24 impressive images of colorful clouds of the Carina Nebula
A large number of molecular clouds and dense dust are hiding inside the cloud of the Carina Nebula, making the area opaque. However, these clouds are less dense than Earth's atmosphere many times. The Carina Nebula is designated NGC 3372 , spread over 300 light-years and lies 7,500 light-years from our Earth in the constellation Carina. Let's explore 24 impressive images of the colorful clouds of the Carina Nebula!
1. Pillars of Destruction (Pillars of Destruction)
 Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
The Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) is a star nursery nursery about 7,500 light years from our Earth. These images show a few pillars of gas and dust protruding from the nebula. Dubbed " Ruins Columns ", these areas are being destroyed by radiation from new stars. Huge telescope (VLT) of the European Southern Hemisphere Observatory in Chile captured images using the MUSE (Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer) spectrophotometer.
2. The R18 area in the Carina nebula
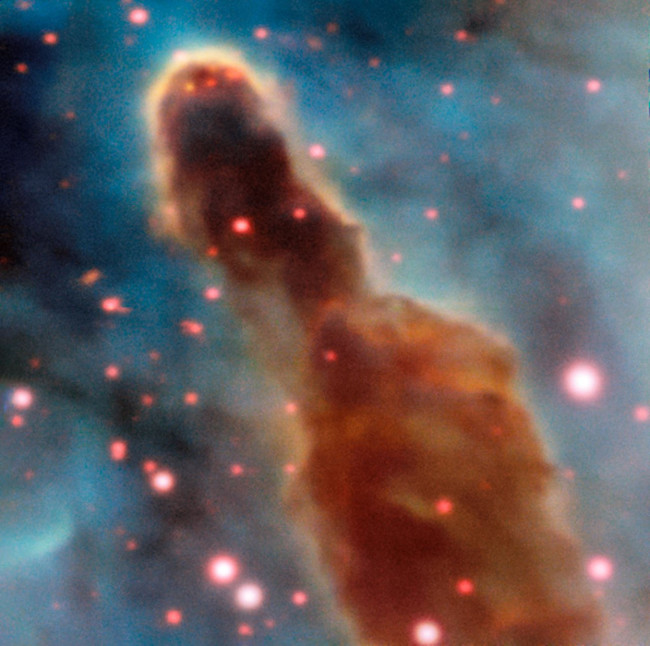 Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
MUSE tool on ESO's huge telescope is captured in the R18 area inside the Carina nebula. The pillars of dirt and gas that produce giant stars are gradually consumed by the stars themselves.
3. The R37 area in the Carina nebula
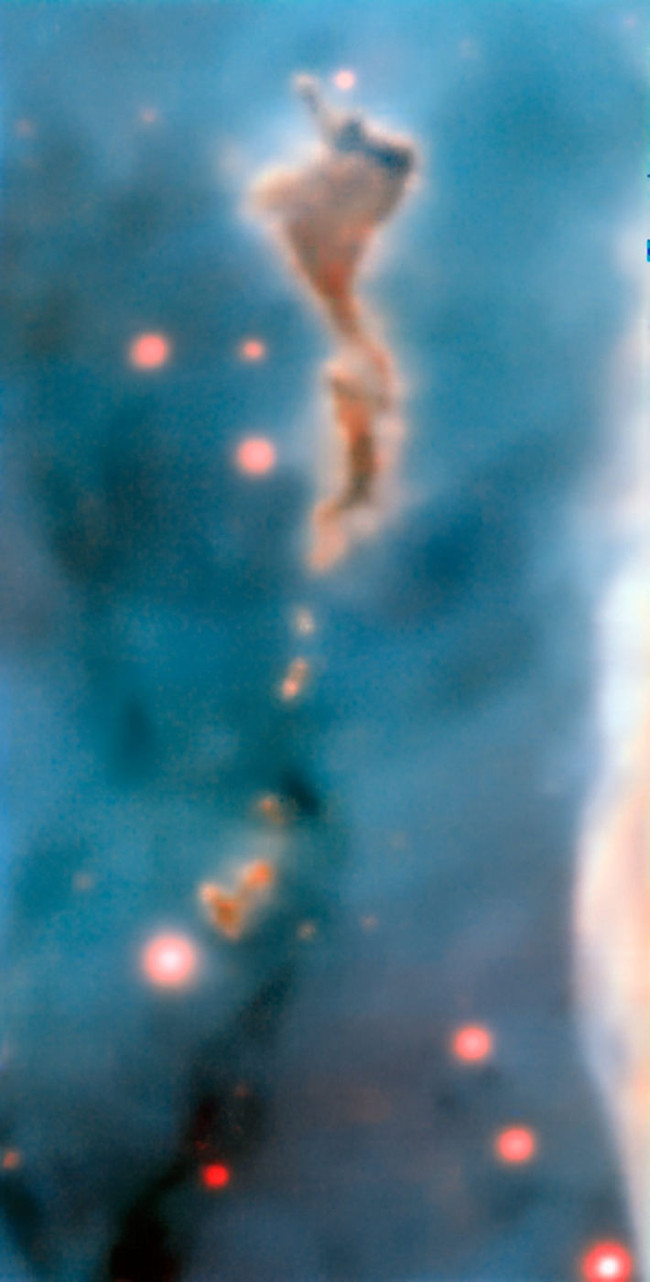
Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
The giant giant star inside the R37 area of the Carina Nebula, located 7,500 light-years from Earth, destroys the clouds of dust and gas that created them. This image was taken using the MUSE spectroscopic instrument on ESO's Extra Large Telescope.
