Emotional map of the body: The relationship between emotions, physiological state and behavior
Human emotions are related to the behavior and physiological states in existential situations or interactions between one person and the other. Although everyone is aware of his current emotions like anger or happiness, the mechanism that leads to those subjective feelings has not been discovered.
Have you blown your nose for being praised? At that time, it seemed like your nose was bulging and your face was red with joy. Then the sad moments to the intestinal brain, limbs are cold, the face is tired, tired and feels like you have no strength left to do anything else? Feelings of human beings are in the shape of all things, and the interesting thing is that physiology in the body also changes in sync with the emotional sequence of "morning and afternoon rain". So what is the secret of this mechanism? The following section will give you lots of interesting information.
We often experience direct emotional states in the body. When walking in the park with the person you love, despite your gentle steps, your heart is pounding with excitement; Then important job interviews, you are so worried that your muscles are tight, your hands are sweating and a sense of fear arises. According to many studies, our emotional system is available to meet the challenges encountered in the environment by regulating the activation process that takes place in the cardiovascular, skeletal (skeletomuscular), systemic Endocrine nerve (neuroendocrine) and the nervous system (Autonomic Nervous System - ADS). (1) The relationship between emotions and body state is also reflected in the way we express emotions, (2) a young bride will get married next week suddenly feeling "cold feet ", realizing the true face of a traitor can make a distressed person and favorite song create a " shiver down the spine " of someone while enjoying, especially if heard at mood - love, scene.

Both previous research - what emotions are (James W., 1884) and recent studies - emotional experiences and the nature of emotions - about the patterns of emotional formation process all assume that , subjective emotional states are triggered by emotional awareness of each area in the body, reflecting changes in skeletal muscle, endocrine nervous system and nervous system. plants. Conscious emotions help voluntary individuals refine their behavior to better meet the challenges of the environment.
Emotions are related to a variety of physiological changes, however, there are still some heated debates that whether body changes associated with different emotions are clear enough to be the basis for Discrete emotional states such as anger, fear or happiness and the distribution of emotional sensations in the body are still unknown.
Scientist Lauri Nummenmaa and colleagues conducted experiments with 773 volunteers from different countries such as Finland, Taiwan and Sweden (all speak their native language). They let volunteers hear different vocabulary, stories and movies. After that, volunteers will feel and paint on people in silhouette areas of the body that they feel increase or decrease while they are listening or watching. At that time, those emotions will be linked to different emotional maps (Bodily sensations maps - BSMs). From here, the research team uses the computer -based self-report topographic method (Computer-based, topographical self-report method - emBODY) to create a complete map of the correlation between emotional and physical activity. Colors change from black => red => yellow (warm, hot colors) to refer to the increase in activity, while the decrease in activity is indicated by the change in the brightness of blue (color cold).
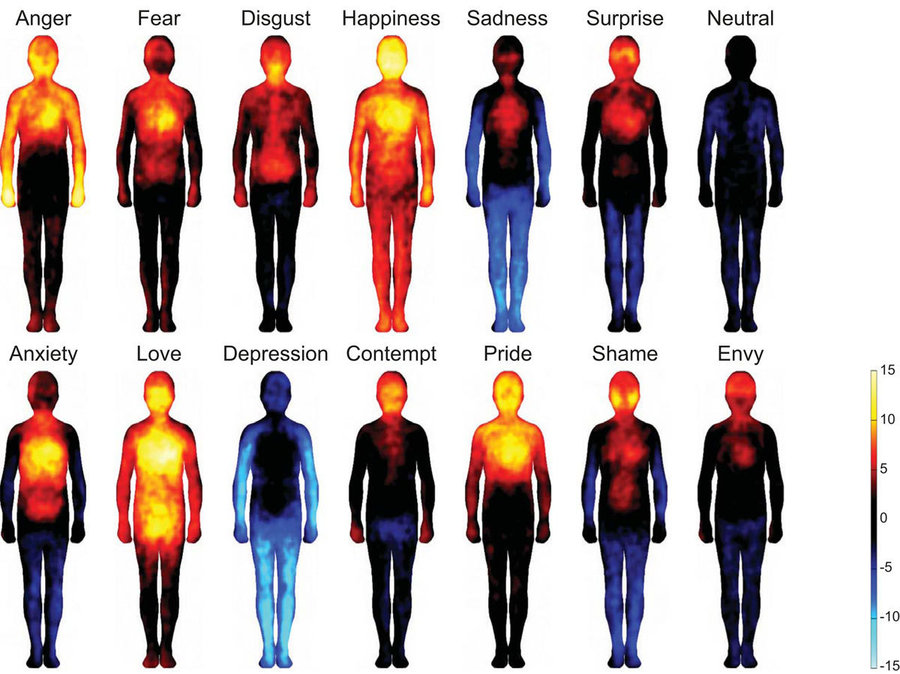
The scientists also conducted five experiments with 36 to 302 participants in each country. In Experiment 1, participants showed that feelings in the body were related to 6 basic emotions - anger, fear, indignation, happiness, sadness, surprise - and 7 emotions. copies (complex) - anxious, in love, depressed, scornful, proud, ashamed, jealous - as well as a neutral state (normal) , all described by sympathetic words corresponding contact. In it, positive emotions include happiness, love and pride; Negative emotions include anger and fear, anxiety and shame, sadness and frustration, resentment, contempt and jealousy; Surprises are not negative and positive emotions - it depends on the circumstances.
