How to Write Standard Code in C++
Method 1 of 2:
Writing Standard Code
-
 Download a C++ IDE (integrated development environment) such as Eclipse, Netbeans, and CodeBlocks, or you can use a plain text editor such as Notepad++ or VIM. You can also run programs from the command line, in that case any text-editor will suffice. It might be handy to choose an editor which supports syntax highlighting and line-numbers. Most programmers find that unix-like systems (linux, OS X, BSD) are the best environments for development.
Download a C++ IDE (integrated development environment) such as Eclipse, Netbeans, and CodeBlocks, or you can use a plain text editor such as Notepad++ or VIM. You can also run programs from the command line, in that case any text-editor will suffice. It might be handy to choose an editor which supports syntax highlighting and line-numbers. Most programmers find that unix-like systems (linux, OS X, BSD) are the best environments for development. -
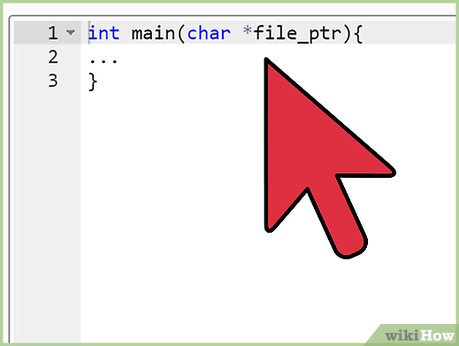
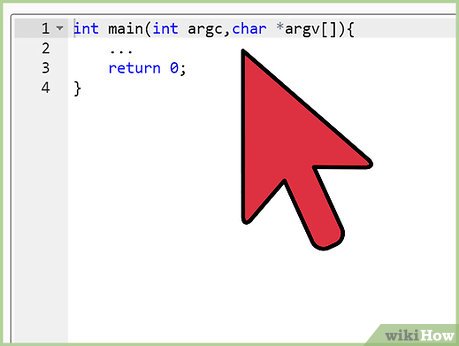
 Create a main program file. The main file must include a function called main(). This is where execution of the program begins. From here, you should be calling functions, instantiating classes, etc. Other files of your application as well as libraries can be included into this file.
Create a main program file. The main file must include a function called main(). This is where execution of the program begins. From here, you should be calling functions, instantiating classes, etc. Other files of your application as well as libraries can be included into this file. -
 Begin writing your program. Insert your code or the program that you need to build (see below for a few examples). Learn the syntax, semantics, Object-Oriented Programming paradigms, data striations, algorithm designs such as linked lists, priority queues, etc. C++ is not an easy language to program in, but doing so teaches you the fundamentals that extend to all programming languages.
Begin writing your program. Insert your code or the program that you need to build (see below for a few examples). Learn the syntax, semantics, Object-Oriented Programming paradigms, data striations, algorithm designs such as linked lists, priority queues, etc. C++ is not an easy language to program in, but doing so teaches you the fundamentals that extend to all programming languages. -
 Insert comments in your code. Explain what your functions do and what variables are for. Choose clear names for variables and functions. Capitalize the names of global variables. In general: make sure that anyone reading your code can understand it.
Insert comments in your code. Explain what your functions do and what variables are for. Choose clear names for variables and functions. Capitalize the names of global variables. In general: make sure that anyone reading your code can understand it. -
 Use proper indenting in your code. Again, see the examples below.
Use proper indenting in your code. Again, see the examples below. -
 Compile your code with
Compile your code withg++ main.cpp
-
 Run your program by typing:
Run your program by typing:./a.out
Method 2 of 2:
Following Examples
- Take a look at Example 1:
/* This Is A Simple Program Just To Understand The Basic OF g++ Style. This Is A Program With g++ Compiler.*/ #include /* include input and output functions */ using namespace std; /* we are using the std (standard) functions */ int main() /* declare the main function; you can have int main(void) too. */ { cout << "n Hello Daddy" ; /* 'n' is a newline (t is a tab) */ cout << "n Hello Mummy" ; cout << "n This Is My First Program" ; cout << "n Date 11/03/2007" ; return 0; }
- Consider this Example 2:
/* This Program Calculates The Sum Of Two Numbers */ #include using namespace std; int main() { float num1,num2,res; /* declare variables; int, double, long.. work too */ cout << "n Enter the first number= " ; cin >> num1; /* put user's value into num1 */ cout << "n Enter the second number= " ; cin >> num2; res = num1 + num2; cout << "n The sum of "<< num1 <<" and "<< num2 <<" = "<<res 'n' ; return 0; }
- Learn from Example 3:
/* Product Of Two Numbers */ #include using namespace std; int main() { float num1; int num2; double res; cout << "n Enter the first number= " ; cin >> num1; cout << "n Enter the second number= " ; cin >> num2; res = num1 * num2; cout << "n The Product of two numbers = " << res 'n' ; return 0; }
- Take a look at Example 4:
// Looping to find a math equation. In this case, it figures out the answer to // Question #1 on Project Euler. #include using namespace std; int main() { // Opening Main. int sum1=0; int sum2=0; int sum3=0; int sum4=0; // Creates the integers needed in order to figure out the answer. for (int a=0; a < 1000; a=a+3) {sum1 = sum1+a;} // Loops until a is 1000 or over, adding 3 to a every loop. Also adds a to sum1. for (int b=0; b < 1000; b=b+5) {sum2 = sum2+b;} // Loops until b is 1000 or over, adding 5 to b every loop. Also adds b to sum2. for (int c=0; c < 1000; c=c+15) {sum3 = sum3+c;} // Loops until c is 1000 or over, adding 15 to c every loop. Also adds c to sum3. sum4 = sum1 + sum2 - sum3; // sum4 takes the sum of sum1 and sum2, and subtracts sum3. cout << sum4; // Outputs sum4, the answer. cin.get(); // Waits for user to press enter. return 0; // Return statement. } // Closing Main.
- Take a look at this example of different styles:
int main(){ int i = 0; if(1+1==2){ i = 2; } } /* This is Whitesmiths style */ int main() { int i; if (1+1==2) { i = 2; } } /* This is GNU style */ int main () { int i; if (condition) { i = 2; function (); } }
Share by
Kareem Winters
Update 05 March 2020