Learn about AMD's Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme APUs
XBased on the existing Zen 4/RDNA 3 microarchitecture and built using a process node TSMC's N4 (4nm), both the Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme are specifically designed from the ground up to power high-performance handheld gaming devices.
With ASUS' ROG Ally being the first Windows handheld console to incorporate these all-new chips, let's compare AMD's Ryzen Z1 with its "Extreme" variant in terms of specs, performance, and specs. value.
AMD Ryzen Z1 Series: Specifications and Features
In terms of specifications, AMD's Ryzen Z1 has been equipped with 6 Zen 4 CPU cores for a total of 12 logical threads running at an advertised base clock of 3.2 GHz and a maximum boost clock of 4.9 GHz. The custom SoC incorporates a more modest RDNA 3 iGPU, notably the Radeon 740M, with 4 compute units (256 shaders) operating in the 1.5 GHz - 2.5 GHz core frequency range.
Meanwhile, the Ryzen Z1 Extreme has an 8-core/16-thread layout with a base frequency of 3.3GHz and a boost frequency of up to 5.1GHz. Besides increasing core/thread count and clock speed, the Extreme variant also integrates a more powerful RDNA 3 based Radeon 780M with 12 compute units (768 shaders) clocked at around 1.5 GHz - 2.7 GHz.
While both APUs remain identical across the 9W - 30W configurable TDP range, the Ryzen Z1 Extreme benefits from a slightly larger cache size than the standard Z1 chip. Due to the two additional cores, the Extreme variant utilizes 24 MB of combined cache (L2 + L3), while the Ryzen Z1 uses an overall cache size of 22 MB.
Like AMD's consumer CPUs from the Ryzen 7000 series, the standard Ryzen Z1 and its Extreme editions offer native support for the dual-channel LPDDR5-5600/LPDDR5X-7500 memory driver. Given the importance of APUs relying on high-bandwidth system memory, both variants should be able to deliver improved performance and reduced latency in the majority of AAA games.
Moving on to the platform level, AMD's Ryzen Z1 series APUs support the latest USB 4.0 interface, allowing for much faster data transfer speeds (up to 40 Gbps) and easy connection to display devices. external display and storage. Furthermore, your gaming experience can be enhanced with AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition using exclusive technologies such as Radeon Super Resolution, Radeon Chill, Radeon Anti-Lag, Radeon Boost and AMD Link.
| Specifications | AMD Ryzen Z1 | AMD Ryzen Z1 Extreme |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Zen4/RDNA 3 | Zen 4/RDNA 3 |
| Process Node | TSMC N4 (4nm) | TSMC N4 (4nm) |
| Cores/Threads | 6/12 | 8/16 |
| Base Clock | 3.2GHz | 3.3GHz |
| Boost Clock | 4.9GHz | 5.1GHz |
| L1 Cache | 512KB | 512KB |
| L2 Cache | 6MB | 8MB |
| L3 Cache | 16MB | 16MB |
| cTDP | 9W-30W | 9W-30W |
| GPU computing unit | 4 | twelfth |
| GPU clock frequency | Up to 2.5GHz | Up to 2.7GHz |
| FP32 Performance (Single Precision) | 2.8TFLOPs | 8.6TFLOPs |
| Memory support | LPDDR5-5600/LPDDR5X-7500 | LPDDR5-5600/LPDDR5X-7500 |
| Meeting day | April 25, 2023 | April 25, 2023 |
Upon taking a closer look at the core specifications of both APUs, it becomes clear that the Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme have striking similarities to some of AMD's upcoming Ryzen 7040U series chips for ultra-fast laptops. mobile. Enthusiasts have pointed out that the standard Ryzen Z1 matches AMD's mid-tier Ryzen 5 7540U, while the Extreme variant is comparable to the top-end Ryzen 7 7840U.