Angry
In this emotional state, the body's activities increase, the hormones are released, increasing blood pressure, and also making the heart beat faster.
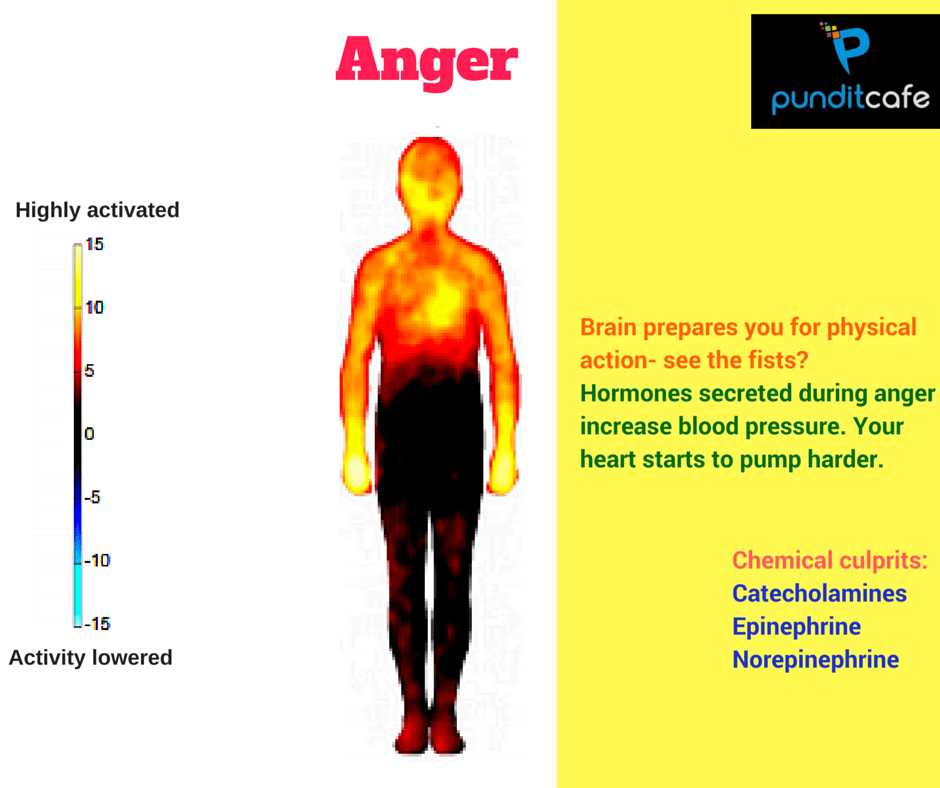
The "culprits" of these manifestations are Catecholamines, Epinephrine and Norepinephrine. When angry, the body will excrete catecholamine, which acts on the central nervous system, causes high blood sugar, strengthens the resolution of fatty acids, toxins in liver cells and blood also increases. . In addition, anger will also affect the sympathetic system, producing Norepinephrine, also called Noradrenaline. These substances follow the blood into the adrenal glands to secrete more Norepinephrine and Epinephrine, also known as Adrenaline, leading to rapid heartbeat and high blood pressure.
Angry
When indignant, activities in the body also occur with intense intensity. Notice that the mouth is yellow but not spread, but it is associated with the abdomen (the red stretches from the abdomen, the esophagus, the stomach and when it reaches the mouth turns yellow - the most active ) reflects a symptom of abdominal discomfort or vomiting.
