Query XML data from a table with XML data type
The purpose of this article is to guide Microsoft SQL Server database administrators in:
• Create XML schema (XML Shema).
• Create a table with XML data type.
• Import XML file into table with XML data type.
• Query XML file.
• Query the XML file and output the result, similar to the output from Transact SQL Statement commands.
Step 1
First, create a C file: XMLCustomer1.XML as shown below. This XML file contains data related to a customer.
2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00
james.brewer
1AE
A-Accessible
761
Stopped
30
2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00
james.brewer
1AE
Not-Accessible
870
Stopped
30
2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00
james.brewer
1AE
A-Accessible
97F
Started
30
Step 2
Create a database (database) and a set of XML Schema as below:
USE [master] GO / ****** Object: Database [XMLTest] Script Date: 04/17/2007 01:49:43 ****** / IF EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sys.databases WHERE name = N'XMLTest ') DROP DATABASE [XMLTest] go to create database XMLTest go to use XMLTest Create XML Schema Collection XMLTrack as N' 'go
Note : updating the Schema collection is based on your own data in the XML file.
Step 3
Create a table with XML data type:
USE [XMLTest]
GO
/ ****** Object: Table [dbo]. [XMLFiles] Script Date: 04/17/2007 02:07:52 ****** /
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID (N '[dbo]. [XMLFiles]') AND type in (N'U '))
DROP TABLE [dbo]. [XMLFiles]
create table XMLFiles (Fileid int identity (1,1),
ImportedDate datetime constraint xmldatestamp default getdate (),
Filename varchar (500),
data xml (XMLTrack))
Step 4
Enter the XML file you just created (C: XMLCustomer1.XML), using the openrowset function as shown below:
USE [XMLTest]
go
INSERT INTO XMLFiles (Filename, DATA)
SELECT 'Customer1' a, *
FROM OPENROWSET (BULK 'C: XMLCustomer1.xml', SINGLE_CLOB)
as mytable
go
Note : The SINGLE_BLOB keyword will import the entire XML file for a column with an XML data type.
Step 5
Query the XMLFiles table, using the SQL operations shown below:
USE [XMLTest] go select * from XMLFiles where FileId = 1 go
This command will produce the following results:
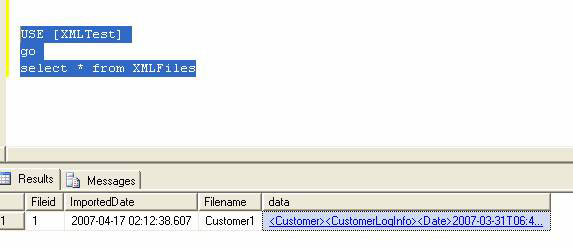
Figure 1.0
When you click on the data, it also displays XML data (Figure 1.1).
2007-03-3106: 40: 38.0000-05: 00 james.brewer 1AE A-Accessible 761 Stopped 30 2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00 james.brewer 1AE Not-Accessible 870 Stopped 30 2007-03- 31T06: 40: 3800000-05: 00 james.brewer 1AE A-Accessible 97F Started 30
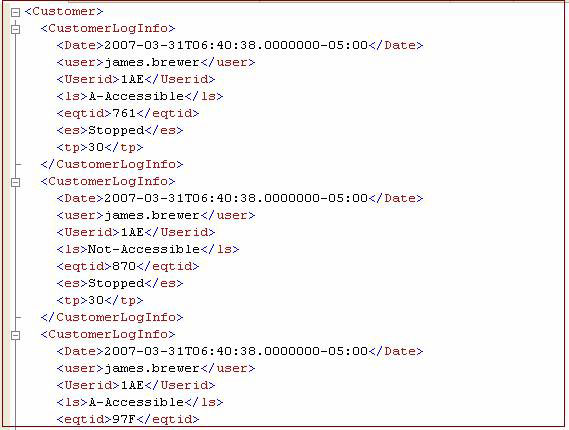
Figure 1.1
Step 6
Now, query the XML data from the table to produce an SQL transaction as the result set. Execute XQuery program as below:
SELECT
ref.value ('Date', 'nvarchar (364)') as [Date],
ref.value ('user', 'nvarchar (364)') as [User],
ref.value ('Userid', 'nvarchar (364)') as [Userid],
ref.value ('ls', 'nvarchar (364)') as [ls],
ref.value ('eqtid', 'nvarchar (364)') as [eqtid],
ref.value ('es', 'nvarchar (364)') as [es],
ref.value ('tp', 'nvarchar (364)') as [tp]
FROM XMLFiles CROSS APPLY Data.nodes ('// Customer / CustomerLogInfo') R (ref)
where Fileid = 1
The program will produce results as shown in Figure 1.2:
Date, User, Userid, ls, eqtid, es, tp 2007-03-3106: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, A-Accessible, 761, Stopped, 30 2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, Not-Accessible, 870, Stopped, 30 2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, A-Accessible, 97F, Started, 30
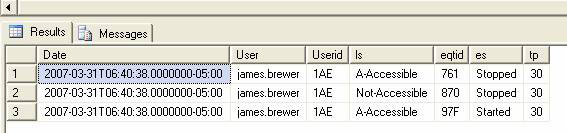
Figure 1.2
Step 7
Now repeat step 4 and re-enter the data.
