INTERSECT operator in SQL Server
In SQL Server (Transact-SQL), INTERSECT operator is used to return records in both data sets or SELECT statements. If a record is available only in one query and not in the other, it will be removed from the result set of INTERSECT.
INTERSECT query
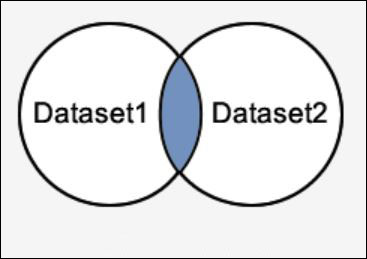
Illustrate the result returned from INTERSECT query
Explanation: INTERSECT query will return records located in the blue fill area. These records are in both database1 and database2.
Each SELECT in INTERSECT must have the same number of columns in the result set with the same data type.
INTERSECT operator syntax
SELECT bieu_thuc1, bieu_thuc2, … bieu_thucn
FROM bang
[WHERE dieu_kien]
INTERSECT
SELECT bieu_thuc1, bieu_thuc2, … bieu_thucn
FROM bang
[WHERE dieu_kien];
Variable name or variable value
bieu_thuc
The column or value you want to compare between the SELECT statements. They do not need to be in the same information field at each SELECT statement but the corresponding columns must have the same data.
state
Table wants to get records from there. Must have at least 1 table in the FROM clause.
WHERE dieu_kien
Option. Conditions must satisfy for the selected record.
Note:
- Two SELECT statements must have the same number of expressions.
- The corresponding column in each SELECT statement must have the same data type.
- The INTERSECT operator returns only the general record between SELECT statements.
For example - with 1 expression
SELECT sanpham_id
FROM sanpham
INTERSECT
SELECT sanpham_id
FROM hangtonkho;
In this example, if sanpham_id appears on both the sanpham and hangtonkho tables, it will be in the result set of INTERSECT.
Now add the WHERE condition to this query.
SELECT sanpham_id
FROM sanpham
WHERE sanpham_id >= 50
INTERSECT
SELECT sanpham_id
FROM hangtonkho
WHERE soluong >0;
The first dataset will filter and return records in the dashboard and sanpham_id greater than or equal to 50. The second data set will filter from the hangtonkho table if the number is greater than 0.
For example - with multiple expressions
SELECT danhba_id, ho, ten
FROM danhba
WHERE ho = 'Anderson'
INTERSECT
SELECT nhanvien_id, ho, ten
FROM nhanvien;
In this example, the query returns the result of the intersection of the two SELECT statements. If there is a record in the list of danhba that danhba_id , ho , ten danhba danhba_id , the name of the INTERSECT query will return those records.
For example - use ORDER BY
Use the ORDER BY clause with INTERSECT query to sort results.
SELECT nhacung_id, nhacung_ten
FROM nhacung
WHERE nhacung_id > 500
INTERSECT
SELECT congty_id, congty_ten
FROM congty
WHERE congty_ten in ('Apple', 'Microsoft', 'SQL Server')
ORDER BY 2;
Because the column name in the two SELECT statements is different, it is easier to reference the column in the ORDER BY clause by their position in the result set. In the above example, we filter the result nhacung_ten / congty_ten in ascending order through the phrase ORDER BY 2.
Because the nhacung_ten / congty_ten is the 2nd in the result set.
Previous article: UNION ALL operator in SQL Server
The following article: EXCEPT operator in SQL Server