4. The R45 area in the Carina nebula
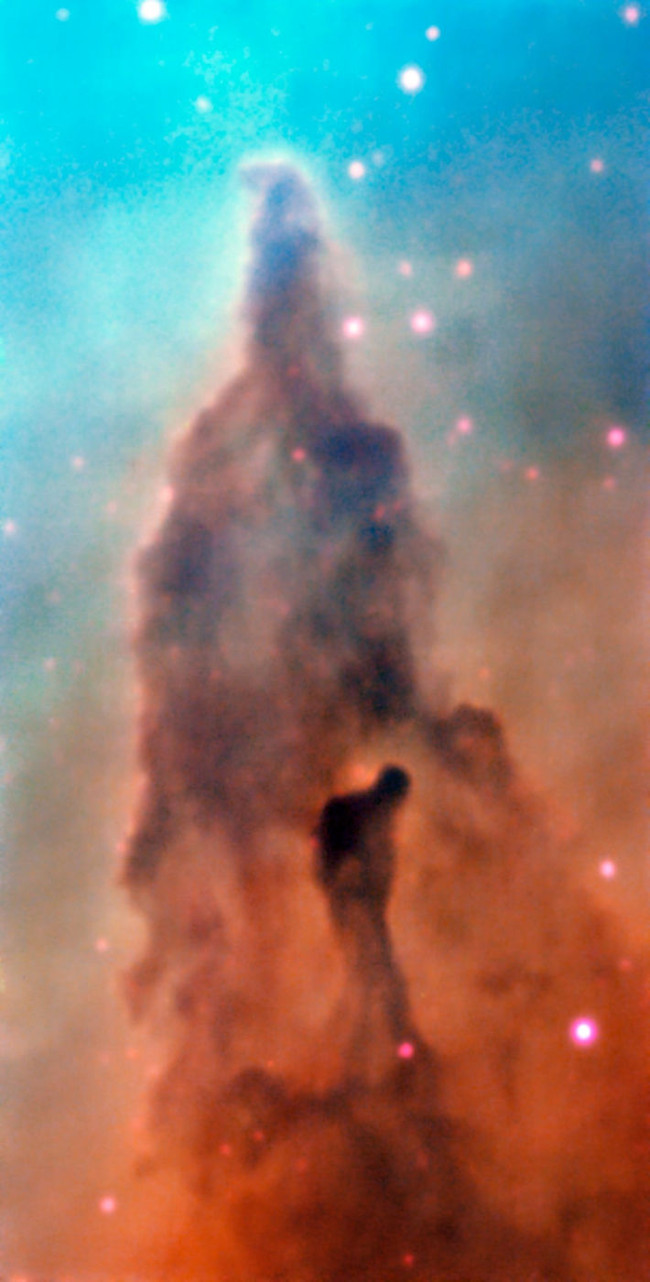 Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
In the R45 area of the Carina nebula, massive stars are born from cosmic gas and dust slowly "swallows" the clouds that gave birth to them.
5. Open star cluster Trumpler 14
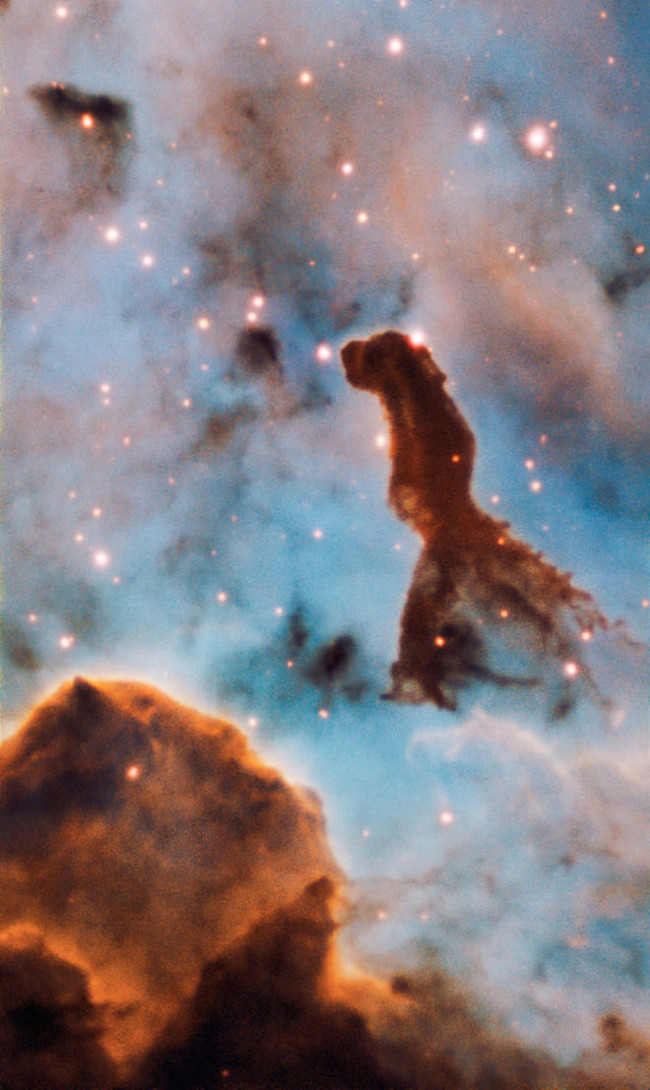 Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
Inside the Carina Nebula, this pillar from the open star cluster Trumpler 14 was captured by the MUSE spectroscopic tool on ESO's huge telescope.
