Green technology
The "green" movement began to flourish in companies producing computer equipment and systems. In general, companies often target 4 goals: reduce power consumption, increase heat dissipation, increase battery life and replace hazardous materials.
Take a look at a few numbers: an average desktop computer costs nearly half of its energy when operating and contributes significantly to your monthly electricity bill, not to mention the CO2 emissions that increase the effect. glass House. According to Climate Savers Computing, if you save power for desktops or laptops, you will save about $ 20 a year and if the majority of consumers are aware of this problem, the impact of computers on the environment will reduce 54 million tons of CO2 per year, equivalent to taking 11 million cars off the earth. According to IDC, the cost of electricity for each desktop and server in the first half of 2007 was 0.0885 USD / kWh.
Previously, technology companies also considered environmental issues but starting in the middle of 2007, the movement "greening the earth" began to flourish where companies produce equipment and machine systems. count. Many companies began offering "Green" technology for their products, partly for the sake of society, partly if they did not comply with environmental standards, their products were not accepted for use. Some specific areas. For example, in the pioneering part of computer components, Gigabyte with Ultra Durable technology, NVIDIA offers HybridPower solutions, MSI has ECOlution, Cooler Power has Green Guard . But in the middle, companies often target 4. Goal: reduce power consumption, increase heat dissipation (reduce noise), increase battery life and replace hazardous materials in products.
Based on these four goals, let's take a look at some of the technologies typical of technology companies that are sure to be implemented in your computer today.
Power modulation
 For motherboards (BMC), most Taiwanese manufacturing companies such as MSI, ECS, Gigabyte, Foxconn . focus on improving the PWM phase modulator (purse-width modulation or Voltage Regulator Module and Power Processing Module) supplies power to the CPU and other parts of the motherboard. With this modulating component, companies try to use solid capacitors instead of electrolytic capacitors as before. The most obvious benefit of solid capacitors is that it is more durable, does not condense like electrolytic capacitors and is less likely to leak electricity (Figure 1) because solid capacitors contain solid polymer compounds while capacitors use liquid electrolytes. Therefore, the life of solid capacitors is usually 6 times higher than that of solid capacitors, especially in harsh environmental conditions, overclocking, continuous running, solid capacitors are much more durable than electrolytic capacitors. Some BMC companies have switched to using solid capacitors to increase the stability and longevity of the board. An important part of using solid capacitors is less electrical leakage than electrolytic capacitors.
For motherboards (BMC), most Taiwanese manufacturing companies such as MSI, ECS, Gigabyte, Foxconn . focus on improving the PWM phase modulator (purse-width modulation or Voltage Regulator Module and Power Processing Module) supplies power to the CPU and other parts of the motherboard. With this modulating component, companies try to use solid capacitors instead of electrolytic capacitors as before. The most obvious benefit of solid capacitors is that it is more durable, does not condense like electrolytic capacitors and is less likely to leak electricity (Figure 1) because solid capacitors contain solid polymer compounds while capacitors use liquid electrolytes. Therefore, the life of solid capacitors is usually 6 times higher than that of solid capacitors, especially in harsh environmental conditions, overclocking, continuous running, solid capacitors are much more durable than electrolytic capacitors. Some BMC companies have switched to using solid capacitors to increase the stability and longevity of the board. An important part of using solid capacitors is less electrical leakage than electrolytic capacitors.
Previous motherboards typically only have 3 PWM phases, but research companies put more PWM phases into the board to increase the power and flexibility for power supply. Current PWM improvements have between 6 and 12 PWM modulators on board. The more modulators, the lower the temperature and the board can provide more power modes, while meeting the power supply faster. For example, with 6 power modulators, the board has 5 power supply modes depending on the operating status of the system. If the system is in idle state (idle), only 1 modulator operates. If you only run the word processing application, the second moderator will be activated .
