Discovered a potential glacier near the surface of Mars, suitable as a base for future astronauts
If we want to be an interplanetary species, the second or the nth house also needs a lot of water. We also cannot bring water from home with us, because the goods on the rocket must be optimized, can not include leftovers even if it is a life-sustaining element.
That's why the space agencies that want to station a garrison on Mars keep an eye out for a source of fresh water. Just recently, a study published in the journal Icarus showed that a subsurface ice storage site could become an optimal discovery point.
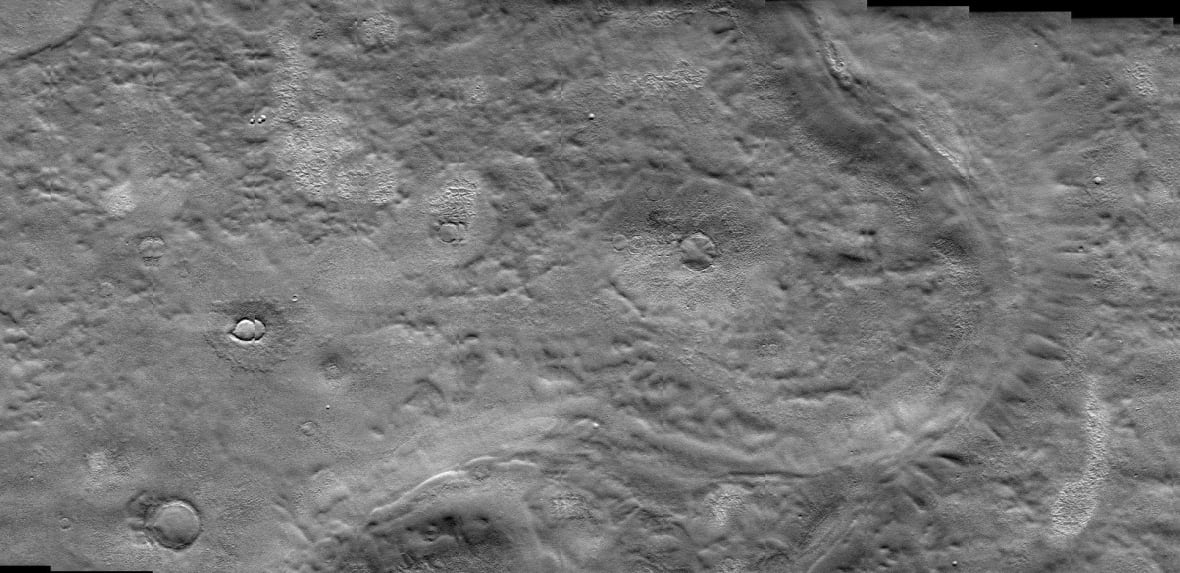

New satellite images show that under the plain of Arcadia Planitia, there may be a glacier lying very shallow above the ground.
The ideal location for the station would be near the Martian equator, where the temperature is quite mild (compared to the harsh conditions of Mars), and would be a suitable place for rockets to take off and land. Satellite images show that in the Arcadia Planitia plain in the Northern Hemisphere of Mars, there may also be ice hidden underground. Both NASA and SpaceX are aiming to explore the area.
In the new study, scientists believe that underneath Arcadia Planitia is not only a layer of ice, but also a rather shallow glacier, similar to an underground glacier located in many regions of Antarctica.
' When you look closely, you will see many features that indicate a glacier is flowing underground. It's just strange that the area has the appearance of a flat plain ,' said Shannon Hibbard, lead author of the report.
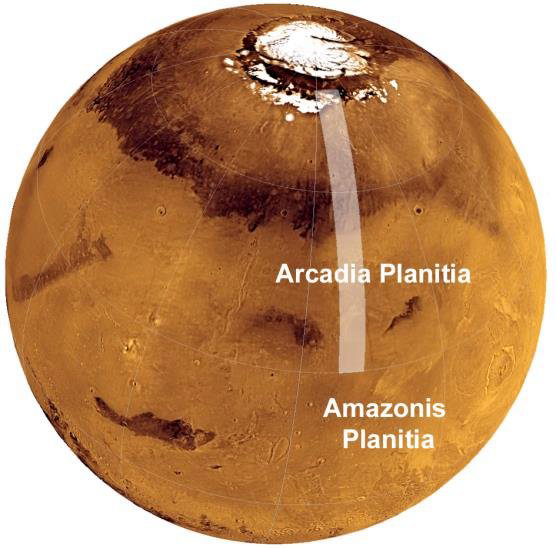

Usually, glaciers only exist in valleys, deep trenches or form at the foot of mountain ranges. Arcadia Planitia is quite flat, so this type of glacier is a bit difficult to form.