6. The R44 area in the Carina nebula
 Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
This picture shows an area of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) called R44 . The great ESO telescope in Chile created the image using the MUSE (Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer) spectrometer.
7. Mysterious Mountain (Mystic Mountain)
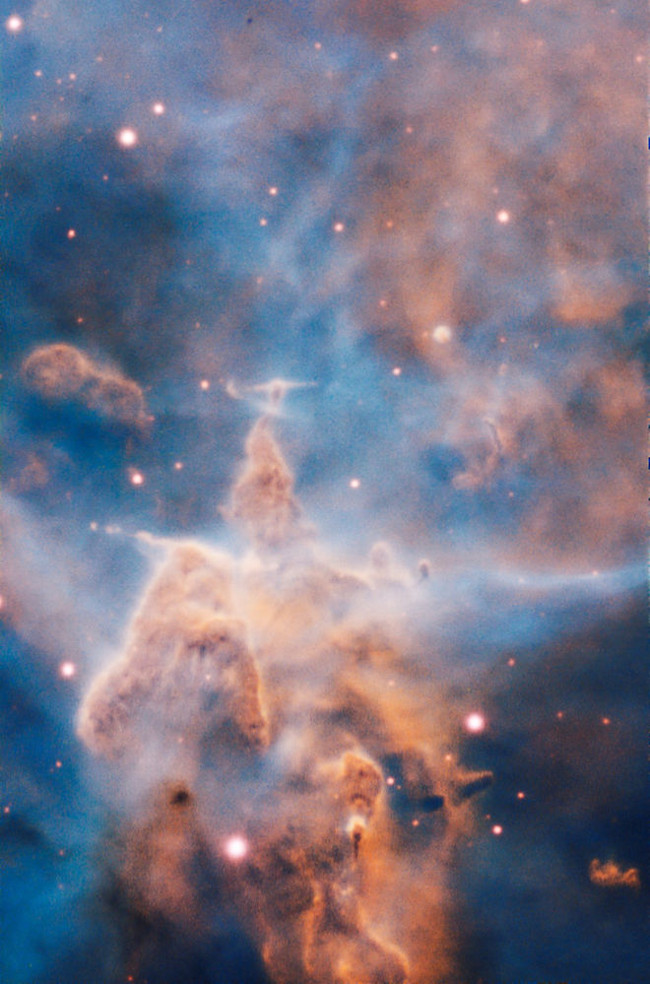 Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
This is the mighty pillar of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) - a 3-light-long cloud of gas and dust that is corroded by bright light from the stars both in the surrounding environment and environment inside the cloud. ESO's huge telescope in Chile created images using the MUSE (Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer) spectrometer.
8. Bok Globules
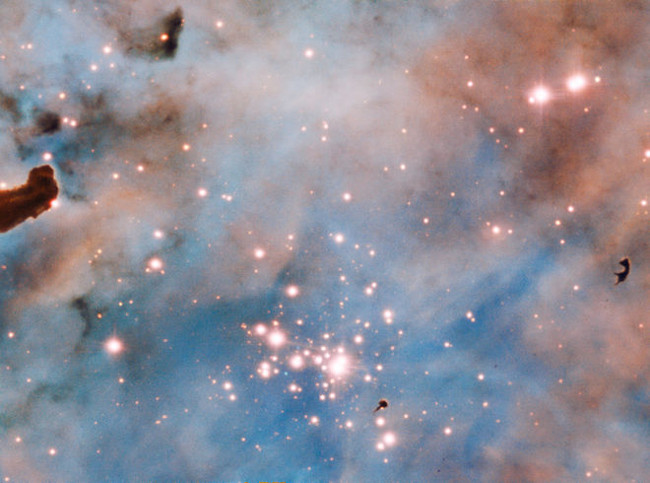 Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
Photo source: ESO / A. McLeod
The dark patches observed in this area of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) are called " Bok Globules ". The small, dark nebula is dense with gas and dust, so not much light can pass through. ESO's huge telescope in Chile created images using the MUSE (Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer) spectrometer.