 Based on this way of operation, BMC manufacturers offer applications that enable users to enable the system's power load capability, even the system automatically adjusts power based on operating status. Gigabyte has Dynamic Energy Saver application with electric modulation like the motor engine gearbox, Asus has EPU through HybridPower technology that automatically adjusts CPU power. Meanwhile, MSI offers a unique power supply solution, dual channel application for power supply. MSI designed 2 modulating groups, each with 4 phases of PWM in high-end BMC series which, according to the company, saved 10% of electricity compared to the normal design. Another unique solution of Gigabyte is the virtual modulation to increase the modulator to 12 phases with Quad Tripe Phase technology.
Based on this way of operation, BMC manufacturers offer applications that enable users to enable the system's power load capability, even the system automatically adjusts power based on operating status. Gigabyte has Dynamic Energy Saver application with electric modulation like the motor engine gearbox, Asus has EPU through HybridPower technology that automatically adjusts CPU power. Meanwhile, MSI offers a unique power supply solution, dual channel application for power supply. MSI designed 2 modulating groups, each with 4 phases of PWM in high-end BMC series which, according to the company, saved 10% of electricity compared to the normal design. Another unique solution of Gigabyte is the virtual modulation to increase the modulator to 12 phases with Quad Tripe Phase technology.
With graphics cards, in the recent CeBIT exhibition held in Germany, NVIDIA introduced a power reduction solution called HybridPower, which is a combination of BMC platform nForce series 7 chipset and NVIDIA graphics card. When loading is heavy, the discrete graphics card will work, and if the load is light, the system will turn off the discrete graphics card, just run the integrated graphics card to reduce power consumption. With this solution, the noise level of the discrete graphics card is also greatly reduced. Accompanied with HybridPower is Hybrid SLI, combining SLI load between discrete graphics card and integrated graphics chip.
Radiators
In addition to improving modulators to reduce power consumption and reduce heat for the system, technology companies also offer new ways of heat dissipation with the goal of quiet operation during efficient heat dissipation and especially less electricity. Fan radiators often have disadvantages such as noise, water radiator is only suitable for computer players and very "power", fanless radiators still have not achieved the desired results.

Heat the chipset with the Stirling engine.
Recently, MSI has introduced a unique cooling technology for the chipset called Air Power Cooler, which belongs to the fan heatsink but does not need to be powered. MSI teamed up with Taiwan Polytech, applying Stirling Engine theory, taking advantage of the heat of the chipset to turn the fan power. However, there is currently no actual test on the feasibility of this solution. Although still dependent on electricity, but with the use of the Stirling engine for heat dissipation, MSI has reduced the electrical energy for this heat dissipation to make the rotor spin.
According to Stirling engine theory, there will be four main processes: cooling, compressing, heating and expansion. These phases are achieved by air movement between two hot and cold transducers. The hot conversion head comes into contact with the chipset and the cold converter contacts the heat sink. Hot air expanded, pushing the inner pump up. After that, that hot air is cooled and the pump drops down. Such a cycle continues. The piston is connected to the motor to make the rotor blades. According to MSI, this engine can convert 70% of heat into air energy. Compared to solar energy, only the energy conversion rate is only about 20 to 30% and needs an absorbing surface as well as higher costs. You can refer to the Stirling engine here.
In addition to the above heat dissipation, some companies use water radiators combined with thin heat sinks to increase the heat dissipation area of the board. Asus has a self-contained cooling solution, Fusion Block System technology - liquid is led through north bridge chip, south bridge chip, MOSFET. Then, the liquid is taken out of the cooling and returned to continue the new cycle through the components on the BMC. According to Asus, this cooling technology will cool 47% more than normal, has the advantage of less noise (due to external cooling fan cooling liquid) and effective cooling but makes the box "tangled "and especially power consumption because of constant pumping.
