Scwcmd register command in Windows
(Applies to: Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012)
The Scwcmd register command helps to expand or customize the Security Configuration Database of the Security Configuration Database (SCW) by registering the Security Configuration Database file containing definitions. about roles, tasks, services or ports.For a better understanding of how to use this command, see the example section below.
Syntax of the Scwcmd register command
scwcmd register / kbname: [/ kbfile:] [/ kb:] [/ d]
The Scwcmd register command parameter
Parameters
Describe
/ kbname:
Specify the name by which the Security Configuration Database extension will be registered.
/ kbfile:
Specify the path and name of the Security Configuration Database file to be used to expand or customize the base Security Configuration Database.To verify that the Security Configuration Database file complies with the SCW schema, use the% Windir% securityKBRegistrationInfo.xsd schema definition file.This option must be provided unless the / d parameter is specified.
/ kb:
Specifying the path to the folder containing the SCW security configuration database files will be updated.If this option is not specified, file% Windir% securitymsscwkbs will be used by default.
/ d
Unsubscribe an extension of Security Configuration Database from the security configuration database.The unregistered extension will be specified by the / kbname parameter (do not specify the parameter / kbfile).Database configuration security to unsubscribe from the extension specified by the parameter / kb.
/?
Show help at thecommand prompt.
An explanation of the Scwcmd register command
Scwcmd.exe will only be available on computers running Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2003.
Example of the Scwcmd register command
To register the Security Configuration Database file named SCWKBForMyApp.xml under the name MyApp in the location kbserverkb, type:
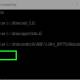
scwcmd register /kbfile:d:SCWKBForMyApp.xml / kbname: MyApp / kb: kbserverkb
To unsubscribe from the Security Configuration Database file named MyApp located at kbserverkb, type:
scwcmd register / d / kbname: MyApp / kb: kbserverkb
See more:
- Instructions for installing Windows Server 2012 step by step
- Install Windows Server 2008
- Learn about Windows Server 2012 (Part 1)
- Learn about the Windows Registry - Part I
You should read it
May be interested
- Del command in Windows
 the del command deletes one or more files. this command is the same as the eraser command.
the del command deletes one or more files. this command is the same as the eraser command. - 10 useful commands in Windows you should know
 command prompt is used to execute batch files, perform tasks quickly, help you troubleshoot and solve some windows problems when the system crashes. however, not all commands in windows are useful and must be done regularly. with the 10 command lines in the following article it is very useful even if you are not an administrator.
command prompt is used to execute batch files, perform tasks quickly, help you troubleshoot and solve some windows problems when the system crashes. however, not all commands in windows are useful and must be done regularly. with the 10 command lines in the following article it is very useful even if you are not an administrator. - How to use the option equivalent to the 'ls' command in Windows
 the 'ls' command (note ls, not is) is one of the first terminal commands veterans teach to linux beginners.
the 'ls' command (note ls, not is) is one of the first terminal commands veterans teach to linux beginners. - The command reg add in Windows
 the reg add command adds new subkeys or entries to the registry.
the reg add command adds new subkeys or entries to the registry. - Rem command in Windows
 the rem command helps write comments (comments) in a batch file or config.sys.
the rem command helps write comments (comments) in a batch file or config.sys. - Instructions for using Command Prompt
 deep in windows is a command-line world that is obscure. in this article, we will show you how to solve errors and make your computer more secure.
deep in windows is a command-line world that is obscure. in this article, we will show you how to solve errors and make your computer more secure. - How to Register DLL Files
 today's tipsmake will show you how to register a dll, which means creating a path from the file to the windows registry. registering a dll can fix startup errors for some programs, but most dll files are already registered or do not support registration. note: you cannot register pre-installed dlls on a windows computer because these files are critical to system operation and windows updates will fix any outdated or dysfunctional dlls power.
today's tipsmake will show you how to register a dll, which means creating a path from the file to the windows registry. registering a dll can fix startup errors for some programs, but most dll files are already registered or do not support registration. note: you cannot register pre-installed dlls on a windows computer because these files are critical to system operation and windows updates will fix any outdated or dysfunctional dlls power. - Rd command in Windows
 the rd command helps delete a directory
the rd command helps delete a directory - Cmd command in Windows
 the cmd command starts a new version of the command interpreter, cmd.exe. if used without parameters, cmd will display copyright information and the version of the operating system.
the cmd command starts a new version of the command interpreter, cmd.exe. if used without parameters, cmd will display copyright information and the version of the operating system. - How to use the command history function in Command Prompt
 command prompt is an extremely familiar command for anyone using windows operating system. besides, a lot of current software also supports the command line to perform actions on the command prompt window, instead of on the screen.
command prompt is an extremely familiar command for anyone using windows operating system. besides, a lot of current software also supports the command line to perform actions on the command prompt window, instead of on the screen.









 Free network tools for Admin
Free network tools for Admin The Fsutil objectid command in Windows
The Fsutil objectid command in Windows What file is CDDA? How to open, edit and convert CDDA files
What file is CDDA? How to open, edit and convert CDDA files What file is AAC? How to open, edit and convert AAC files
What file is AAC? How to open, edit and convert AAC files Secedit command in Windows
Secedit command in Windows WiFi - 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n and 802.11ac standards
WiFi - 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n and 802.11ac standards