9. Observe in detail the intense image of the Carina Nebula
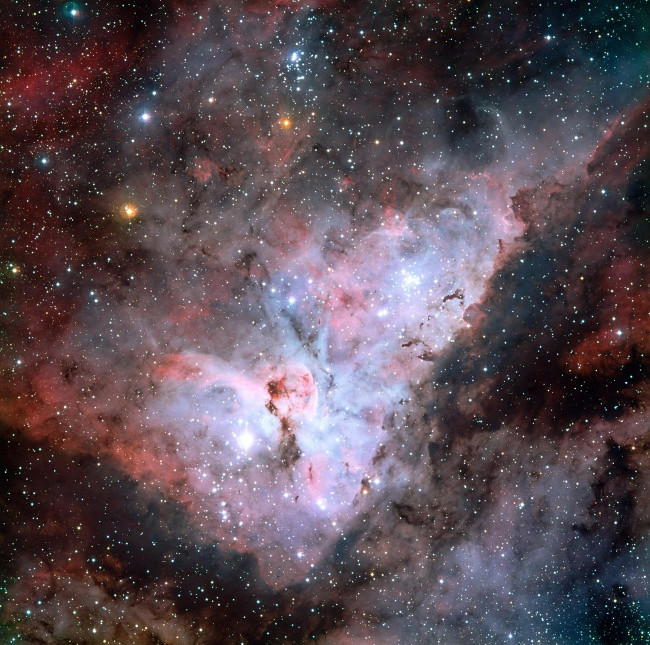 Photo source: ESO
Photo source: ESO
Some astronomical objects known inside and near the Carina nebula can be seen on this wide field image: the bottom left of the photo is one of the most impressive binary stars in the Universe. Eta Carinae, superstar star with the famous Keyhole nebula near the star. The collection of extremely bright and young stars above and to the right of the superstar Eta Carinae is an open star cluster Trumpler 14. A second open star cluster - Collinder 228 is also in the picture, just below the superstar Eta Carinae . The north side is on the upper and east side on the left.
10. Eta Carina Nebula
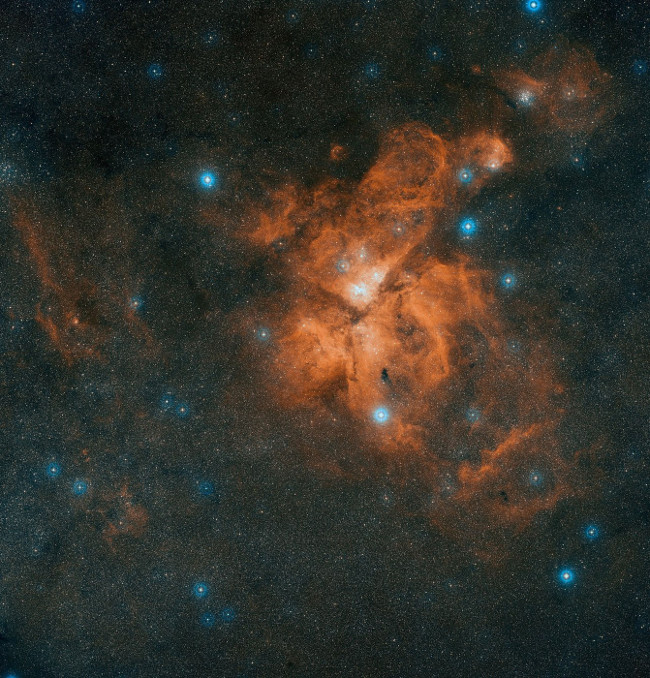 Image source: ESO / Digitized Sky Survey 2;Acknowledgment: Davide De Martin
Image source: ESO / Digitized Sky Survey 2;Acknowledgment: Davide De Martin
Digitized Sky Survey 2 creates this color mixture of Eta Carina nebula from multiple exposures.
11. The Carina Nebula is observed with an ALMA telescope
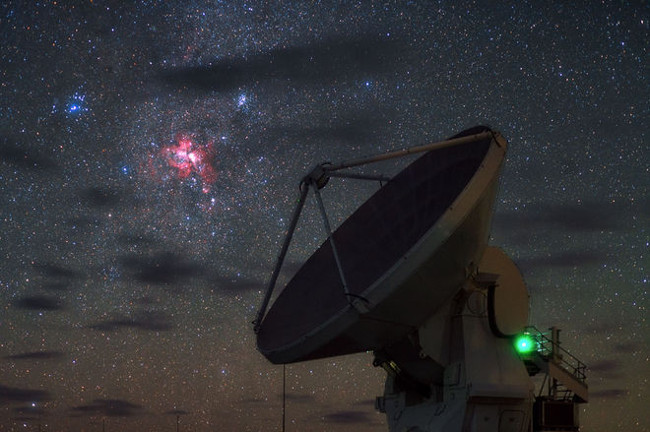 Photo source: ESO / B. Tafreshi
Photo source: ESO / B. Tafreshi
The Carina Nebula shines through the ALMA Telescope on the Chajnantor Plateau in Chile Andes. Images are published on November 30, 2015.
12. Eta Carina Nebula
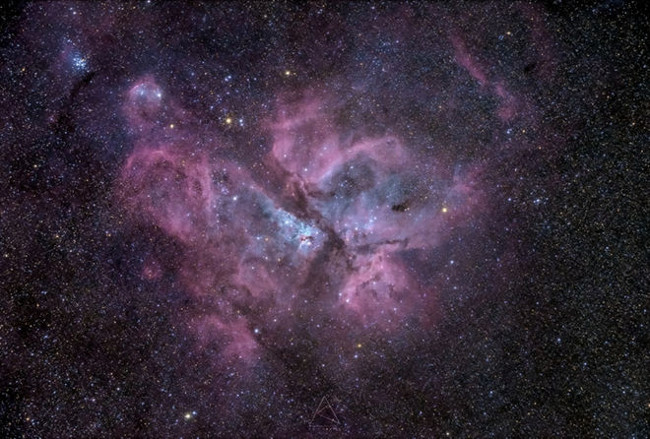 Photo source: Amit Kamble
Photo source: Amit Kamble
Astronomer Photography Amit Kamble captured the Eta Carina nebula on February 19, 2015, based in Auckland, New Zealand.