In response to these questions, AMD clarified that while the Ryzen Z1 series APUs adhere to the same hardware configuration as the Ryzen 7 7840U/Ryzen 5 7540U, they have been purpose-designed to meet the requirements. own handheld gaming device. As a result, the engineering team had to validate a completely new power configuration with further optimizations to maintain consistent voltages.
Compared to the Ryzen 7040U series, which is limited to a limited TDP range of 15-30W, AMD's Ryzen Z1 series APUs can consume as little as 9W in the most demanding or low power scenarios. is 30W under heavy workloads. In addition to these tweaks, AMD's XDNA AI engine has also been disabled (not removed at the hardware level) on the Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme, helping to reduce production costs.
AMD Ryzen Z1 Series: Gaming Performance and Power Efficiency
In theory, AMD's Ryzen Z1 can deliver up to 2.8 TFLOPS of theoretical performance, similar to Nvidia's GeForce GTX 1650 desktop variant. Meanwhile, the Z1 Extreme boasts a whopping 8.6 TFLOPS of compute throughput, making it comparable to the GeForce RTX 3050.
For comparison, Valve's Steam Deck with Zen 2 plus a custom RDNA 2 SoC can only manage 1.6 TFLOPS of graphics performance. In contrast, current-generation consoles like the Xbox Series X and PlayStation 5 hit 12.1 TFLOPS and 10.3 TFLOPS, respectively. Since raw TFLOP ratings are not an accurate measure of gaming performance in real-world scenarios, AMD has backed up its claim by sharing internal benchmarks of both APUs in several AAA titles. popular.
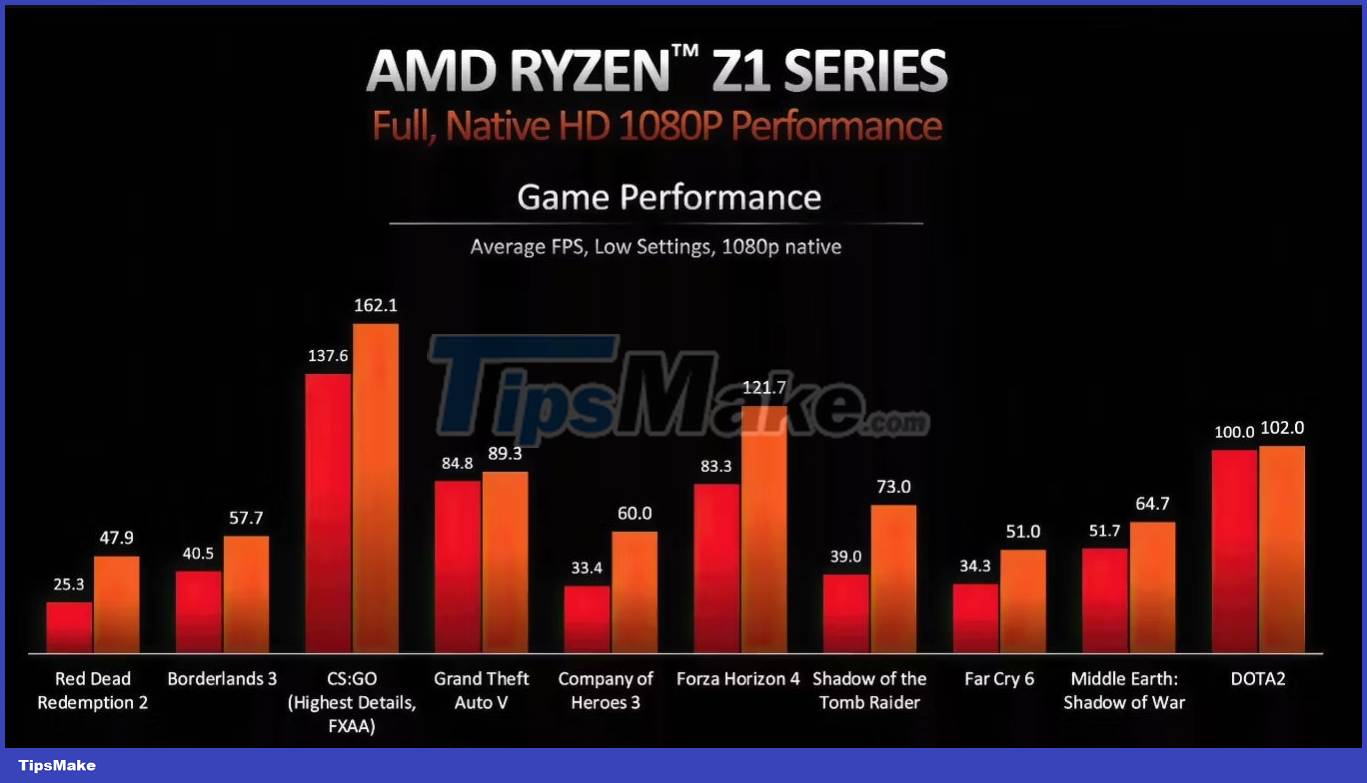
According to AMD's presentation slides, all of the benchmarks listed in this chart were conducted at 1080p using low graphics settings. As can be clearly seen from the test results, the Ryzen Z1 maintained an average frame rate of 54 FPS, while the Extreme variant surpassed the 60 FPS mark in all but the most demanding AAA games.
While it's unclear whether the games tested were based on the Low or lowest possible preset, both APUs were able to outperform the Steam Deck significantly. Besides 1080p data, AMD introduced comparative 720p performance on both chips using RSR (Radeon Super Resolution) upscaling technology.
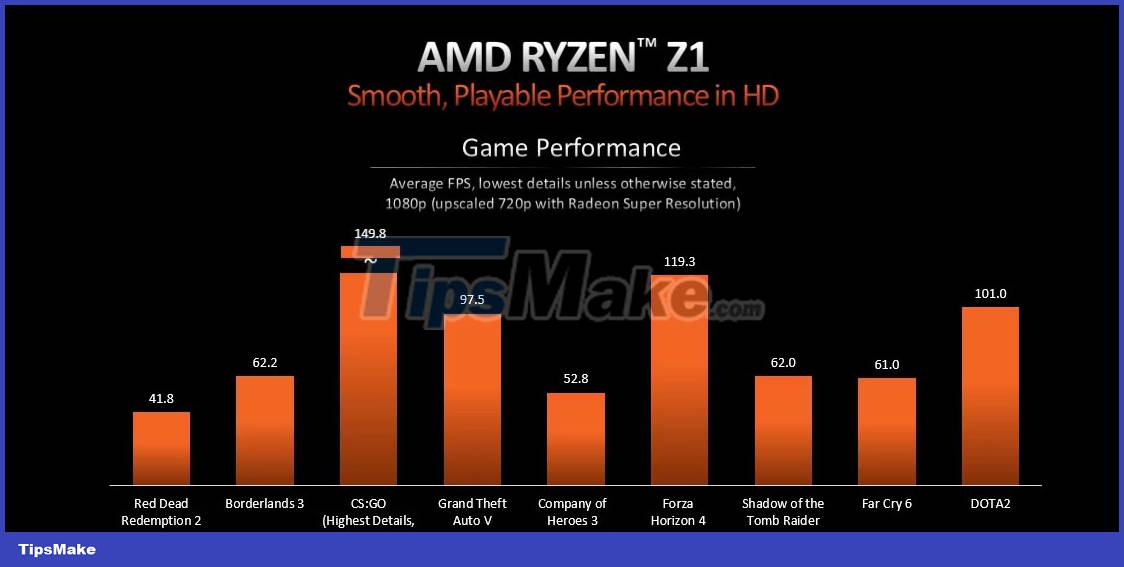
With 720p output upscaled to 1080p, the average frame rate of the Ryzen Z1 increased by about 18%, even in graphics-intensive titles like Far Cry 6 and Red Dead Redemption 2. As for the Z1 Extreme, it delivers a more responsive gaming experience across all benchmarks.
