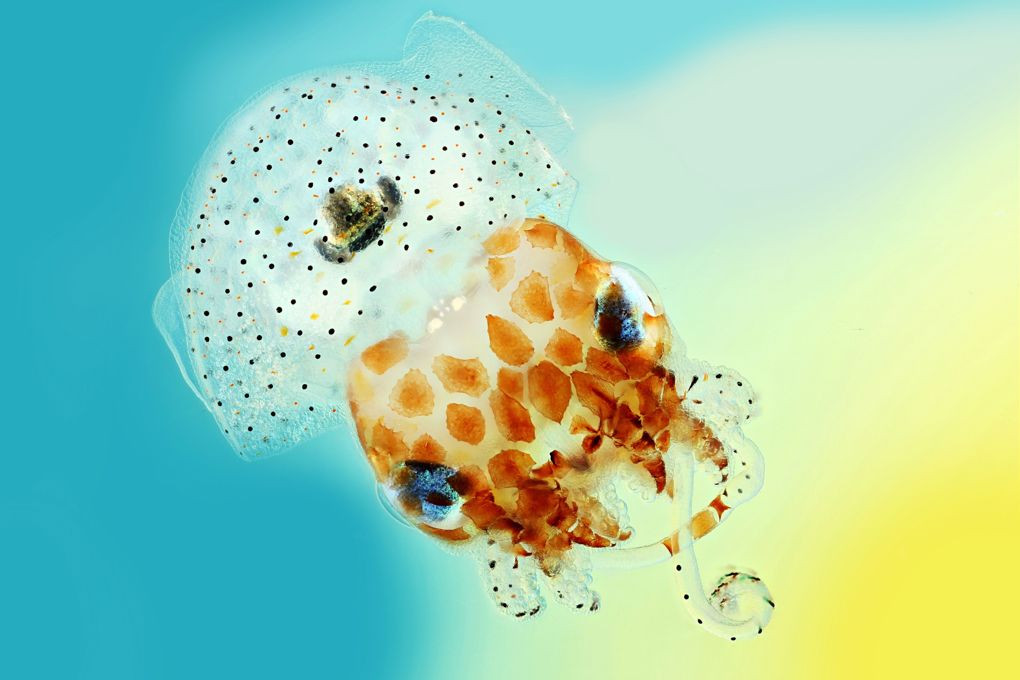

During the day, Bobtail Hawaiian squid bury itself in the sand, when night falls they begin hunting. Their favorite food is shrimp species near coral reefs. To avoid being detected by marine animals, their glowing organ is located below, mimicking the surrounding night light both in intensity and wavelength. Their glowing organ is home to the bright bacteria called Vibrio fischeri. They give bioluminescence to squid in exchange for shelter and food.
Brain on a chip
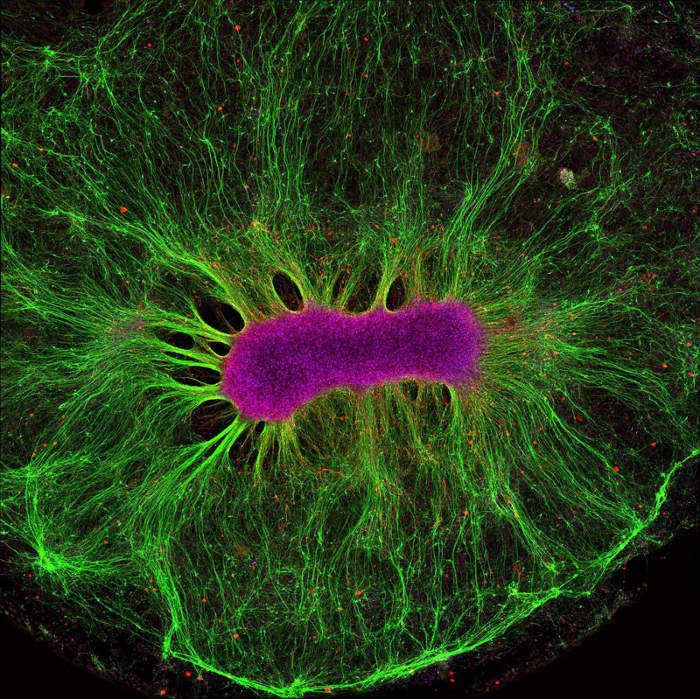
A stem neuron develops on a synthetic gel. Stem cells (dark red) have the ability to produce nerve fibers (green) outside the body.
