How does Saharan dust affect Atlantic hurricanes?
In June 2025, dust from the Sahara Desert rose up off the coast of Africa into the Atlantic Ocean. Although this is an annual phenomenon, it has an impact on the development of tropical storms and hurricanes, temperatures, and even the appearance of sunsets and sunrises.
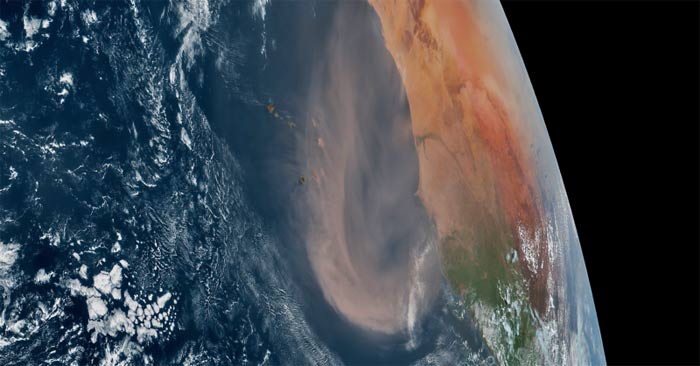
What is Saharan dust?
Saharan Dust or Saharan Air Layer (SAL) is exactly what it sounds like: dry, dusty air from the Sahara Desert. This Saharan dust develops throughout the spring through early fall. But it becomes more active in mid-June, peaking from late June to early August.
Saharan dust 'flares' can occur about every three to five days as tropical waves move east to west along the southern edge of the Sahara Desert. As the tropical waves move west, they push Saharan dust high into the air, forming the Saharan Air Layer. This dust layer can travel thousands of miles across the Atlantic Ocean, often reaching as far as the Caribbean, Gulf Coast, and southeastern United States. The Saharan Air Layer lies about a mile above the surface and can be as thick as 2.5 miles.
How does Saharan dust affect tropical weather?
By definition, a tropical storm is a low pressure system that forms over warm ocean waters that are at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 degrees Celsius). But there also needs to be enough moisture to extend into the sky. The Saharan air layer can be more than 2 miles (3 kilometers) thick. It is a 2-mile (3-kilometer) layer of dry, dusty air (50 percent drier than the typical tropical atmosphere) that extends into the sky, cutting off moisture from the surrounding environment. As this layer moves across the Atlantic, the dry air limits the amount of moisture in the air. So it also limits the development of tropical systems.
The Saharan Air Layer can also contain strong winds, sometimes reaching over 20 miles per hour. Tropical cyclones also require low-level wind shear to develop. Wind shear is when winds change direction and/or speed with altitude. Too much wind shear can tear apart or weaken tropical cyclones. So if the Saharan Air Layer contains gusty winds, this can add wind shear to the atmosphere, which also makes it harder for tropical cyclones to develop.
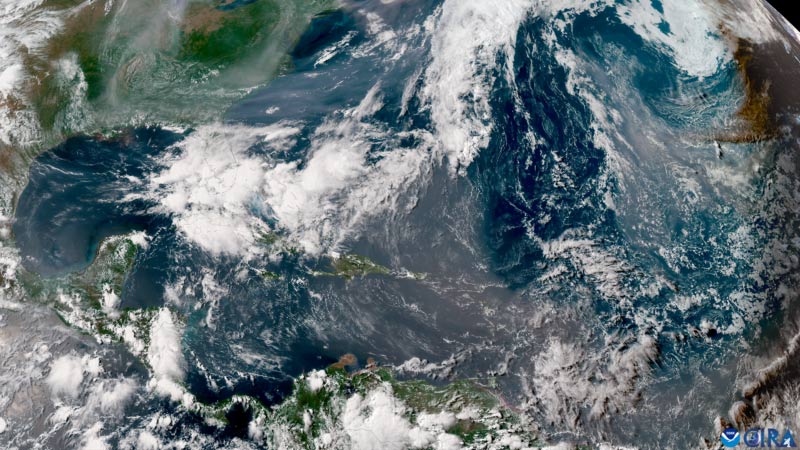

Impact on other types of weather
While forecasters often focus on the Saharan Air Layer when forecasting tropical weather, it also affects other types of non-tropical weather. In addition to adding dry air to the atmosphere, it also warms the surrounding atmosphere. This warm layer of the atmosphere is stable, preventing large clouds from forming, let alone precipitation. This means that if Saharan dust reaches land, it limits the chance of rain and allows temperatures to rise rapidly, creating hot, mostly dry days.
When Saharan dust moves inland, sunsets and sunrises are more vibrant! The light contains all the colors of the rainbow, including long and short wavelengths. Blue has shorter wavelengths, while warmer colors (like yellow, orange, and red) have longer wavelengths. Sunsets and sunrises generally have more red in them because of the longer wavelengths of that light, and the colors pass through more layers of the atmosphere when the sun is at a lower angle. When Saharan dust is in the air, it increases this effect, creating more vibrant colors at sunrise and sunset. Unfortunately, when Saharan dust is high in the air, air quality can be poor. If you have a respiratory condition or sensitivity, or a weakened immune system, avoid going outside when Saharan dust is present or wear a mask when you go outside.

In short, Saharan dust blows across the Atlantic every year, becoming more active in June. This dust can limit the formation of tropical storms and even clouds.
You should read it
- ★ What happens when two storms clash?
- ★ Stunned with images of three major storms in the ocean recorded by the ISS space station
- ★ Unbelievable but true, CAT in the world began to run out
- ★ Why do storms around the world often have women's names?
- ★ What is fine dust? The harmful effects of inhaling ultra-fine dust in the air you need to know