Parents need to know these things to protect them when chickenpox is coming into season
Chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by Varicella Zoster virus.The disease usually breaks out in late winter early spring and is very contagious.People with chickenpox need proper care and treatment to avoid dangerous complications.
- 10 common diseases in children in the fall, symptoms and prevention
- How to prevent and treat pinkeye
- Stroke: Causes, identification signs and emergency 'golden time'
According to statistics, the percentage of children under 10 years old is more likely to get chickenpox than adults and about 90% of children under 10 years of age are infected between the ages of 2-7 years old.

Chickenpox is highly contagious
- The virus that causes chickenpox is transmitted mainly through the respiratory tract. Normal people if inhaling saliva shot when patients with chickenpox cough, sneeze . is very susceptible to infection.
- In addition, if the average person who takes care of a chickenpox patient is exposed to broken water bubbles, the affected skin or sores may also become infected.
- Chickenpox can be passed from mother to child through the placenta if an unfortunate pregnant woman becomes infected.
Symptoms of chickenpox
People with chickenpox often have the following signs:
- Initially, the patient may have fever, headache, fatigue, but there are some cases especially in children who may not have this warning.
- The appearance of 'straws' - small round notes. After 1-2 days, they will develop into blisters, boils. Rice husks appear scattered on the body from the body, face, limbs, even in the mouth, throat, gastrointestinal tract . Normally, the blisters will dry, scab and fall off after 4 - 5 days.
Unusual complications of chickenpox
The development of chickenpox is relatively short, so many people think that this is a mild disease, not dangerous. Without proper care and treatment, the disease can also cause dangerous complications.
- Chicken pox is very itchy, if the patient cannot tolerate it, scratching it will break them and leave a scar.
- Bacteria that enter the chickenpox can continue to enter the blood causing many dangerous diseases such as septicemia, hepatitis, pneumonia, nephritis, meningitis, hemorrhage, .
- Many cases of chickenpox patients have complications into encephalitis: after young chicken pox suddenly become struggling, excited, may be convulsed, lethargic. These cases can cause long-term neurological sequelae such as deafness, developmental delay, epilepsy.
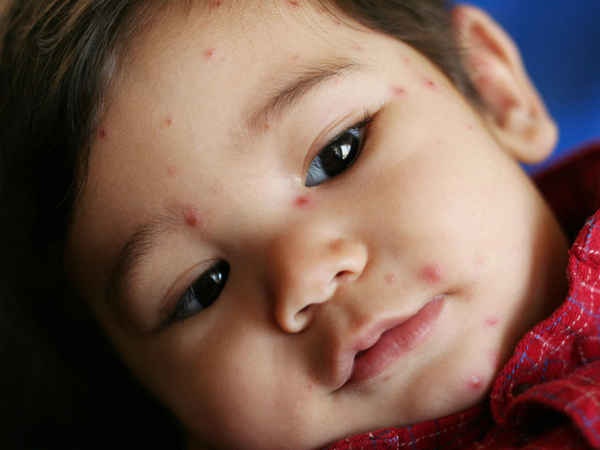
How to care and treat chicken pox patients
- Isolation of sick people at home, lying in private rooms, airy, with sunlight until completely removed.
- Use personal items separately: face towels, cups, cups, bowls and chopsticks.
- Add vitamin C, eat soft, liquid, easily digested foods, drink plenty of water.
- Clean the nose and throat with physiological saline solution of 9% o.
- Pay attention to clean your feet, hands and skin to avoid complications.
- Wear loose, light, thin, soft clothes, absorb sweat.
- Change your clothes and bathe daily with clean warm water.
- If the patient has a high fever, fever-reducing medications may be used according to the physician's instructions.
- Use Milan blue solution to spot broken water spots.
- In the case of infected rice straw: pus has pus, redness of the surrounding skin . antibiotics can be used to treat.
- Especially for children with chickenpox, parents need to pay attention to nail clippers, cloth gloves can be used to wrap children 's hands to prevent scratching and scratching water spots causing complications of secondary skin infections.
- If the patient feels tired, uncomfortable, convulsions, coma or haemorrhage on the straw, it should be immediately taken to the medical facility for monitoring and treatment.
Note: Healthy people who take care of chickenpox patients must wear a mask, after hand contact, wash their hands immediately with soap.
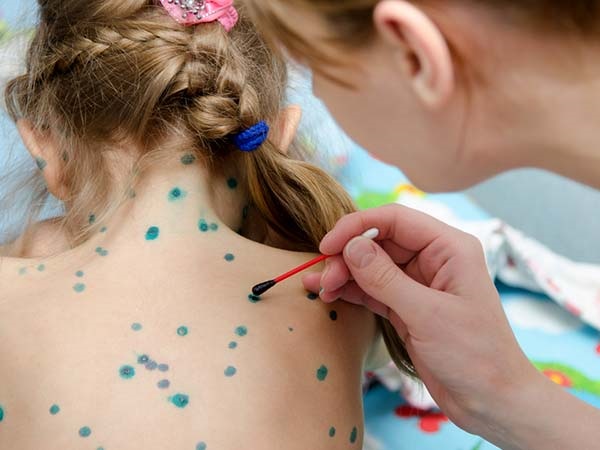
Prevention of chickenpox
The simplest and most effective way to prevent chickenpox is to vaccinate children. Vaccination for children aged 12 months and older, for children over 13 years old, requires 2 doses given 4-8 weeks apart.
See also: 4 ways to deal with asthma attacks - bronchial asthma