The golden age of antibiotics is over, the immediate future will be a nightmare for humans
In 1928, penicillin, the first antibiotic found by Alexander Fleming. Scottish biologists are considered to have opened a golden era of medicine. Meanwhile, the antibiotic pills are called western medicine . They have saved millions of patients every year from death caused by infections.
However, that wonderful story seems to be coming to an end. After more than 70 years of antibiotics were introduced into medicine, its golden age was no longer maintained. There are millions of people who die each year in an era without antibiotics, and then will be a similar number in the coming years. The nightmare called " antibiotic resistance " is threatening humanity because of our own drug abuse in the past.
What is antibiotic resistance?

Antibiotic resistance is a phenomenon that occurs when germs or bacteria are not destroyed by antibiotics . They not only exist but also produce new generations of bacteria, also have resistance to chemicals and chemicals to treat infections .
A strain of bacteria can develop bases against one to dozens of different antibiotics . Meanwhile, the infection becomes difficult or even impossible to treat. In some cases, patients may have to undergo surgical removal, or even death from antibiotic resistance.
Why is antibiotic resistance a nightmare for humans?
If you come back before 1943, when antibiotics have not yet appeared, all the deaths around us do not come from cancer or cardiovascular disease. People will die because of injuries when they fall, hit bullets, labor accidents . Most wounds lead to infection and end someone's life.
However, all changed after Fleming found penicillin . The infection is considered a death sentence, and can suddenly be treated after a " snap of a finger " with antibiotics. Like a miracle, it opened a golden era in western health. Antibiotics are considered medicinal herbs.
So far, more than 70 years have passed, and we suspect that there are times when a golden age of something can last that long. It's not too early to think about the collapse of the antibiotic era, when bacteria are increasingly resistant to drugs.

Talking about a modern civilization, we often imagine power plants, computers, handheld devices . But who knows that antibiotics are one of the pillars that support that world. If the antibiotic era collapsed, how would civilization shake?
First, we will lose all defense shields for people with weak immune systems. They include cancer patients, HIV-infected people, premature babies . This means the death of all these people.
Next, human surgical techniques are disabled. Many surgeries are required to use preventive antibiotics. When antibiotics are ineffective, the hospital operating room is not covered.
We will not be able to perform heart surgery, kidney transplantation, catheterization for stroke patients . We cannot operate even if we simply correct the knee joint. It is not possible to have a caesarean, and even in the most modern hospitals, 1 out of 100 pregnant women will die.

Infection causes fear from trivial diseases. Strep throat causes heart failure. Pneumonia kills 3 in 10 children infected. Skin infections are synonymous with amputation. Remember the first case of penicillin treatment. Albert Alexander had previously lost an eye in the state of pustules, only starting from scratching his face while gardening.
Then you dare to do anything when any damage can kill people. Do you dare to ride a motorbike, rollerblade, climb stairs to fix the roof or put your children to play on the floor?
When will these things happen?
Are you startled to know that we were in this nightmare?
To this day, human beings have under 100 antibiotics . The number is not much different from the early years of the 21st century. But in 2000, an American patient was first confirmed by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to resist all antibiotics. except for two types.
In 2008, Swedish physicians faced the case of an Indian patient who was infected with an antibiotic-resistant all but one.
But don't think it's just a single case. Each year, the United States and Europe alone have about 50,000 deaths due to infection without cure. A project funded by the British government called " Antibiotic Resistance Assessment Program " estimates the total number of deaths of this type in the world at 700,000 people per year. In 2050, the number will be up to 10 million with the current rate of antibiotic resistance developing.
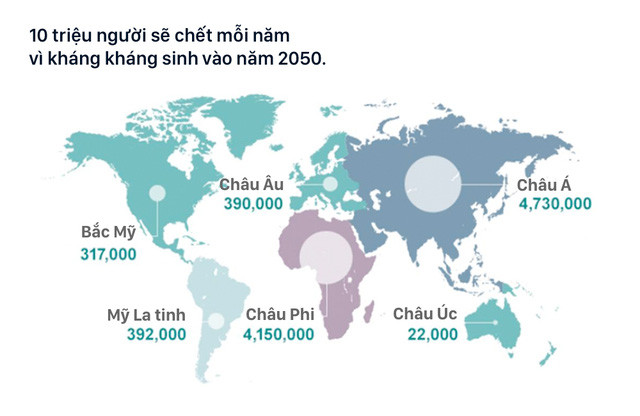
Ignoring the numbers, you can also learn that nightmares have come to yourself and your loved ones. In the past, urinary symptoms caused by urinary tract infections could be completely cured with a short-term antibiotic. Now, you may have to use several drugs.
Recent research indicates that your child is at risk of being in 25% of children with urinary tract infections who must use 3 different antibiotics. The remaining 25% must be treated with 2 drugs and only half of children can be cured with a single drug.
On April 30, 2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) stated in a report that humanity is really in the nightmare of antibiotic resistance. It is a serious threat and medical challenge in this moment. WHO said " do not act today, our future will have no cure ".
Fleming, the father of antibiotics, knew everything

