Compare Pseudo-Classes and Pseudo-Elements in CSS
CSS supports a series of selectors to define styling elements. Each selector has its own rules. While most selection methods are simple, pseudo-classes and pseudo-elements offer more flexibility. They let you select elements based on status or position in a structure, or they select specific pieces of content.

These selectors can be difficult to use, and it's easy to confuse pseudo-class with pseudo-element . So how to distinguish the difference between them?
What is Pseudo-Class in CSS?
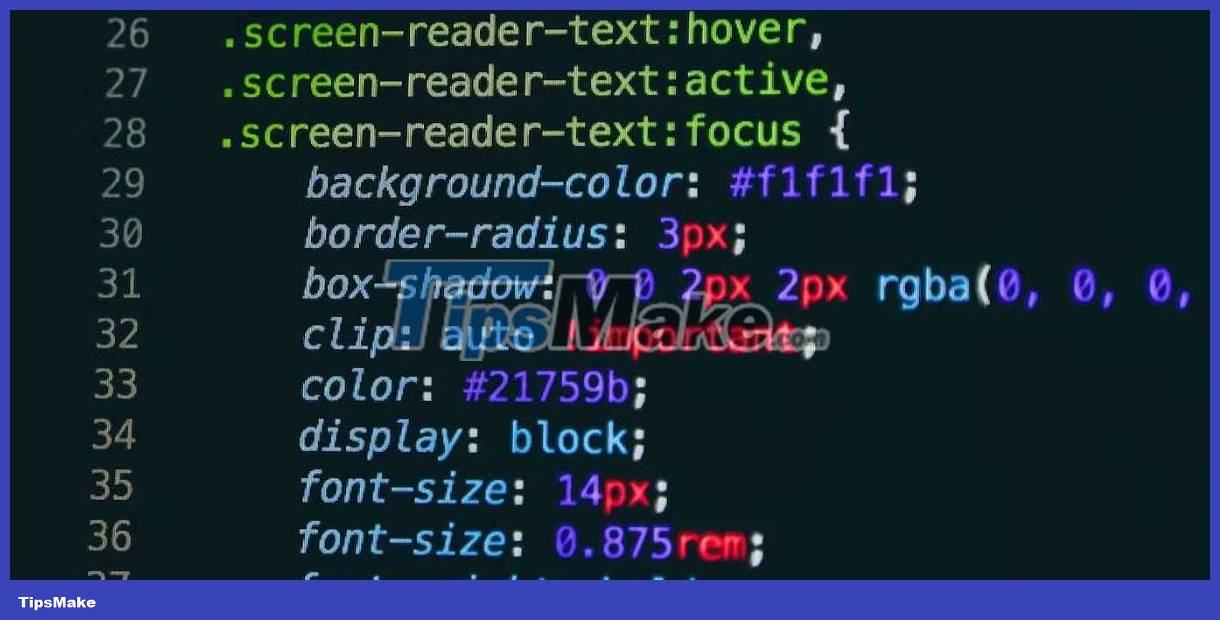
CSS Pseudo-Class is like a special keyword that you can use with selectors to style elements in different ways. These keywords help you target elements when specific behavior occurs, such as when a user hovers over an element, clicks on it, or enters data in an input field.
Pseudo-classes make your website more interactive and responsive by changing the display of elements or behavior based on user actions. When used with other CSS selectors, they provide precise styling and interaction control.
Syntax and usage of CSS Pseudo-Class
The syntax for CSS pseudo-classes includes a sign (:) after the name of the pseudo-class. Here is the basic syntax:
selector:pseudo-class { /* styles */ }In this syntax:
- Selector indicates the element or element that you want to select and apply styling to. It can be an HTML element, class, ID, or a more complex selector like a combination. This selector is optional, but you will usually use one of them. Without it, your pseudo-class will target all the elements it can apply to.
- pseudo-class is a keyword that represents a specific state or condition you want to target.
CSS classifies pseudo-classes into several groups based on their functionality and the conditions they target. Here are the main categories with some examples:
| User interaction | |
|---|---|
| :hover | Select an element that the mouse pointer points to. |
| :active | Selects an element when the user activates it, usually with a mouse click. |
| :visited | Select the link the user has visited. |
| Structure | |
| :first-child | Selects the first child component of the parent component. |
| :last-child | Selects the last child component of the parent component. |
| :nth-child(n) | Select components based on their position in the parent, allowing you to target specific child components. |
| Related to forms | |
| :disabled | Select the disabled form element. |
| :checked | Select rounded buttons or checked cells. |
| UI component state | |
| :invalid | Select invalid form element. |
| :required | Select the required fields of the form elements. |
| :optional | Select form elements that are selection fields. |
| Related links | |
| :link | Select a link that has not been accessed. |
| Language-based | |
| :lang() | Selects the element based on the language specified in the 'lang' attribute. |
What is Pseudo-Element in CSS?

CSS Pseudo-Element is like a special keyword that you can use with selectors to style specific parts of an element's content or insert additional data. These keywords allow you to target and style elements based on their content structure.
Pseudo-element enhances website design and layout by giving you the ability to style elements in the traditional way that is only possible with real HTML elements.
Syntax and usage of CSS Pseudo-Element
Pseudo-element in CSS has a syntax that involves using two colons (::) after the name of the pseudo-element. Here is its basic syntax:
selector::pseudo-element { /* styles */ }In this syntax:
- The selector targets the element to which you want to apply the pseudo-element. It can be any valid CSS selector, including none.
- pseudo-element is the name of the pseudo-element you want to target. You can only use one pseudo-element in a selector because they don't really make sense together.
Here are some pseudo-elements:
| ::before | Inserts content before the content of the selected element. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ::after | Inserts content after the content of the selected element. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ::first-letter | Styles the first character of a text within an element | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ::selection | Style the text the user has selected with their cursor. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ::marker | Style the checkbox of a list item (for example, a bullet or number in a list). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ::cue | Apply styles to signals in media elements like Similarities and differences between pseudo-class and pseudo-element in CSS
pseudo-class and pseudo-element are both important in CSS for styling and interactivity. Although they have some similarities, they have their own roles in web design and programming. |
You should read it
- ★ Science has found evidence of the immortality of pseudo-particles: they replicate themselves after decay
- ★ What is a mechanical keyboard? Distinguish between mechanical and pseudo-mechanical keyboards
- ★ What is RNG?
- ★ How to customize the new iOS 14 widget on your iPhone
- ★ New worms appear to attack Google