5 factors to keep in mind when buying a CPU
This guide helps make the process as simple as possible to choose the best CPU in 2024.
1. CPU brand
There are mainly two desktop CPU manufacturers: Intel and AMD. Intel has led the CPU market for many years and is the only choice for high-performance systems. AMD used to fall to second place and was only a reasonable choice for cheap and affordable HTPC systems. But the two companies are currently fighting fiercely in the CPU market. In fact, AMD's Ryzen CPUs are now suitable for gaming after failing to overcome Intel's shadow for many years.

Intel's 14th generation CPU and AMD's Ryzen 7000 CPU are competing for the attention of desktop manufacturers. Both brands offer a variety of options across their latest and previous generation product lines. And while AMD's Ryzen
2. Number of CPU cores
One of the first things to pay attention to is how many cores the CPU has. In general, more cores will result in higher performance. Most CPUs have at least 4 cores, which is usually suitable for gaming and basic office use. If you're building a new mid-range or high-end system, choose at least a 6-core CPU.
Ideally, you should consider the latest generation parts – or at least no older than two years. Furthermore, gamers should almost always prioritize overall performance over high core count, while workstation and productivity users should strive to have as many cores as possible within the budget.
3. Clock speed
Clock speed explains the speed at which individual cores can run on the CPU. Typically, the more cores there are, the slower their clock speed will be. This is why gamers and non-workstation users should value faster single-core performance over high core counts, while productivity users should do the opposite. You'll notice that AMD's fastest Threadripper CPU, the 96-core Threadripper Pro 7995WX, has a boost clock of 5.1 GHz, which is lower than the base clock of some modern 6-core chips.
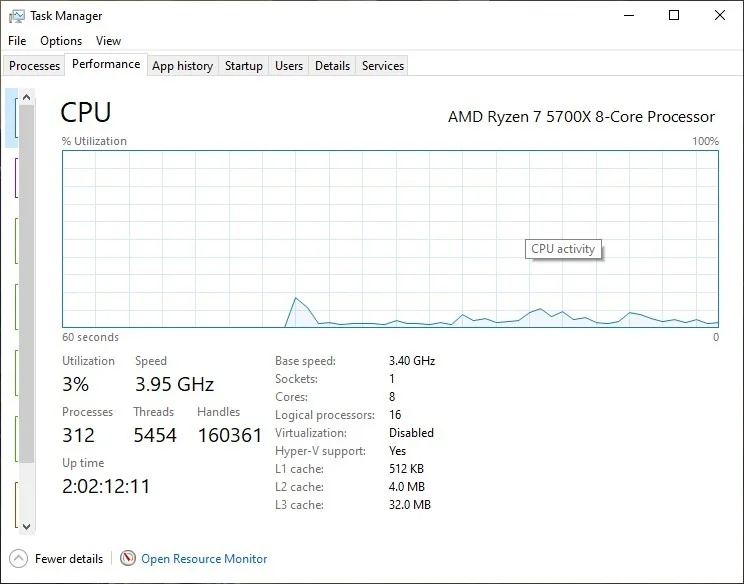
For most users, clock speed is more important than core count when comparing the performance of modern CPUs. If you use your computer for gaming, work, or general web browsing, a faster CPU is much better than a CPU with more than 8 cores.
4. Thermal Design Power (TDP)
Thermal Design Power, or TDP, is the maximum amount of power (in watts) that the CPU is designed to draw from the computer and affects the amount of heat it will generate. The lower the core count and clock speed, the lower the TDP.
However, modern mainstream CPUs are increasingly consuming more power than previous workstation CPUs, as they deliver better performance over the generations. The power efficiency crown in the current generation of CPUs belongs to AMD, as Ryzen 7000 CPUs typically offer higher performance per watt than Intel's 13th and 14th generation CPUs.
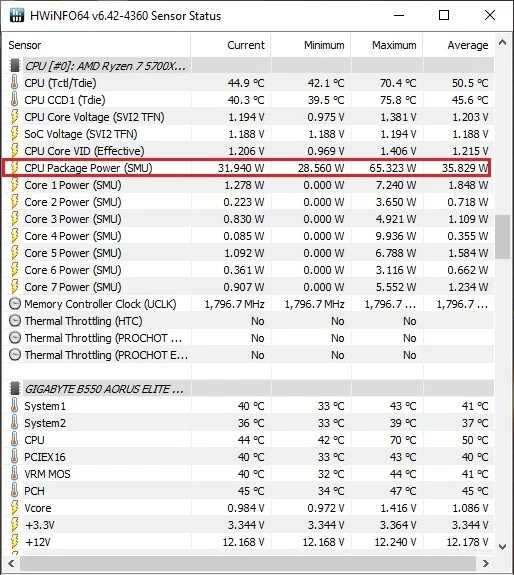
TDP has limited impact when comparing different CPUs in desktops, as desktop CPUs are often placed in relatively large cases with CPU cooling hardware capable of dissipating the heat generated. Despite having more efficient chips, AMD still lags slightly behind Intel's most powerful processors in terms of overall performance.
5. Platform
The platform of a CPU refers to the physical socket it is compatible with and the processor generation to which it belongs. The CPU platform will determine the remaining upgrade path for the processor and the features it has access to.
One such feature is support for the newer DDR5 memory standard. Intel and AMD offer DDR5 support on the latest processors and motherboard chipsets. Another feature is overclocking, which is much more complicated when comparing the two brands. If you're comfortable overclocking your CPU and want to get more performance, you'll find AMD's processors much more flexible.
While it is possible to overclock AMD Ryzen CPUs with Ryzen Master on a variety of chipsets, Intel still reserves overclocking capabilities for the more expensive and high-end 'K' series CPUs. But Intel CPUs typically offer more overclocking headroom, allowing users to get more out of its chips.
You should read it
- ★ Suggest the style of masquerade for men on Halloween night
- ★ Want to load page speed on Edge browser faster, enable this feature
- ★ How to download and convert YouTube video formats on SaveClipBro
- ★ 10 ways to avoid losing laptops and data when traveling
- ★ The secret to distinguish and use memory cards