Currently, researchers are learning how to shrink parts on chips, helping them connect with each other. These systems can be used to accurately predict the effectiveness and toxicity of drugs and vaccines, thereby eliminating animal tests in medical research.
Blood vessels of an African gray parrot
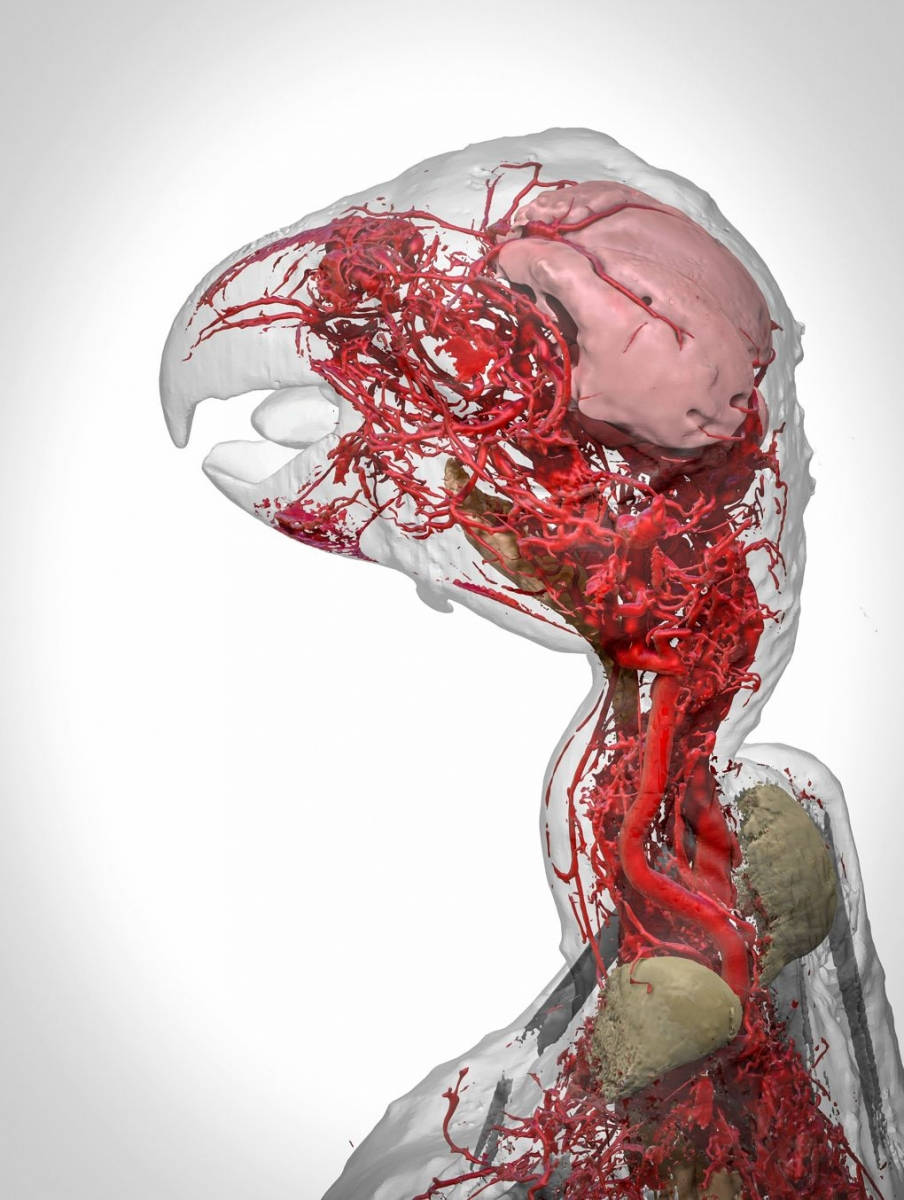
A 3D image reproduces the detailed vascular system details in the head and neck of an African gray parrot. This is done using a new contrast agent called BriteVu, which allows scientists to study the patient's vascular system in great detail.
- The world of microbes shimmering and fantasy on your teeth
- Photos of "The Old Earth and Now": How has the earth changed over the last 100 years?
- 17 stunning photographs taken under a microscope reveal a whole new world
You should read it
- ★ Using electricity to stimulate the spinal cord helps the paralyzed person walk
- ★ Anti-rejection drugs can reduce spinal cord injuries
- ★ Successful manufacture of new medical ink marks the goal of radiotherapy to treat skin cancer
- ★ Common antihypertensive drugs are linked to skin cancer risk
- ★ Artificial intelligence can help detect melanoma skin cancer