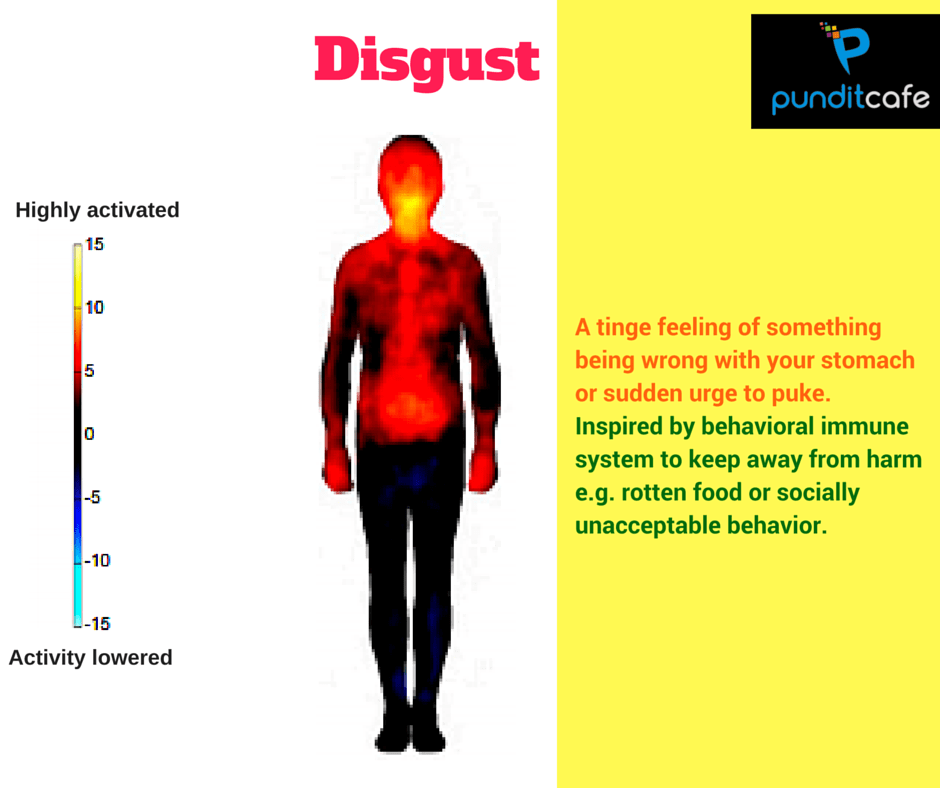
This phenomenon appears to be the effect of Behavioral immune system - it can be understood that psychological mechanisms allow body organs to recognize hazards and activate reactions. applications to prevent them, such as when eating rotten fruits or facing unacceptable behaviors.
Happy
You can see when happy, the body works very hard, almost does not appear blue on the emotional map. In it, the yellow color concentrates on the face, showing that the emotions are clearly expressed outside, such as smiling and smiling face. This is why when we feel happy, we just want to jump up and run to embrace others.
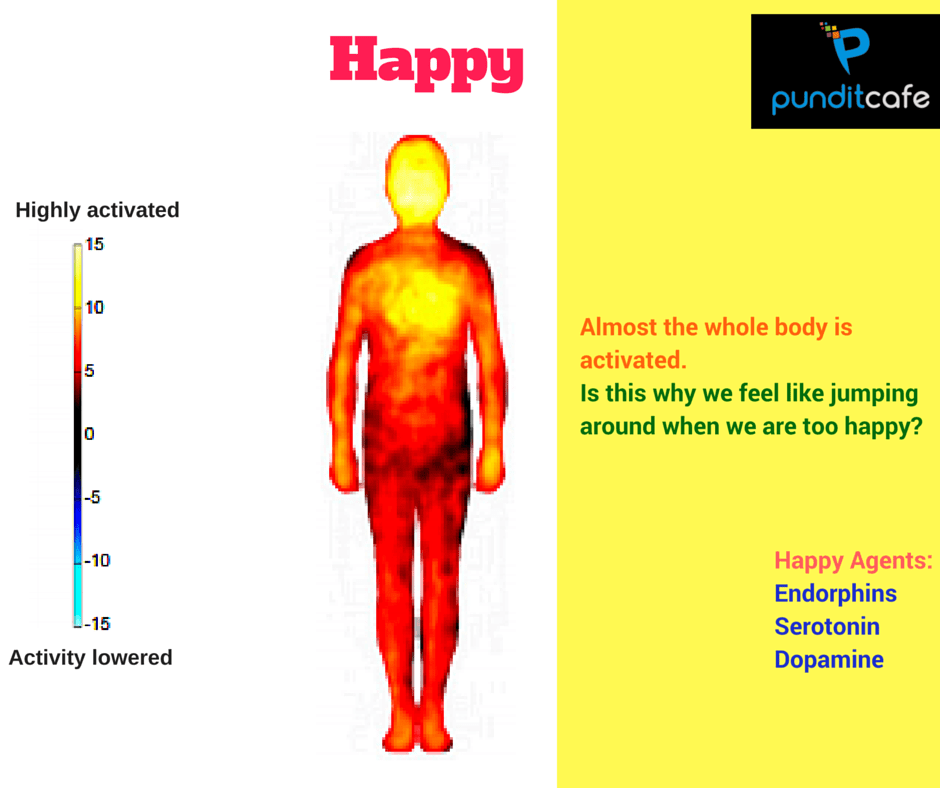
Being responsible for this feeling is because the body releases hormones such as endorphines, serotonin and dopamine.
