Marvel at the strange surviving animals after the 'head left the neck'
In the world, there exist such vigorous animal species that even though their heads are broken, they can . live a little longer. Find out about some animals with special body composition and this strange ability.
- The most mysterious and mysterious animal rains in the world
The 10 most powerful venom animals in the world, if you meet you should stay away
Cockroaches
This is the 'champion' who lives the longest after the head leaves the neck. Because the blood of cockroaches does not rotate quickly, it has very low pressure. This gives them plenty of time to 'block' the wound, limiting the amount of blood lost.
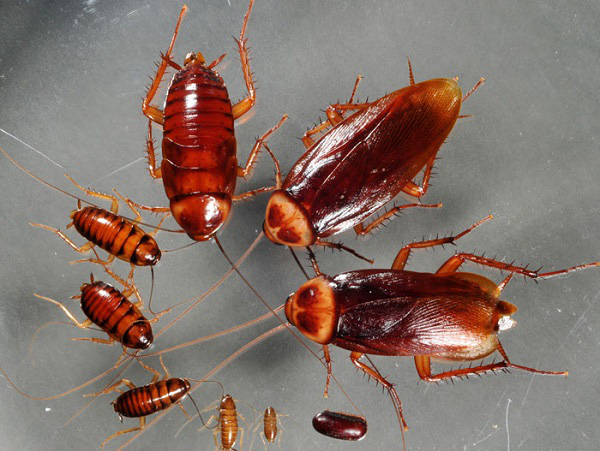

In addition, cockroaches have a very special body structure, they have a system of nerve nodes distributed throughout the body. So without the brain in mind, this backup system could still allow them to act and respond to external effects as usual. Cockroaches only 'die' when infected and starving.
The researchers also demonstrated that the head, after being separated from the body of the cockroach, can be 'tougher' if it is fed and frozen.
Chicken
Certainly many people who have ever met the case of 'cut off' chickens are still capable of running around the yard but the chickens that are cut off from their heads and still live are still miraculous.

That's the story that happened 70 years ago, a rooster nicknamed "Miracle Mike" in the United States who lived for a year and a half after being beheaded. Ask the owner to use eye drops to drip drops of milk, water, food into the throat and use the syringe to draw fluid in the trachea daily, but the chicken still resilient to continue.
It was not until one night that the chicken exuded so much fluid that the owner could not find the cylinder to suck, so he had to die because he was breathing.
Snake
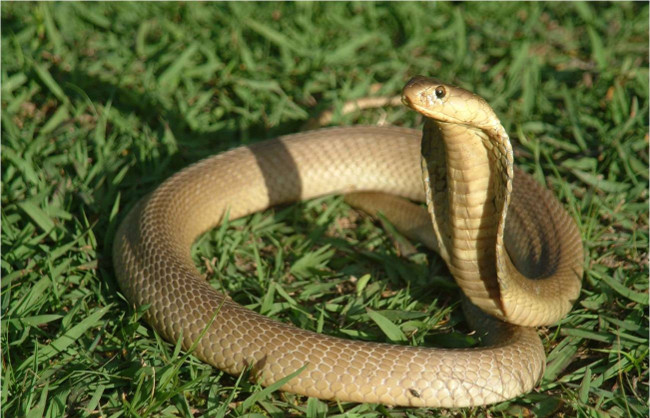