Meanwhile, many other companies such as Gigabyte, Cooler Master . go in the direction of expanding air exposure to heat dissipation for motherboards, power, graphics cards . they attach to heat sinks. The more metal panels the better, the most commonly used is still copper, often referred to as stacked-fin. The best illustration of this option is MSI's Circu-Pipe technology, which "hit a circle" to maximize the air exposure area. Another is that the leg-molded heat sinks, often called pin-fin, have the same effect. Usually a battery-fin radiator doesn't need a fan to cool it. Aluminum and copper are two metals that are commonly used because of good thermal conductivity and heat loss, easy to process and lower cost than other metals.
In addition to the default heat sink solutions of BMC manufacturers, graphics cards, power supplies, etc., some other companies offer separate heat sinks for PC players, customers must be familiar with the brands. Like Thermaltake, Thermalright, Zalman, Cooler Master . Their cooling solutions are quite varied, but most are also based on water radiators and fans. They pay much attention to cooling efficiency and noise, and of course the ventilation and . the design of the system, but do not focus much on the power saving ability of removable heat sinks.
Increased battery capacity - fuel cell
There are many different battery technologies that most consumer electronics now use two lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) technologies. Comparison between these two technologies, lithium-ion batteries have the advantage of being able to handle heavy loads, such as those used for laptops, digital cameras, dialers . while NiMH batteries are worse in terms of load. heavy, more likely to leak electricity, often applied in AAA, AA, C and D batteries. Moreover, lithium-ion batteries charge faster than NiMH batteries.
Even a few car manufacturers now apply both of these battery technologies to their new models, not fuel. However, the weakness of lithium-ion batteries is hot and when operating long, this heat will affect the battery's stability a lot, but it is easy to see a lot of laptops and mobile phones in the past time. recalled. Meanwhile, NiMH batteries have less heat problems.
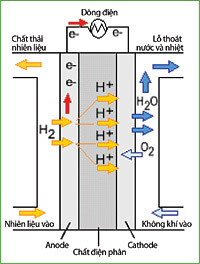
PEM fuel battery.
However, these are two battery technologies that are quite "old": NiMH appeared in the mid-1980s and Lithium-ion was born in 1991 (Sony produced). Fuel cell is a new trend because it does not release toxic substances to the environment and is easy to reuse and charge, of course fuel cells have a longer use time than the previous two seniors.
Fuel cell structure and how it works
Fuel cell structure is quite complex and different depending on the type of fuel used and the equipment used. However, most fuel cells consist of 4 components:
• Fuel tank (cell stack)
• Fuel handling unit
• Power adapter
• Heat recovery system
In addition, fuel cell systems have other auxiliary components to control humidity, temperature, air pressure and water discharge systems.
Fuel tank (cell stack)
This is the most important part of the battery. Here, direct current (DC) is generated from chemical reactions. A battery cell cannot supply enough energy for a device.
Therefore, the single cell binds into a chain in the fuel tube. The amount of electricity produced by each cell depends on several other factors such as the type of material (methane, alkali, phosphorus .), cell size, operating temperature and air pressure supplied to that cell.
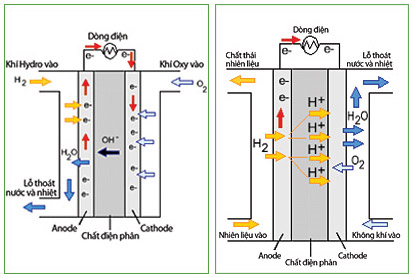
Alkaline Fuel Batteries & Fuel Cell Phosphorus.
Fuel processor
The fuel processor transfers the fuel through the appropriate state for the fuel cell used. If hydrogen gas has been supplied to the cell, this processor has no task or simply purifies hydrogen gas.
If the battery uses hydrogen-rich fuel such as methane, gas, diesel or gasification, there will be a phase of hydrocarbon conversion into a mixture of hydrogen and carbon compounds. In many cases, after this process, the reactive substances will be re-purified to remove impurities such as CO or sulfur (S) before hydrogen is transferred to the fuel pipe to supply the cells, avoid catalysts in chemical reactions. This process is also called "poisoning" because it reduces the efficiency and durability of fuel cells.
