4 important astronomical discoveries of the ancient Greeks
The arrival of the telescope is the time when astronomy marking began to enter the stage of modern science. Before that, the main research method applied by ancient astronomers was visual observation combined with rudimentary astronomical instruments that were found from even earlier periods. However, not so that astronomy this time lacked major discoveries, but even the opposite.
Here are four important astronomical discoveries of the ancient Greeks, which greatly influenced the history of human exploration of the universe.
The planets orbit the Sun
The ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician Aristarchus of Samos (310 BC - 230 BC) was the first to propose the theory of heliocentric modeling, placing the Sun at the center of the universe and the Left. Land revolves around the Sun. He argued that the Sun is the central flame of the universe, and that the remaining planets that humans observe are the orbiting flames in a certain order.
 Aristarchus of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos This is an amazing finding, because many people think that the theory of the Sun in the center and the Earth orbiting the Sun must take until the 16th century to be launched by Nicolaus Copernicus. In reality, however, Nicolaus Copernicus was the one who raised the first modern form of heliocentricism in his own book, and the one who inspired Nicolaus to develop the main work was Aristarchus of Samos. .
The size of the moon
Continuing is an important discovery of Aristarchus of Samos. He was the first to theorize about the size and distance of the Sun and Moon. It also provides the most basic calculations of dimensions and distances relative to the Sun and Moon, laying the foundations for many important measurements later.
It has long been observed that the Sun and Moon appear to be the same size in the sky and the Sun is farther away. Aristarchus realized this after witnessing an eclipse, which occurred when the Moon passed in front of the Sun at a certain distance from the Earth.
In addition, when observing the Moon in the first or third quarters of the year, Aristarchus discovered that the Sun, Earth and Moon would form a right triangle.
Because Pythagoras had determined how the length of the sides of the triangle was related in the past few centuries (pyramid theorem), Aristarchus used the square triangle theorem to estimate that distance. from Earth to the Sun is between 18 and 20 times that of the Moon. He also calculated that the size of the Moon is approximately one-third that of Earth, based on the duration of the total lunar eclipse.
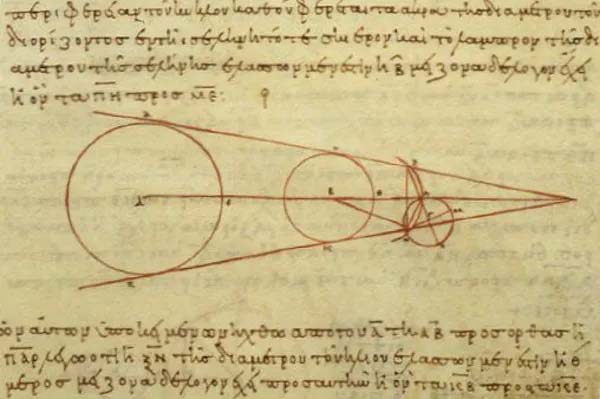 Aristarchus Diagram
Aristarchus Diagram Regarding the problem of the distance between the Sun and the Moon, the number given by Áitarchus is too low, in fact 390. However, the value of the size ratio of the Earth to the Moon that he gave is accurate. Surprisingly (the Moon is only 0.27 times the diameter (almost 1/3) of the Earth).
Perimeter of the Earth
Eratosthenes (276 BC - 195 BC) was an astute astrophysicist of Greek civilization, and one of his life's accomplishments was the earliest calculation of the circumference of the Earth. . Eratosthenes' method of calculation is based on measuring the length of the shadows of the pillars placed vertically on the ground at noon on the summer solstice, at different latitudes.
The sun is so far away that wherever the sun hits the Earth, they are almost parallel. Therefore, the difference in the shade of the object shows how far the Earth's surface is curved. Eratosthenes used this theory to estimate the circumference of the Earth, and his results were about 40,000 km - a very accurate number.
 Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes Another ancient astronomer called Posidonius (135 BC - 51 BC) used a new method of calculation, but gave the same result. Posidonius lived on Rhodes Island for most of his life. There, he often observed the star Canopus located very close to the horizon. However, when moving to Alexandria, Egypt, Posidonius realized that the position of Canopus had changed, increasing to about 7.5 degrees above the horizon.
Given that 7.5 degrees is 1/48 of a circle, Posidonius multiplied the distance from Rhodes to Alexandria to 48 and arrived at a value of approximately 40,000 km - the circumference of the Earth.
The first astronomical computer
The world's oldest surviving mechanical computer, the Antikythera Mechanism, was discovered in an ancient shipwreck off the Greek island of Antikythera in 1900.
This device has been damaged over time, but when intact, it took the form of a box containing dozens of elaborate copper gears. When manually rotating, the outer dial gears will display the Moon's cycles, lunar eclipse times, and the positions of five different planets known at the time, including Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn, according to the time of year.
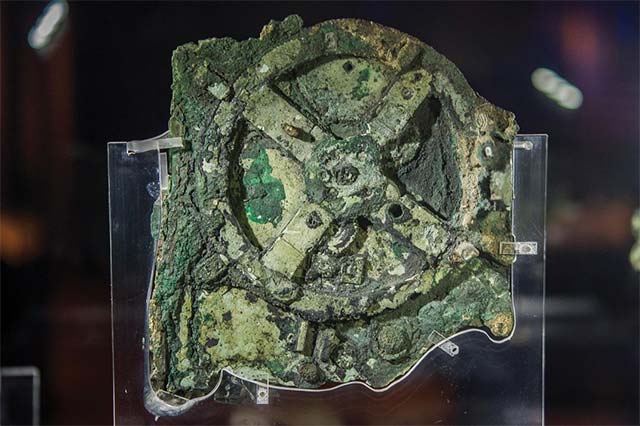 Antikythera Mechanism
Antikythera Mechanism It is still unknown who authored this unique astronomical computer. However, according to the scientists, it dates from the 3rd century to the 1st century BC, and may even be the work of Archimedes.
You should read it
- ★ True moon, snow moon and comet will appear together today
- ★ Admire the unique photograph of the Moon and Earth taken from Mars
- ★ Do you think the Sun stands still and the Earth revolves around it? Just wrong!
- ★ Top 10 interesting facts about the Moon you may not know
- ★ What's interesting is what happens if the Moon is 400km from Earth?