Scientists found the 555 million-year-old fossil of human ancestors
It may not look like anyone, but the evolution is so harsh, making today's animal ancestors nothing like their descendants.
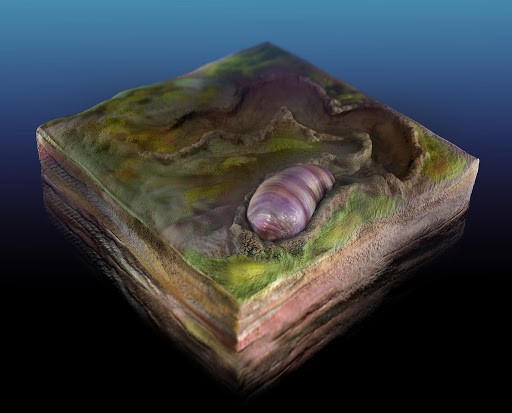
Ikaria wariootia is thought to be the source of most living animals, including humans.
The now extinct species is bilaterian, which means that besides the usual head and tail, their bodies are left and right with identical structures. . The Ikaria wariootia worm is thought to be the first clear common ancestor of most animals living today.
Over more than 100 million years, evolution has diversified animals into countless species. However much, these living things still have to originate from the origin of life, that is, it will have to have a certain ancestral species and then through evolution, to split many species like today. For centuries, scientists have been trying to go against animal pedigrees to find common ancestors of humans with domestic dogs and wild wolves in the forest.
Traces of the first animals appeared on ancient rocky shores near Nilpene, South Australia, in the form of small fossils like tunnels dug by a tiny creature, the markings on this rock. whose scientific name is Helminthoidichnites. For more than a decade now, scientists have been trying to learn about ancient creatures that can dig these tunnels, but efforts to find fossils of mysterious creatures remain in vain.
I can't see it forever, but when I find it, it's like digging up a gold mine. The team, led by recently graduated PhD student Scott Evans, discovered more than 100 fossilized specimens of ancient worms. They have made new discoveries thanks to 3D laser scanning technology. It is difficult to take pleasure in the archaeological team when finding the creature that is said to be their own ancestor.
According to research, the Ikaria wariootia can be as large as the size of a grain of rice. Its name is made up of two parts: ' ikaria ' means' meeting place in the native Adnyamathanha language, while ' warioota ' refers to the Warioota tributary that flows near the archaeological site.

Three fossilized samples of Ikaria wariootia.
These tiny worms lived in the Ediacaran Period, but they were not the only animals that existed during this time. They are also not the ancestors of EVERY species we know - because there are still some species of bodies that are not symmetrical, such as jellyfish or seals, but Ikaria wariootia is most likely a 'symmetrical species'. The oldest 'ever discovered.
Analyzing the trenches left behind by the Ikaria wariootia, it can be seen that they are living in sediments in shallow water, have a way similar to modern earthworms, most likely to eat the dead creatures. water or other organic matter they find in water. Looking at their path, it can be said that Ikaria wariootia knows to find food and oxygen to live, and be able to sense the things around them.
Attempts to learn about ancient life also helped scientists in the process of finding alien life. Indeed, part of the research fund comes from NASA's extraterrestrial biology research program. If we understand the complex process of life formation on the planet we stand on, we will apply this knowledge to the journey to find extraterrestrials, or at least an environment that can be nurtured. That creature.
Besides, the discovery of Ikaria wariootia will be a big milestone in the process of redrawing animal genealogy, most likely this is just one of many discoveries possible when studying fossils from the Ediacaran Period. . Archeological sites in southern Australia, China or Russia will give us more answers.
You should read it
- ★ Mysterious journey of finding egg shell protein Ostrich 3.8 million years old
- ★ The mystery of the 290-million-year-old giants challenges scientists around the world
- ★ Giant bat fossils have been discovered
- ★ Finding new fossils can represent the world's oldest fungus
- ★ Discovered an old 14,000 year old campsite in Argentina