13. Close-up of the Hubble Space Telescope of the Carina Nebula
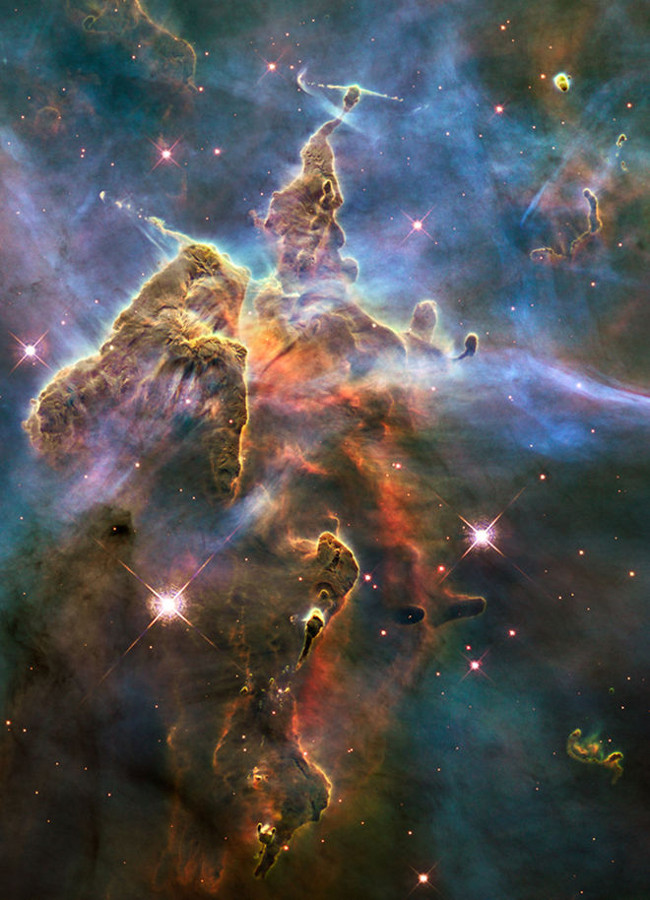 Photo source: NASA, ESA, and M. Livio and the Hubble 20th Anniversary Team (STScI)
Photo source: NASA, ESA, and M. Livio and the Hubble 20th Anniversary Team (STScI)
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope captures this scene of a " star nursery " called the Carina Nebula, located 7,500 light-years from Earth on February 1-2, 2010.
14. The shining diamonds of the star cluster open Trumpler 14
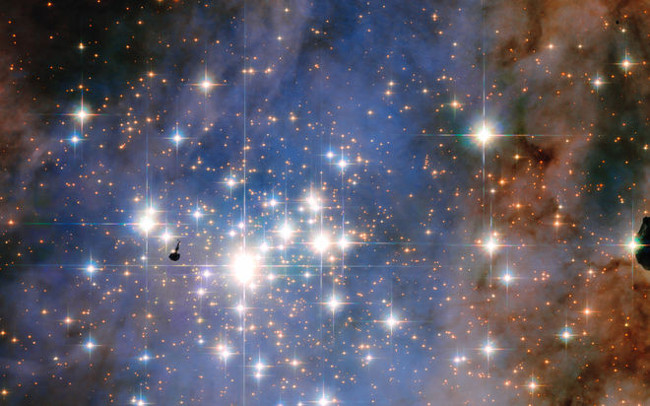 Photo source: NASA and ESA, Jesús Maiz Apellaniz (Instituto de Astrofisica de Andalucia)
Photo source: NASA and ESA, Jesús Maiz Apellaniz (Instituto de Astrofisica de Andalucia)
This image taken with NASA / ESA Hubble space telescope has an open star cluster Trumpler 14 in the Carina nebula. One of the largest gatherings of hot, large and bright stars in the Milky Way, this open star cluster contains some of the brightest stars in our entire galaxy.
15. Panoramic Photo of Carina Nebula taken by ALMA telescope
 Photo source: ESO / B. Tafreshi
Photo source: ESO / B. Tafreshi
The photo ESO Ambassador Babak Tafreshi took a panoramic view of the antenna of the Atacama Large Millimeter / submillimeter Array (ALMA) organization under the sky above the Chajnantor Plateau, in the Andes Mountains. Images are published on November 11, 2013.