Sad
When sad, most areas of the body are slow, except for the chest and face. The red part of the chest is caused by the vagus nerve. This is the largest parasympathetic flora of the body, controlling movement, feeling most of the viscera in the chest and abdomen (including heart, lungs, digestion, secretion). Urinary and genital).
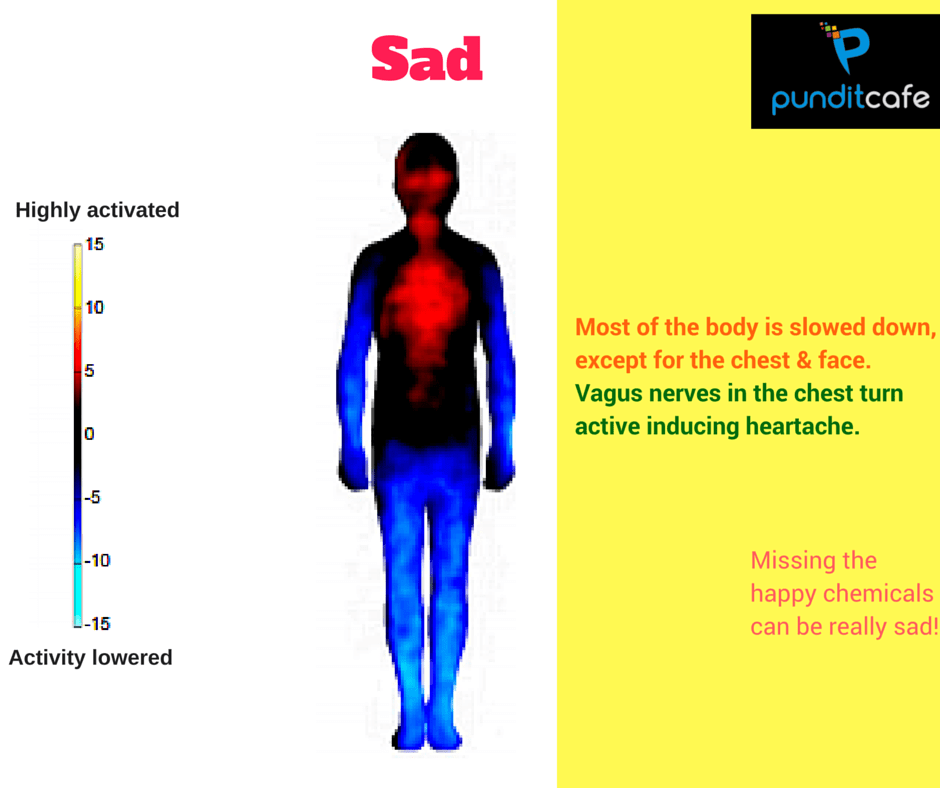
When faced with extreme pain situations, people may faint due to the vagus nerve. This happens when a part of the nervous system regulates the heart rate and blood pressure malfunctions in the trigger reaction, such as when blood is seen, heart rate slows and blood vessels in the legs widen. This allows blood to clot in the legs, reducing blood pressure. Reducing blood pressure and slowing heart rate quickly reduces blood flow to the brain. This is the reason that when feeling sad, almost all parts are inactive, especially the face and chest area increase activity.
Fear
When frightened, the heart beats fast and blood pressure rises, triggering "fight or flight" reactions. In addition, because the blood glucose content is also accelerated, people have more energy to fight or run to survive.