USE [XMLTest] go INSERT INTO XMLFiles (Filename, DATA) SELECT 'Customer1' a, * FROM OPENROWSET (BULK 'C: XMLCustomer1.xml', SINGLE_CLOB) as mytable go
Step 8
Query the table as shown below:
USE [XMLTest] go select * from XMLFiles go
The result is:
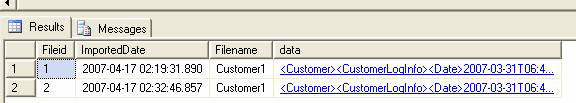
Figure 1.3
Step 9
To display all data from both rows, we can write the query as shown below:
SELECT
ref.value ('Date', 'nvarchar (364)') as [Date],
ref.value ('user', 'nvarchar (364)') as [User],
ref.value ('Userid', 'nvarchar (364)') as [Userid],
ref.value ('ls', 'nvarchar (364)') as [ls],
ref.value ('eqtid', 'nvarchar (364)') as [eqtid],
ref.value ('es', 'nvarchar (364)') as [es],
ref.value ('tp', 'nvarchar (364)') as [tp]
FROM XMLFiles CROSS APPLY Data.nodes ('// Customer / CustomerLogInfo') R (ref)
where Fileid = 1
union all
SELECT
ref.value ('Date', 'nvarchar (364)') as [Date],
ref.value ('user', 'nvarchar (364)') as [User],
ref.value ('Userid', 'nvarchar (364)') as [Userid],
ref.value ('ls', 'nvarchar (364)') as [ls],
ref.value ('eqtid', 'nvarchar (364)') as [eqtid],
ref.value ('es', 'nvarchar (364)') as [es],
ref.value ('tp', 'nvarchar (364)') as [tp]
FROM XMLFiles CROSS APPLY Data.nodes ('// Customer / CustomerLogInfo') R (ref)
where Fileid = 2
The results are in the form of Figure 1.4.
Date, User, Userid, ls, eqtid, es, tp 2007-03-3106: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, A-Accessible, 761, Stopped, 30 2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, Not-Accessible, 870, Stopped, 30 2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, A-Accessible, 97F, Started, 30 2007-03-3106: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, A-Accessible, 761, Stopped, 30 2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, Not -Accessible, 870, Stopped, 30 2007-03-31T06: 40: 38.0000000-05: 00, james.brewer, 1AE, A-Accessible, 97F, Started, 30
Note: If you are planning to display all data from each row with an XML data type, you can create a stored procedure with a temporary table or pointer .
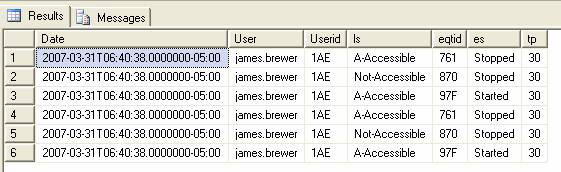
Figure 1.4
Conclude
This article illustrates how to create an XML Schema, create a table with an XML data type, import an XML file into a table with an XML data type, query the XML file, and produce the same result as the actual result set. shown by SQL Transact commands.