16. There are more than 14,000 stars
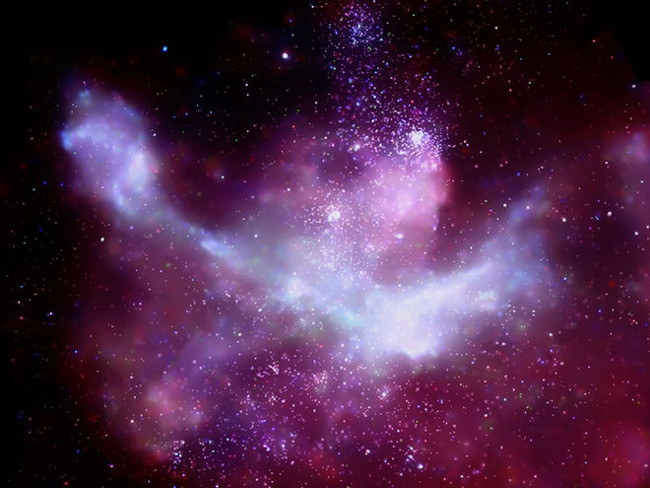 Photo source: NASA / CXC / Penn State / L. Townsley et al.
Photo source: NASA / CXC / Penn State / L. Townsley et al.
The Carina Nebula is a star-forming region between the Sagittarius and Carina branches of the Milky Way galaxy located 7,500 light-years from Earth. NASA's space observatory (Chandra X-Ray Observatory - CXO) has discovered more than 14,000 stars in the region.
17. The Carina Nebula is observed from the Spitzer space telescope
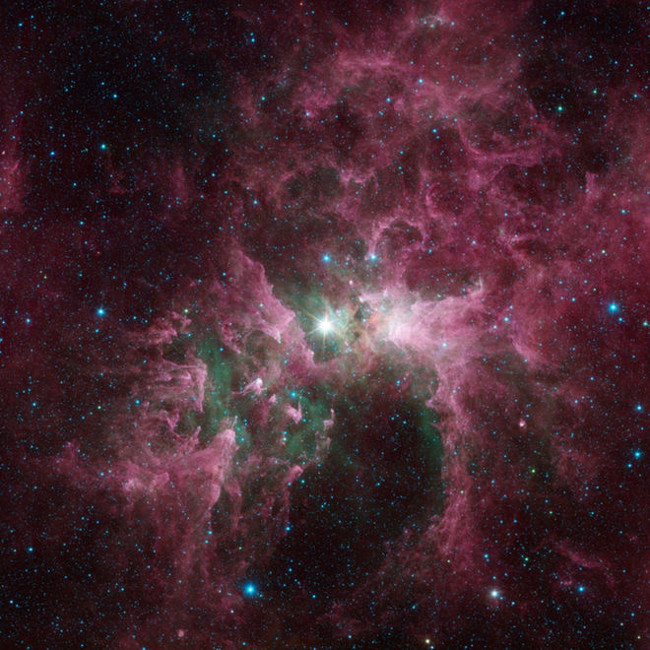 Photo source: NASA / JPL-Caltech
Photo source: NASA / JPL-Caltech
Giant stars that can destroy the surrounding environment are observed in the image of the Carina Nebula from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope.
18. Carina Nebula taken by a VLT telescope surveyed
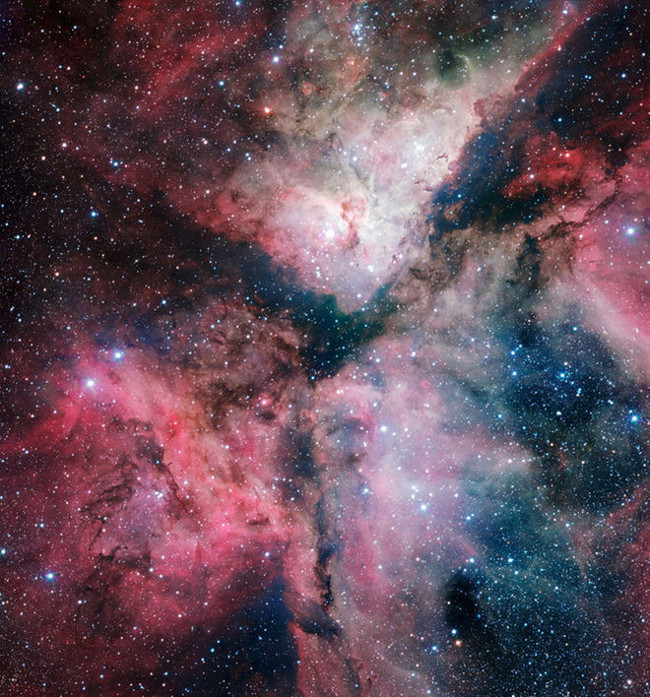 Photo source: ESO.Acknowledgement: VPHAS + Consortium / Cambridge Astronomical Survey Unit
Photo source: ESO.Acknowledgement: VPHAS + Consortium / Cambridge Astronomical Survey Unit
The formation of the giant Carina nebula was captured in detail with the VLT telescope surveyed at ESO's Paranal Observatory. This photo was taken with the help of Sebastián Piñera, during the Chilean President's visit to the observatory on June 5, 2012 and was announced on the occasion of the opening of a new telescope in Naples on December 6. year 2012.