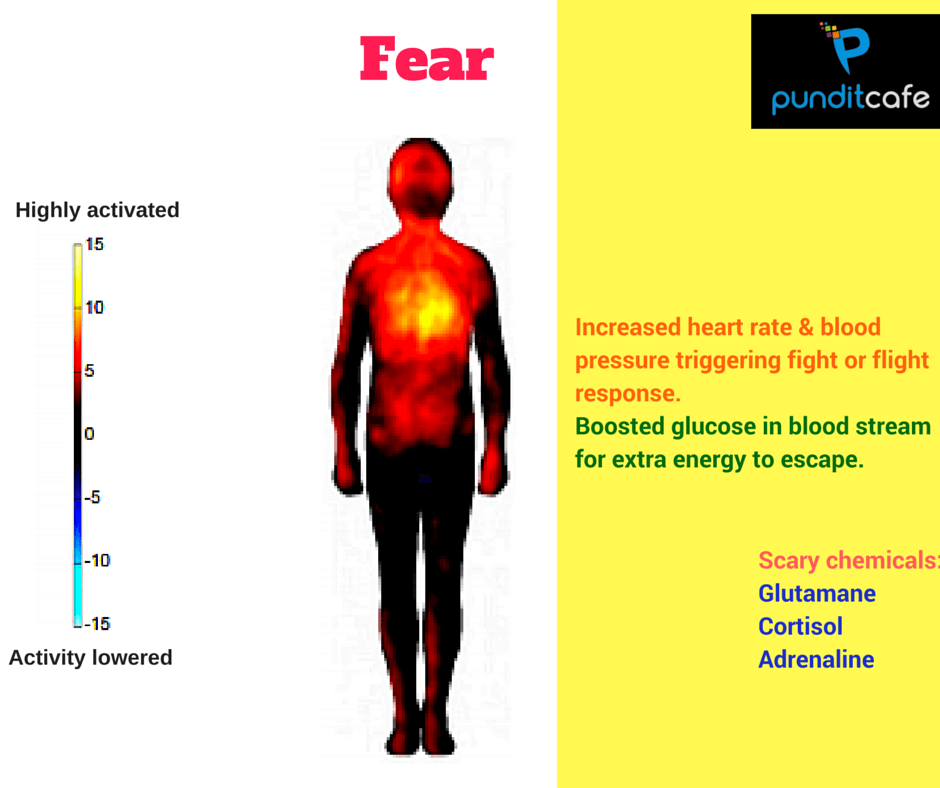
At that time, the body had to mobilize all its strength to cope. The lobes of the brain will order the release of necessary hormones, adrenaline, norepinephrine, cortisol . rushing into the bloodstream. The heart beats fast to pump blood to the large muscles, the lungs gasp and accelerate the oxygen pump, the blood sugar soars up to enhance the energy emergency, the pupils are enlarged to see clearly, the ears prick up, the nose bulges out. . In short, everything must be in a ready position. While the big blood vessels transfer blood to the muscles, the peripheral blood vessels shrink, so that if there is any injury, the blood will not be lost much . So the feared person often turns pale, blue stick, limbs stiff .
Shy
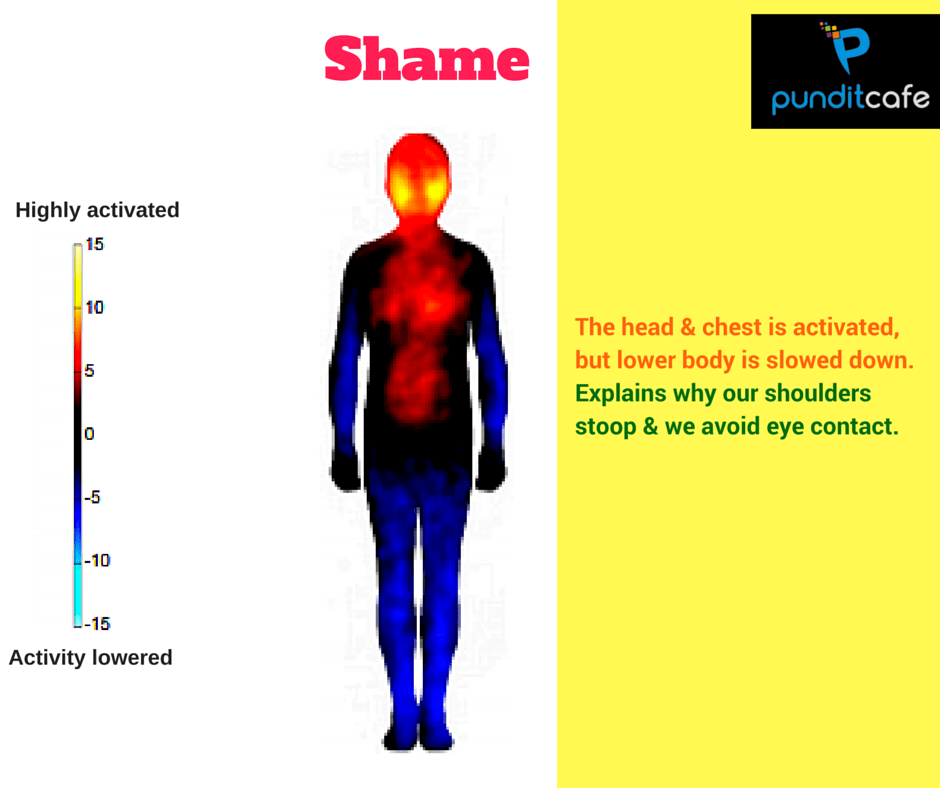