Alexander Fleming, a Scottish biologist considered the father of antibiotics when he discovered penicillin in 1928. In 1943, the first commercial penicillin doses were released. Two years later, Fleming received the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
But right after that interview, he warned of the prospect of being unhappy when the bacteria could become resistant. " People who abuse penicillin today, they are responsible for the deaths of patients infected with penicillin-resistant bacteria later, " Flenming said. " I hope this danger can be controlled ."
And that's right. In 1943, penicillin was released and in 1945, penicillin-resistant bacteria appeared. People go looking for new antibiotics. In 1972, vancomycin was prepared and vancomycin-resistant in 1988.
Imipenem was born in 1985 and in 1998, imipenem resistance appeared. One of the latest human antibiotics, daptomycin was born in 2003, only one year later, it became resistant to bacteria.
This is like a sheep jumping game. The drug is born, bacteria are resistant to it and then we look for a new drug. But it seems that humans are short of breath when a new strain of bacteria is born every 20 minutes, pharmaceutical companies need a decade to study an antibiotic.

What can we do?
First of all, let's talk about why bacteria can become resistant. From a cellular perspective, it is the genetic genetic modification of the bacterial DNA that: avoids the penetration of antibiotics into them, helps the enzyme synthesize enzymes to inactivate or decompose antibiotics, changing Metabolic pathways and they release antibiotics from the cells.
Ignoring these complexities, you should be aware of people who have helped their genetically modified bacteria. Those are collectively called names: abuse of antibiotics .
Have you ever used antibiotics to treat flu without knowing it's caused by the virus and not the bacteria? Have you ever arbitrarily reduced the dose or duration of antibiotic treatment of a doctor to half without knowing it facilitated bacteria to survive and create resistance genes?
Then when we use antibiotics in animal husbandry, veterinary medicine, agricultural production and fisheries, it is a condition for the bacteria in animal resistance to drugs and then affect humans. Using biocides in regular cleaning also creates resistant strains of bacteria.
So far, antibiotic resistance has become a global problem that only comes from small things but everyone does so often. Global solutions will also have to be set. It is possible that we should strictly prohibit the use of antibiotics in livestock and fisheries. Set up a gate to control antibiotic prescriptions to avoid indiscriminate abuse or build up an alarm system to monitor the upcoming resistance .
But then these are too big things and need a small source of funding. Why don't we start with the actions of each individual?

You should read it
- ★ Artificial skin can support antibiotic resistance
- ★ What is antibiotic resistance? Why is it dangerous?
- ★ Nearly half of seniors are prescribed unnecessary antibiotics because of a common cold
- ★ NASA launched E. Coli into space to study antibiotic resistance of bacteria
- ★ 10 reasons why antibiotic resistance is scary right now