19. Caterpillar - a Bok Globule in the Carina nebula
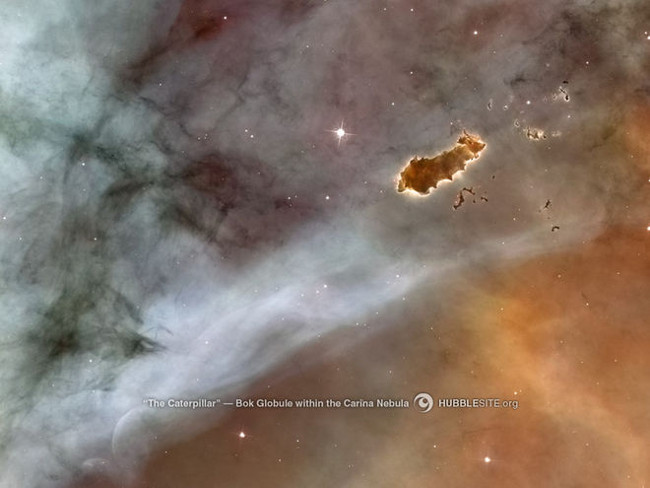 Photo source: NASA, ESA, N. Smith (University of California, Berkeley), and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI / AURA)
Photo source: NASA, ESA, N. Smith (University of California, Berkeley), and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI / AURA)
A Bok Globule in the Carina Nebula nicknamed " Caterpillar " is located on the right.
20. Evaporate the Blob in the Carina Nebula
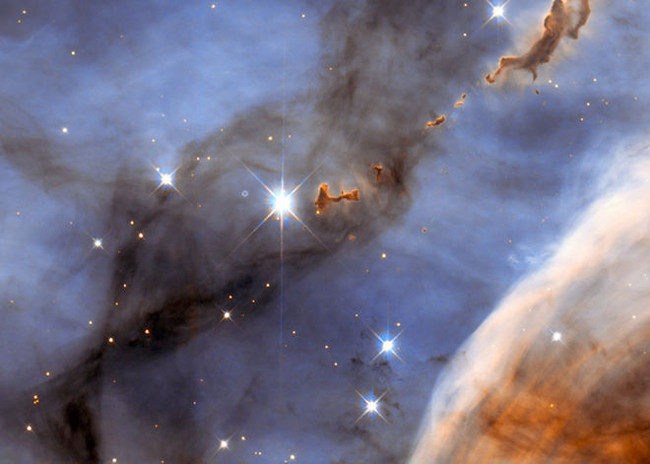 Image source: ESA / Hubble, NASA
Image source: ESA / Hubble, NASA
The Carina Nebula lasts about 30 light-years, lies about 7,500 light-years from Earth and can be seen with a small telescope when facing the constellation Keel (Carina).
21. Infrared image of the Carina nebula from ESO's huge telescope
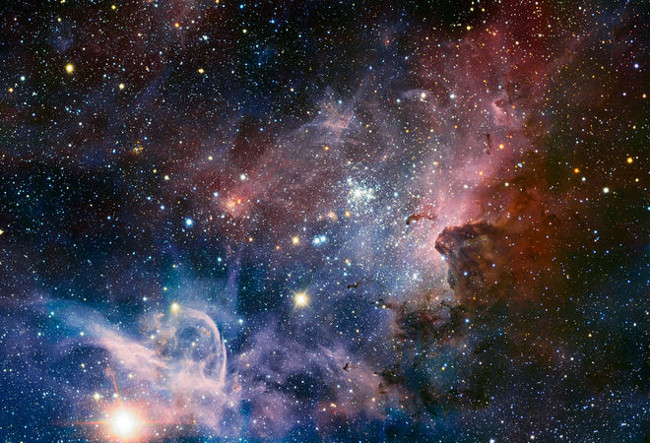 Photo source: ESO / T. Preibisch
Photo source: ESO / T. Preibisch
Panoramic photo of the Carina Nebula - a giant star-forming area in the southern sky, taken with infrared light using the HAWK-I camera on the Southern Europe Observatory's Extra Large Telescope in Chile and published on February 8, 2012. Many of the previously hidden features scattered in the space of gas, dust and young stars have appeared.
22. Infrared image of Carina nebula
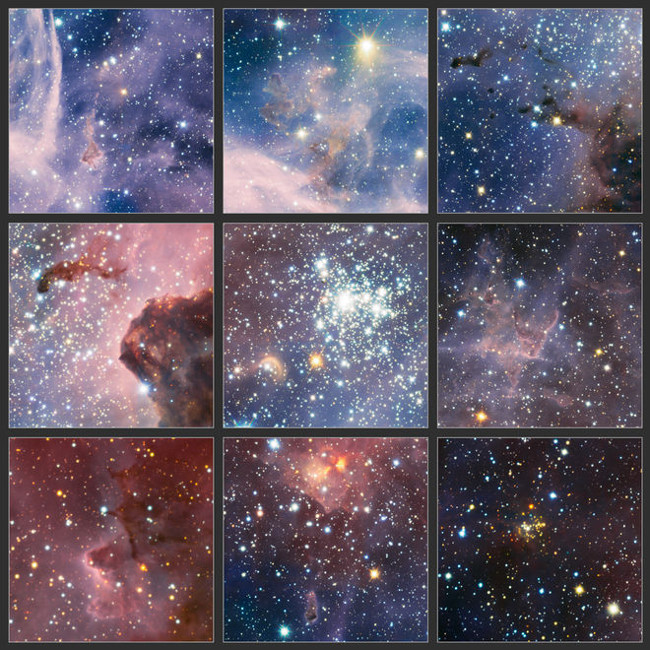 Photo source: ESO / T. Preibisch
Photo source: ESO / T. Preibisch
These striking features are part of a large panorama of the Carina Nebula - the giant star-forming region in the southern sky, taken with infrared light using HAWK-I cameras. on ESO's huge telescope in Chile. Photos published February 8, 2012.