There is nothing confusing when feeling embarrassed, face is the most active area. The cheeks are usually flushed, corresponding to yellow; However, unlike the head and the chest, the lower part of the body (legs and arms) is reduced. This is why we often avoid looking into other people's eyes, stooping our shoulders and bowing slightly when we are ashamed.
Proud
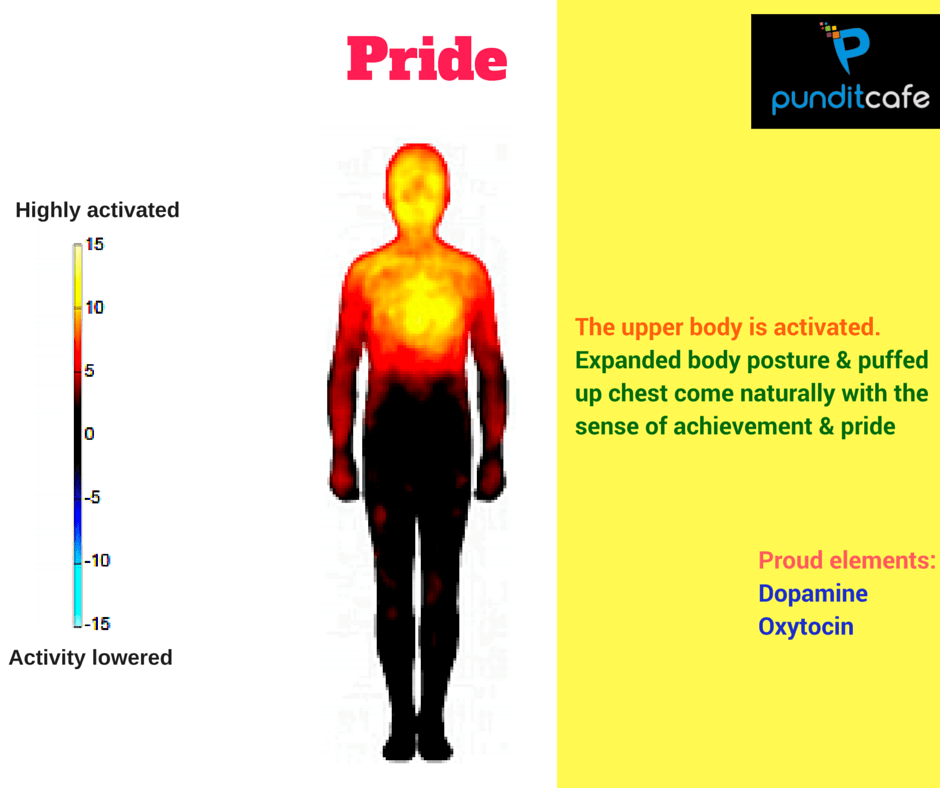
When feeling proud, the upper body works very well (almost to the highest level). The human posture is wide open, the chest is puffed out (a little bit proud) naturally with the feeling of achieving something and pride. At this time, in the body, hormones dopamine and oxytocin are also released which makes us feel excited.
You should read it
- ★ Science proves: People who often cry are the most powerful
- ★ 11 signs to let you know that person is trying to hide his feelings
- ★ 9 types of human personality that managers, people and marketers need to know
- ★ 11 clear signs that you are a low EQ
- ★ What is physiological saline? The effect of physiological saline and its use