Detecting dangerous backdoors targeting both Windows, macOS and Linux
This backdoor-type malware is currently actively targeting Windows, Linux and macOS - the world's three most popular PC operating system platforms - with extremely sophisticated evasion of detection.
If you do not know, a backdoor is a tool (program or program-related) used by a hacker to install on a system to bypass the security barrier of a device or software remotely. Because the computer's security system cannot see the backdoor, the victim may not realize that their computer has this dangerous vulnerability. In other words, users will not know the existence of a backdoor on their system until it is detected.
Detecting backdoors in devices is generally extremely difficult. This new malware was discovered and named by researchers at Intezer, who first saw signs of its activity in December 2021, after investigating an attack on a server fairly large-scale Linux-based web.
Similar to other types of backdoors, SysJoker's fear lies in the fact that it is very good at evading detection, allowing it to cause long-lasting, insidious damage without the victim realizing it.
A 'Joker' who doesn't like attracting attention
This malware is written in C++. In particular, it will have many different variants, each of which is tweaked to suit each operating system it targets. It is worth mentioning that all of them went undetected on VirusTotal, a popular online malware scanning website that uses 57 different antivirus engines.
On Windows, SysJoker uses PowerShell commands to perform the following malicious tasks:
- Fetch the SysJoker ZIP from the GitHub repository.
- Extract it on "C:/ProgramData/RecoverySystem/".
- Deploy payload.
The malware then 'sleeps' for up to 2 minutes before creating a new folder and replicating itself as Intel Graphics Common User Interface Service ('igfxCUIService.exe').

Next, SysJoker will gather information about the machine using a sequence of Living off the Land (LOtL) commands. SysJoker uses various temporary text files to record the results of commands. These text files are then deleted immediately, stored in a JSON object, then encoded and written to a file named "microsoft_Windows.dll'.
After collecting system and network data, the malware improves its stability by adding a new registry key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/Microsoft/Windows/CurrentVersion/Run
The next step for the malware is to gain access to the hacker-controlled C2 server using a hard-coded Google Drive link.
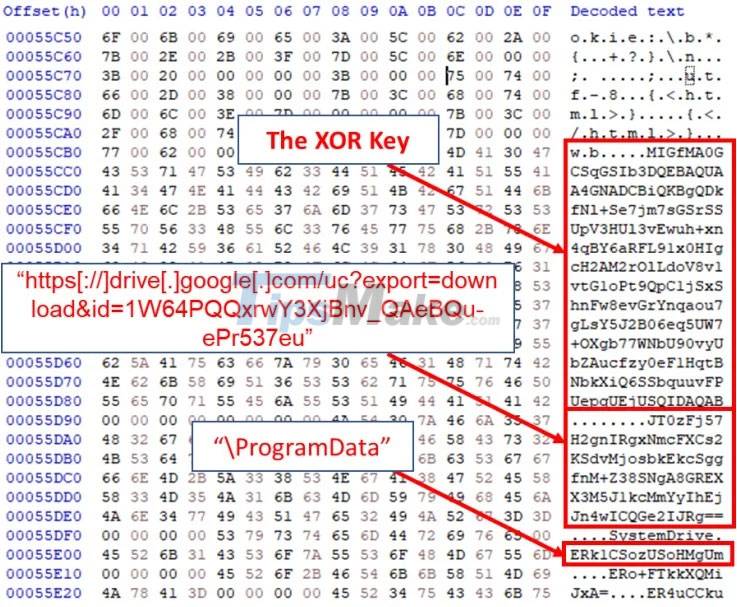
The association hosts the "domain.txt" file, which the agent regularly updates to make available servers for live signaling. This list is constantly changing to avoid detection and blocking.
System information collected during the first stage of infection is sent as the first handshake to C2. C2 responds with a unique token that serves as the identifier of the infected endpoint.
From there, C2 can command the backdoor to install more malware, run commands on the infected device, or even command the backdoor to remove itself from the device.
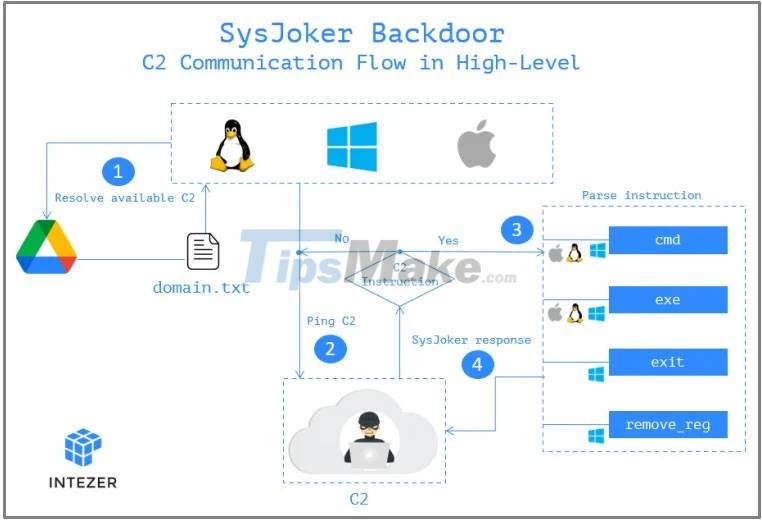
The same procedure is also found on Linux and macOS variants.
Detect and prevent
Intezer provided the full range of Intrusion Indicators (IOCs) in its report. Thereby administrators can use it to detect the presence of SysJoker on their systems.
Here are some IOCs for each operating system:
On Windows, the malware files are located in the folder:
C:/ProgramData/RecoverySystem at C:/ProgramData/SystemData/igfxCUIService.exe and C:/ProgramData/SystemData/microsoft_Windows.dll
For long-term survival, the malware generates an Autorun "Run" value of "igfxCUIService" to launch the igfxCUIService.exe malware executable.
On Linux, files and directories are created in "/.Library/'. Backdoor persistence is established by creating the following cron job: @reboot (/.Library/SystemServices/updateSystem).
On macOS, files are created on "/Library/" and stabilized via LaunchAgent at the path: /Library/LaunchAgents/com.apple.update.plist.
The C2 domains shared in the Intezer report are as follows:
- https[://]bookitlab[.]tech
- https[://]winaudio-tools[.]com
- https[://]graphic-updater[.]com
- https[://]github[.]url-mini[.]com
- https[://]office360-update[.]com
- https[://]drive[.]google[.]com/uc?export=download&id=1-NVty4YX0dPHdxkgMrbdCldQCpCaE-Hn
- https[://]drive[.]google[.]com/uc?export=download&id=1W64PQQxrwY3XjBnv_QaeBQu-ePr537eu
If you discover your system has been compromised by SysJoker, follow these 3 steps:
- Kill all malware-related processes and manually delete associated files and persistence mechanisms.
- Run a memory scanner to ensure that all malicious files have been 'pushed' from the system.
- Investigate potential entry points, check firewall configurations, and update all software tools to the latest available versions.