23. Matte Carina Nebula and infrared light
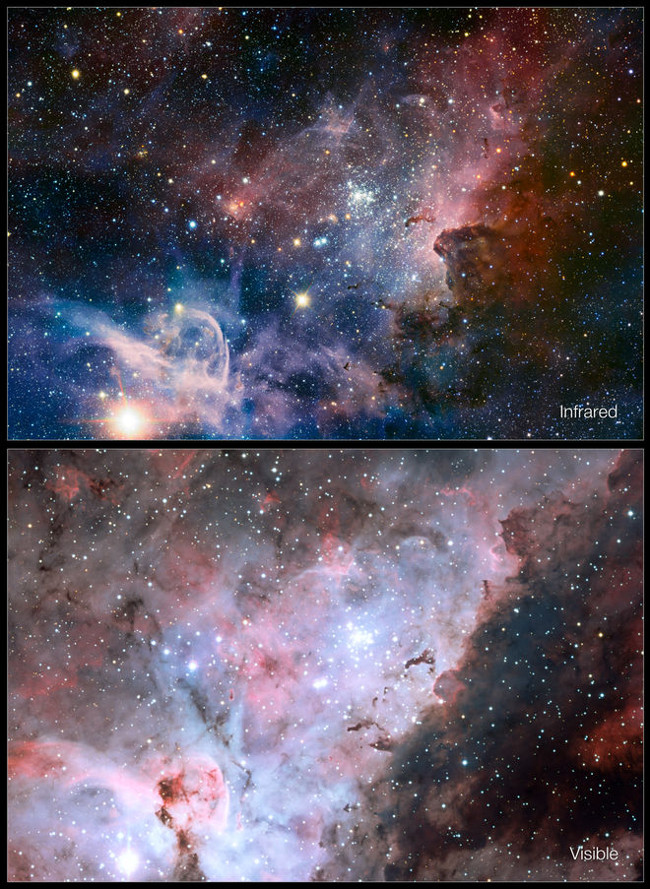 Photo source: ESO / T. Preibisch
Photo source: ESO / T. Preibisch
Image of the Carina nebula - an area of giant star formation in the southern sky, comparing images taken with dim light with images taken with infrared light. Photos published February 8, 2012.
24. Dust clouds of the Carina Nebula
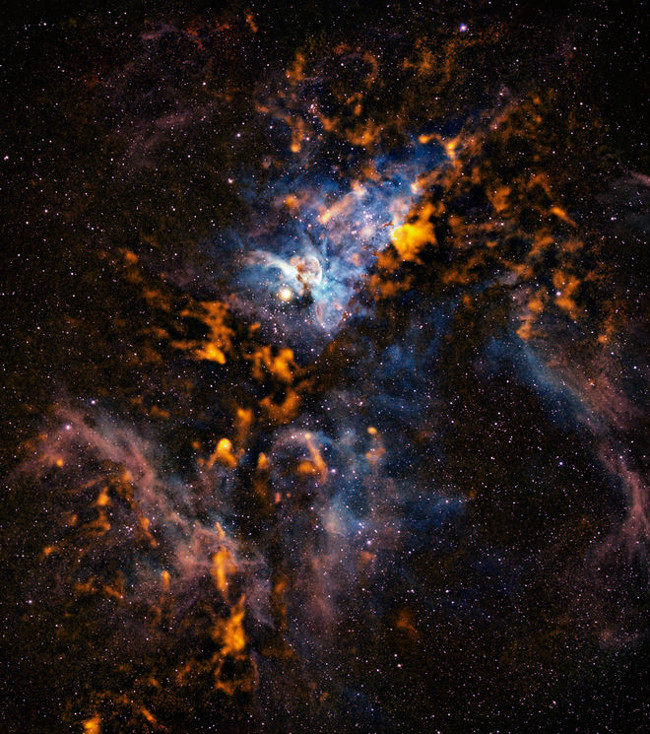 Credit: ESO / APEX / T.Preibisch et al.(Submillimetre);N. Smith, University of Minnesota / NOAO / AURA / NSF (Optical)
Credit: ESO / APEX / T.Preibisch et al.(Submillimetre);N. Smith, University of Minnesota / NOAO / AURA / NSF (Optical)
The image of the Carina Nebula shows dust clouds from the stars formed in the "bustling star nursery".
You should read it
- ★ The most spectacular cosmic photos 2017
- ★ Admire the moment millions of new stars are born in the Lupus 3 nebula
- ★ Amazing blue meteor attacks the red heart nebula
- ★ Before 'returning to Thanos', what was the fate and appearance of Nebula in the comics?
- ★ Admire the giant stars forming in the corner of the Tarantula Nebula