Some fuel cells use molten carbonate and solid oxide to operate at high enough temperatures and self-reacting to produce hydrogen for the cell. However, this self-reaction process still needs to be filtered before "clean" hydrogen is transferred to the cell. Any way, CO2 is formed but how to use carbonate to melt and special oxide less CO2.
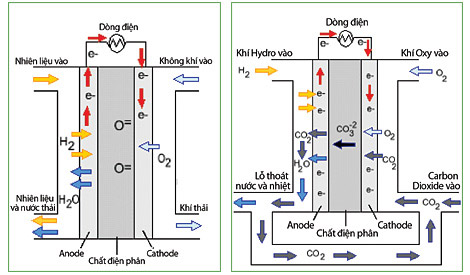
Molten Carbonate Fuel Batteries & Solid Oxide Fuel Batteries.
Converters and regulators of electric current
The converter and current regulator receive current generated from the cell and convert that current to the device used, from a simple device to a complex application power grid.
Cooling system
The structure of fuel cells is not the most heat generating system. However, there are still a few types of fuel cell structures that work very hot, especially fuel cells that use solid oxide and molten carbonate. This heat can be used to create steam or hot water or convert into electricity through a gas turbine or some technology to make full use of the generated temperature.
Constraints on hazardous substance use
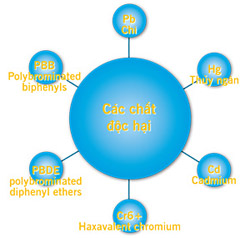
According to statistics, US landfills contain about 2% of electronic waste. But this 2% contains up to 70% of hazardous waste. These toxic substances can be lead, mercury, and cadmium. In the process of uncontrolled waste disposal such as by burning, decomposing these toxic substances adversely affects the environment and human health. You may be surprised with the figure: 6% of the CRT screen of lead-containing computers. Among the toxic waste group, there is a substance that can cause cancer: polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Capacitors, PVC wires, and transformers previously produced contain a large amount of PCBs.
Recently, you may have seen many RoHS logos (www.rohs.gov.uk/) appear on many electronic components or product packaging. This icon is green, easy to understand because this is a certificate of product that meets environmental standards. While the RoHS standard comes from the United Kingdom, RoHS has different requirements in each geographic region. RoHS (Restriction of Use of Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment) prohibits the use of hazardous materials in the manufacturing process, first applied in EU countries since July 1. / 2006. Hazardous substances include: lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), hexavalent chromium (Cr6 +), polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE). These substances are considered to adversely affect the environment during production as well as product regeneration. After the new product appears, testers will use a RoHS analyzer, also called fluocent X-ray or an XRF metal analyzer to "scan" products to ensure toxic levels. The above harm does not exceed the permitted dose.
 RoHS divided into 7 product lines and equipment such as motherboard, graphics card, computer . in group 3 of RoHS (see frame " Product items that RoHS offers "). Some products such as radar detectors, semiconductor manufacturing machines . are not yet listed in the specific category. In each of these categories, there are constraints on different uses. For example, RoHS is accepted by European countries, so all electronic devices manufactured or imported into this territory are RoHS compliant. China also has its own RoHS standard but is also based on the European RoHS standard and comes into effect later, starting in March 2007. Japan is not RoHS compliant and has its own standard called J-MOSS (Japanese industrial standard for Marking Of Specific Chemical Substances) effective July 7. Taiwan has a law binding the use of hazardous substances, also based on RoHS, WEEE standards (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment, also called e-waste) and ELV (End-of-Life Vehicles). The North American region has its own law, EWRA (Electronic Waste Recycling Act), which has been in place since January 2007. The EWRA law is also based on RoHS but less restrictive. For example, LCD monitors, CRTs, and plasmas according to RoHS are limited to 6 metals, while EWRA only restricts 4 heavy metals not to use "allowable doses": 0.01% cadmium, 0.1% hexavalent chromium, lead 0.1% and mercury 0.1%.