After being cut off from the neck, the snake's head can still live for about an hour longer.
The reason is that the thermal sensor receptors located in the deep grooves between the eyes and nose of the snake make it catch heat radiation from hot blood prey. Thanks to the prolonged neuron reflex, those receptors remain active for a while after the head is separated from the body.
When warm-blooded animals appear at a certain distance, these receptors act to pull the immediate response of the snake's muscles to make a bite and inject venom from the canine teeth. The amount of venom of the severed head is still strong enough to kill the victim.
Flatworms
This animal is considered 'immortal' because they are almost unaffected by the loss of their heads.
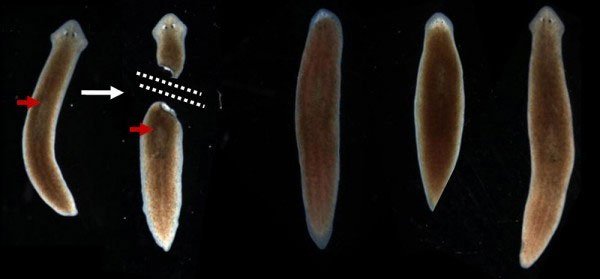
When a flat worm's body is cut off, two new worms will be created. A worm will grow a new head from the tail and another will tail from the bottom of the body.
Mantis
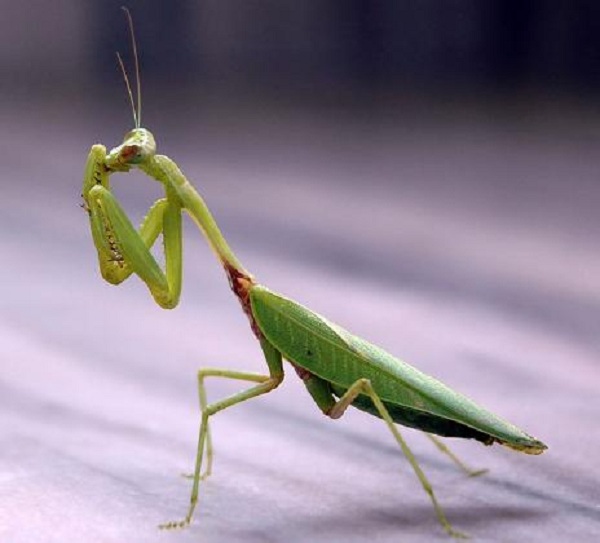

With male mantis, mating is actually a gamble. Female mantises often chew the mantis's head when mating to provide more nutrients to its offspring. But losing the head does not affect the ability of the male mantis to fertilize the female. After pumping the sperm, the male mantis is forced down by the female.
Octopus
Octopus is a special animal, 8 octopus tentacles are not entirely dependent on the central brain. Each of their tentacles has nerve cells, which allow tentacles to still react to stimuli even after being cut off from the head.

Fruit fly
Fruit flies can still fly, beans, cows, and even do the same thing when they lose their heads.
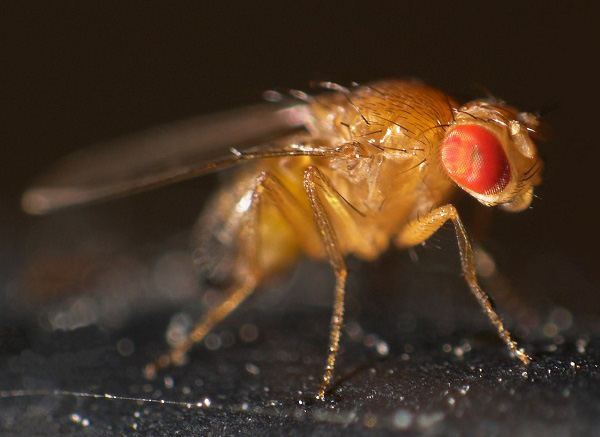

The reason is because of their special body composition, fruit flies have a 'side brain' in the chest, which replaces the main brain that helps the body function normally. In addition, light-sensitive cells throughout the fruit fly's body remain active when they lose their head to help them react to light as usual.
A frog

Frogs whose heads are cut off can still function normally like jumping and swimming in the water . The reason is that the frog's nervous system does not depend entirely on the strong brain and unconditional reflexes of the muscle. When stimulated, electrical impulses are emitted to the muscle, which requires muscle contraction.
Salamander
Water salamanders are particularly famous for their regeneration. They are considered immortal because they can replicate any part of the body from the limbs, tails, even the heart and brain.

You should read it
- ★ Scientists successfully concatenated two-headed mice
- ★ How to Clean Your Printer's Print Head
- ★ Italian doctor declares successful implementation of a human head transplant on the body
- ★ Can a wireless mouse without a USB head be used?
- ★ Medical discovery: Head injuries can alter genes in the brain