But this is also good news for the future Martian community. ' We wanted the base ground to be low, as close to the equator as possible, and Arcadia Planitia was pretty close, ' Ms Hibbard said. If this area had underground ice, Arcadia Planitia would become an ideal place to live.
Based on some past studies, it is estimated that the amount of ice under Arcadia Planitia is approximately 13,000-61,000 km 3 . Scientists think that between 3.5 and 16 percent of this ice is the volume of the glacier.
Formation process takes millions of years
The axes of both Earth and Mars are tilted at 23.5 and 25 degrees, respectively (which is also why both the first house and the potential roof have seasons). However, according to Tanya Harrison, a planetary scientist at Planet Labs, Mars can be tilted up to 60 degrees.
' There was a time in the last tens of thousands of years to millions of years when the ice moved from what was the pole of Mars to where it is today at the equator, because the old equator became a pole ,' she Harrison said.
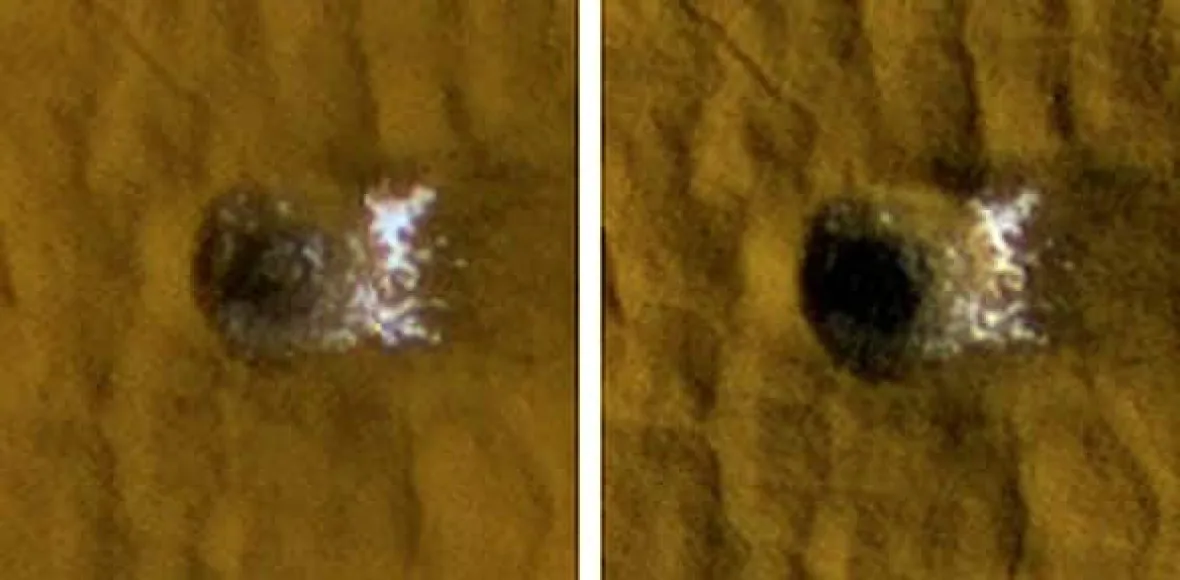
The image shows a 12-meter-wide crater in the Arcadia Planitia area. From the photo on the left (taken in 2008) and the image on the right (taken in 2009), you can see that the ice melts over time.
This discovery intrigues Tanya, because it shows us a Mars many, many millions of years ago. ' Usually, when we think of a glacier flowing, we think of it flowing over a mountainside, where steep slopes cause matter to flow from high to low. But if you have flat plains, it's hard to get anything out of the way '.
"So seeing these ice streams on Mars is really exciting, because we've never seen anything like this," she continued. The water from the ice can be used for irrigation, refreshment or even to make rocket fuel.
According to study co-author Gordon Osinski, existing radar technology in Mars orbit can only look underground in the middle, starting from a depth of 30 meters to a few kilometers underground, so it is not yet available. precisely confirmed the composition located near the surface of Mars.
But when we get a ground probe to the plains of Arcadia Planitia, we'll soon know about 20 meters below the surface, we'll know if there's ice, and how much ice there is.
You should read it
- ★ How to Clean a Boat Water Tank
- ★ Is the water you use everyday really clean?
- ★ NASA reveals its latest snapshot of the Martian surface with a resolution of 1.8 billion pixels
- ★ New technology removes salt from water with the lowest energy consumption
- ★ What bad thing would happen to Earth if the sea was no longer salty?