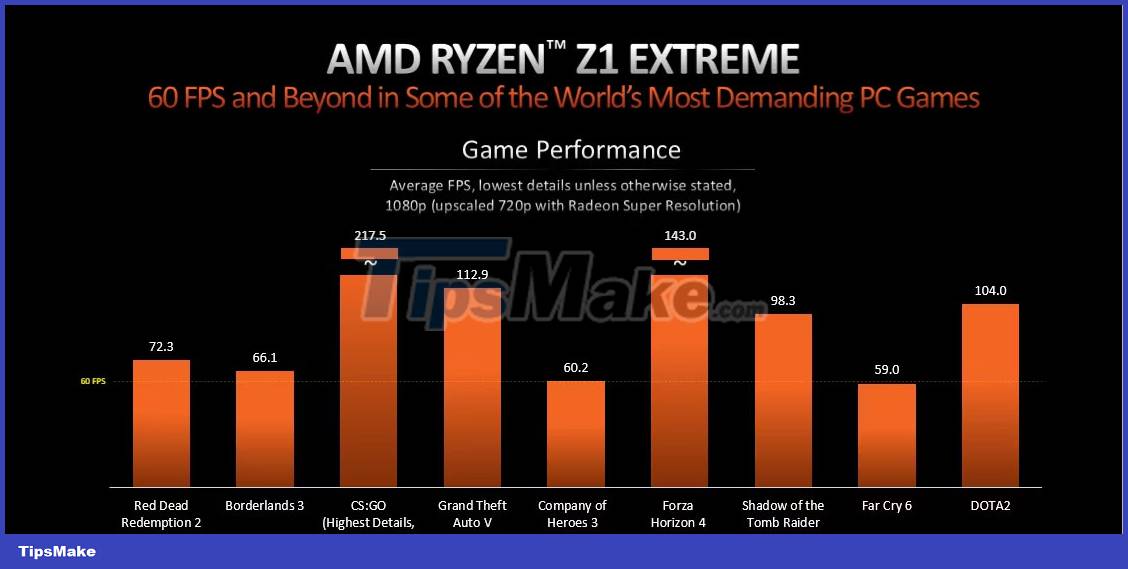
While the test results seem impressive at first glance, it should be noted that both APUs are running at a maximum TDP limit of 30W (Turbo mode). Even when switching to Performance mode with 15W available power, the ASUS ROG Ally handheld console offers reasonable, though not exceptional, improvements over the Steam Deck.
However, when switching to Silent mode, which locks the TDP to just 9W, the Ryzen Z1 and Z1 Extreme struggle to perform on par with AMD's aging but capable Aerith SoC. Due to the power-hungry nature of both APUs in this respect, we recommend setting a fixed frame rate and TDP limit of around 18W, especially if you plan to play non-tether games.
AMD Ryzen Z1 vs. Z1 Extreme: Which APU is the best value for money?
Considering the specs, performance and efficiency benchmarks of both APUs, it's safe to believe that ASUS ROG Ally, powered by AMD's Ryzen Z1 Extreme, offers a better price-to-performance ratio than with the standard Z1 model. However, despite achieving a competitive advantage over the Steam Deck in terms of processing power, the Ryzen Z1 fell short of expectations in terms of graphics capabilities.
However, with a few minor tweaks to the pricing structure and power management, the standard Ryzen Z1 could be an attractive option for future handhelds primarily aimed at classic gaming. .
You should read it
- ★ Top best CPU for PC 2020
- ★ AMD's Ryzen Threadripper 2990WX achieved 6Ghz overclocking speed on all 32 cores, breaking many records
- ★ AMD Ryzen 5 3600X Review: Great multi-threaded support, overclockable
- ★ AMD announced the Ryzen 3 3300X and Ryzen 3 3100 CPUs for desktops
- ★ AMD released the 2nd generation Ryzen computer processor with SenseMI technology