AMD: Ryzen AI 300 more than meets the requirements of Microsoft Copilot+ PC, beating Qualcomm, Apple, Intel
Back in December 2023, AMD introduced the Ryz 8040 (Hawk Point) series mobile APUs, while also revealing some brief information about the next generation Strix Point series. Previously, 'Team Red' wanted to follow a similar naming scheme as the Strix Point APUs would be labeled as "Ryzen 8050 series". However, more and more leaked information shows that this plan has changed, as AMD seems to be considering choosing the "Ryzen AI" brand, in line with the explosive growth trend of the market. Hardware supporting artificial intelligence.
Today, at COMPUTEX 2024, AMD officially confirmed its new naming scheme for the Ryzen AI 300 series CPUs. It seems that this move is a solution for AMD to separate AI PC processors from the product line for traditional work and gaming, similar to how we have the Ryzen Threadripper line that only caters to the HEDT (high-end desktop) segment. This announcement comes alongside the Zen5 and Zen 3-based 5000XT series processors for desktop.
If you're wondering why AMD chose the '300' series, it's because this is the third generation of AMD processors to feature an NPU after the Ryzen 7040 (Phoenix) and Ryzen 8040 (Hawk Point).

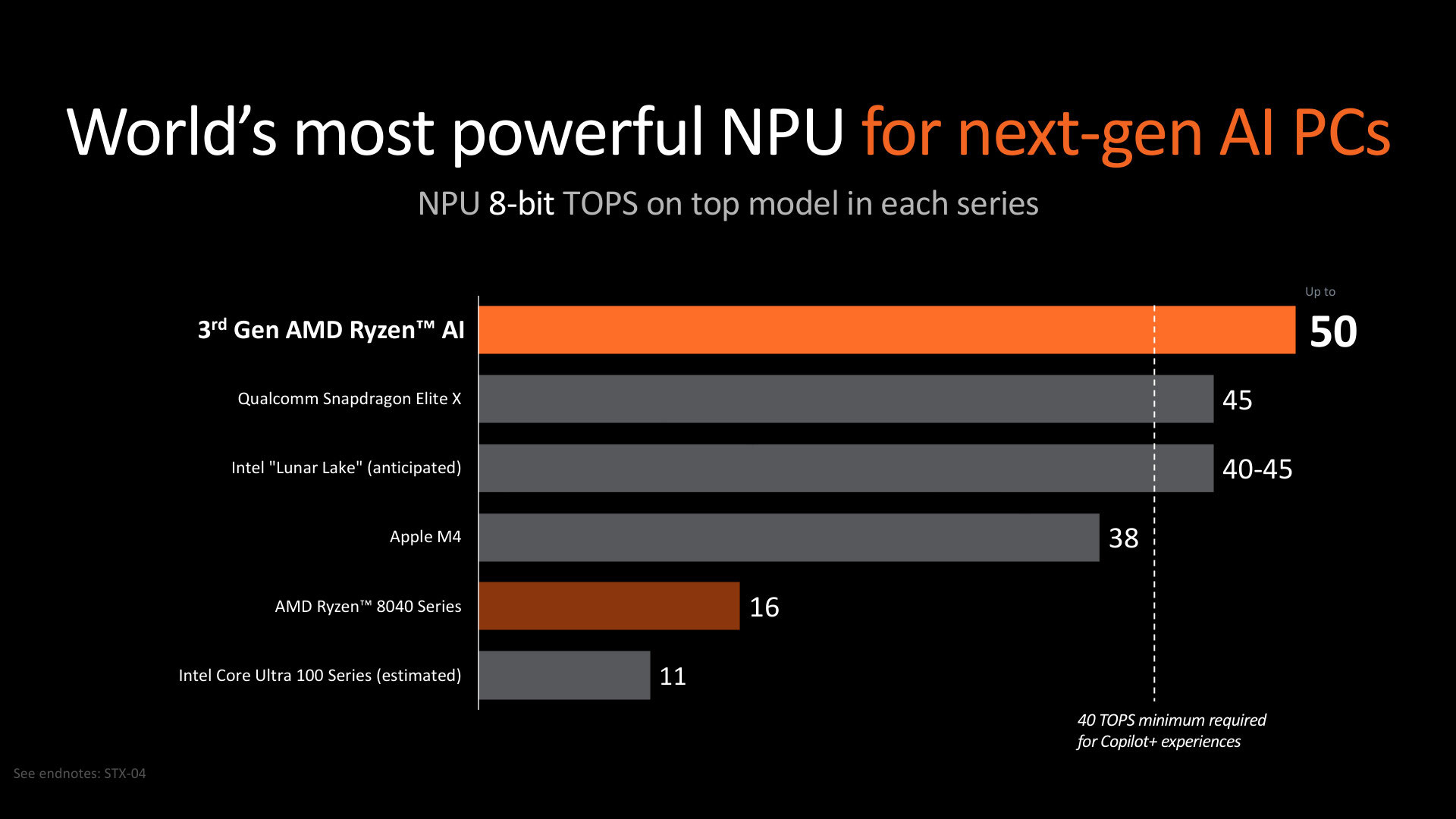
As can be seen in the two slides above, both Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 and Ryzen AI 9 365 come with NPUs rated to deliver up to 50 TOPS (Terra Operations Per Second) AI throughput. This is the main standout feature of these new APUs, and also meets Microsoft's minimum requirement of 40 NPU TOPS for PC Copilot+ AI. Previously, such capabilities were only supported on Qualcomm Snapdragon .
Although both APUs have similarly performing NPUs, the HX 370 has more cores, better suited to the CPU and GPU than the 365. Of the 12 cores on the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370, up to 4 cores are Zen 5 and the remaining is Zen 5C. In the case of Ryzen AI 9 365, the number of Zen 5C cores is 4, while the number of Zen 5 cores remains the same at 4.
What makes the Ryzen AI HX 370 superior to the Ryzen AI 365 is the additional graphics performance. Both chips feature the new RDNA 3.5 graphics architecture, and the HX 370 will have 16 CUs (compute units) compared to 12 CUs on the 365. When combined with high-speed memory, the HX 370 can gives much faster performance.
AMD also shared details on how it was able to achieve the leap in AI processing power on its new NPUs. They are based on the XDNA 2 architecture, and Team Red actually kept their earlier promise when they claimed that the second generation XDNA would be three times faster.
AMD says this is achieved through a combination of doubling power efficiency and five times (5X) increasing AI compute capacity. The company is also combining the best of both the INT8 and FP16 platforms to deliver high performance and high precision respectively, calling the design approach the FP16 "Block".
You should read it
- ★ Top best CPU for PC 2020
- ★ AMD Ryzen 5 3600X Review: Great multi-threaded support, overclockable
- ★ AMD announced the Ryzen 3 3300X and Ryzen 3 3100 CPUs for desktops
- ★ AMD's Ryzen Threadripper 2990WX achieved 6Ghz overclocking speed on all 32 cores, breaking many records
- ★ AMD released the 2nd generation Ryzen computer processor with SenseMI technology