RoHS divided into 7 product lines and equipment such as motherboard, graphics card, computer . in group 3 of RoHS (see frame " Product items that RoHS offers "). Some products such as radar detectors, semiconductor manufacturing machines . are not yet listed in the specific category. In each of these categories, there are constraints on different uses. For example, RoHS is accepted by European countries, so all electronic devices manufactured or imported into this territory are RoHS compliant. China also has its own RoHS standard but is also based on the European RoHS standard and comes into effect later, starting in March 2007. Japan is not RoHS compliant and has its own standard called J-MOSS (Japanese industrial standard for Marking Of Specific Chemical Substances) effective July 7. Taiwan has a law binding the use of hazardous substances, also based on RoHS, WEEE standards (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment, also called e-waste) and ELV (End-of-Life Vehicles). The North American region has its own law, EWRA (Electronic Waste Recycling Act), which has been in place since January 2007. The EWRA law is also based on RoHS but less restrictive. For example, LCD monitors, CRTs, and plasmas according to RoHS are limited to 6 metals, while EWRA only restricts 4 heavy metals not to use "allowable doses": 0.01% cadmium, 0.1% hexavalent chromium, lead 0.1% and mercury 0.1%.
However, it is clear that if this constraint is applied, manufacturers have to look for alternative materials. For example, in the past, for electronics people, talking about welding and welding is to think of lead rolls and capacitor connections on the board with lead. Manufacturers have thought of a lead-based tin substitute. However, when used for a while, around tin solder appears tiny tin crystal fibers, affecting joints, leaks and electrical touches. Another approach is tin-zinc alloy and limiting the appearance of crystal fibers.
So far, many RoHS-compliant manufacturing technologies have introduced new capabilities for products thanks to the replacement of production materials. For example, RoHS products have better thermal shock, avoid lead interference on the board, the transfer rate of aluminum is not inferior to other metals .
Greenpeace organizes a solution to clean the environment, especially in areas that are considered hot spots, which are landfill boards and electronic components. These hot spots appear in China, India and Taiwan. For example, the southern Taiwan Erren river is currently heavily polluted (try dropping a fish into the river it will die after 2 minutes); The average life expectancy of people living in this region is 50 years old and the rate of cancer is 27%. One of the most commonly used solutions for cleaning is using a 75% hydrochloric acid mixture and 25% nitric acid. In the Erren River, for example, people put it directly into the river to reduce pH. The results are quite positive, this compound erases lead, zinc, copper, antimony, cadmium and nickel.
According to the US environmental organization, arsenic and cadmium only need 1 mg / l to be classified as toxic water but the "hot" areas in China and Taiwan, this rate is up to 12.2mg / l. Nanotechnology is also "noticed" because it is considered to affect the environment and human health.The process of handling and the materials used by nanotech companies are organized by SVTC (Silicon Valley Toxics Coalition). ) monitoring to ensure that it does not affect human health and the environment, this organization oversees mainly in Silicon Valley, where a lot of nanotechnology research companies and centers are concentrated (see About 110. The US government spent $ 1.44 billion in this field in 2008 but only spent about 4% of that money on environmental protection applications.
The climate is heating up every day, protecting and preserving a clean environment of not only manufacturing companies but also everyone's responsibility. Some companies have made policies for their own employees about energy saving as well as environmental protection. For example, Gigabyte offers a series of terms such as turning off the computer and turning off the lights during lunch break, turning off the off-peak elevator system, not printing if not absolutely necessary .
You should read it
- ★ CO2 emissions will be used as fuel for cars in the future
- ★ The source of biofuels from coffee can be used to operate buses
- ★ Top 5 best heat sinks 2019
- ★ The computer does not need a fan to dissipate heat thanks to the copper foam heat sink
- ★ Ships traveling around the world for 6 years do not need fuel