Variable in PHP
The main way to store information in PHP programs is to use a variable.
Here are the most important things you should know about variables in PHP.
All variables in PHP are denoted with $ at the beginning.
The value of a variable is the value of its most recent assignment.
Variables are assigned with the = operator, the variable is on the left and the expression is evaluated on the right.
Variables can, but do not need, be declared before assigning values.
The variable in PHP has no intrinsic types, ie an unknown variable whether or not it will be used to store a number or a string.
Variables, used before they are assigned, have default values.
PHP does a great job of automatically converting from one type to another when needed.
Variable in PHP is similar to Perl.
PHP has a total of 8 data types that we use to build variables.
Integer - integer. Example 1989
Double - real number. Example 3.14159 or 49.1.
Boolean - there are 2 TRUE or FALSE values.
NULL - is a special type, it only has the value: NULL
String - is a string of characters.
Array - is a named and indexed set of other values.
Object - is the instance of the classes that the programmer defines itself, it can encapsulate different types of values and functions, which are specific to classes.
Resource - is a special variable that keeps references to external resources to PHP (for example, connecting Database).
The first 5 types are simple variable types, the next 2 types (arrays and objects) are complex types that can encapsulate arbitrary values of arbitrary types, while simple types cannot .
In this chapter, we will explain simple variable types. Array and Object will be explained separately in later chapters.
Integer type in PHP
They are all numbers, including vowels and positive integers, but do not include real numbers. It is the simplest type. They can be assigned to a variable or used in the expression as follows:
$ bien_int = 10001;
$ bien_int_1 = -10002 + 10003;
Integer types can be in decimal, octal, and hexadecimal. The default is decimal, octal - the integer is specified starting with 0 and hexadecimal starting with 0x.
For most popular platforms, domain values range from –2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647.
Double type in PHP
They look like 3.14159 or 49.1. By default, type double will print the smallest decimal position number. For example, you follow the following code:
php $ bien_double_1 = 2.2888800 ; $ bien_double_2 = 2.2111200 ; $ ket_qua = $ bien_double_1 + $ bien_double_2 ; print ( "$ bien_double_1 + $ bien_double_2 = $ ket_qua
" ); ?>
Save the above program in a file named test.php in htdocs , then open the browser and type the address http:/// localhost: 8080 / test.php will result:

Boolean type in PHP
They have only two values: true or false. PHP provides a pair of constants to use as Boolean types: TRUE and FALSE, which can be used like:
if ( TRUE ) print ( "Print this line to the browser.
" ); else print ( " Do not print this line to the browser.
" );
Interpreting other data types into Boolean types
This is the rule to determine the validity of any value that is not a Boolean type.
If the value is a number, it is false if it is 0 and true if not 0.
If the value is a string, it is false if the string is empty (no character exists) or the string "0", if not true.
The value of type NULL is always false.
If the value is an array, it is false if it does not contain other values and if not true. For an object, containing a value means that a member variable has been assigned a value.
Valid resources are true (although there are some functions that return resources when they succeed, and return FALSE if they fail).
Do not use double as Boolean.
Each of the following variables has a true value embedded in its name when used in a Boolean context.
$ true_num = 3 + 0.14159;
$ true_str = "I want to move"
$ true_array [49] = "Mot carries parts";
$ false_array = array ();
$ false_null = NULL;
$ false_num = 999 - 999;
$ false_str = "";
NULL type in PHP
NULL is a special type that has only one NULL value. To provide the variable NULL variable, you simply assign it as follows:
$ my_var = NULL;
By convention, a special constant NULL is capitalized, but it is actually case-insensitive, and you can write as follows:
$ my_var = null;
A variable that has been assigned NULL will have the following properties:
It estimates FALSE in a Boolean context.
It returns FALSE when tested with the IsSet () function in PHP.
String type in PHP
They are character sequences, like "Hoc PHP with high quality and high quality". Here are the string examples in PHP.
$ string_1 = "Dreaming of a story";
$ string_2 = "Hoc PHP QTM ears";
$ string_0 = ""; // for example a string without characters
Consider the following example to compare the difference when using single quotes and quotation marks:
php $ bien_1 = "name" ; $ bien_2 = '$ bien_1 will not be printed!' ; print ( $ bien_2 ); print "
" ; $ bien_2 = " $ bien_1 will be printed! " ; print ( $ bien_2 ); ?>
Save the above program in a file named test.php in htdocs , then open the browser and type the address http:/// localhost: 8080 / test.php will result:
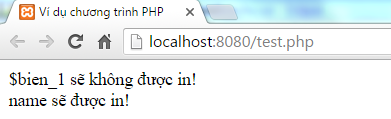
Explanation : We find that the first sequence has not changed. The second string variable $ variable has been replaced with name. Thus, the string using single quotes is a static string, while the string using double-flashing is a dynamic string, varying according to the value of the variable.
There is no limit to the length of the string, it can be arbitrarily long if the memory allows.
Strings limited by double quotes are handled by PHP in two ways:
Character strings beginning with () are replaced with a special character
Variables (starting with $) are replaced by the string representation of its value.
Replacement rules:
n is replaced with newline character (new line)
The r is replaced by the carriage-return character, which is meant to bring the cursor to the beginning of the line but not the line.
t is replaced by tab characters
$ is replaced with a $ sign
"replaced with a quotation mark"
is replaced with an apostrophe
Syntax Here Document (Heredoc) in PHP
You can assign multiple lines to a single string variable using the syntax here document as follows:
php echo <<< END The article "Here Document" in PHP . This is the best way to make a living .
END ; ?>
Start with <<
For example, if you need to display double quotation marks "then you need to use a slash as follows:
php $ x = "The example illustrates how to quote" quotes "in PHP!" ; print $ x ; ?>
With Heredoc, you don't need to use a slash
php $ x = <<< EOF With the help of a "blink" in PHP ! EOF ; print $ x ; ?>
Both examples give results:

Variable scope in PHP
Scope can be defined as the available scope of the variable declared in the program. Variables in PHP can be one of four areas:
- Local variable in PHP
- Function parameters in PHP
- Global variables in PHP
- Static variables (or static variables) in PHP
Name the variable in PHP
Here are the rules for naming a variable in PHP:
Variable names must start with a letter or underscore character (_).
A variable name can contain numbers, letters, and underscores (_), but you cannot use characters like +, -,%, (,). &,. etc
There is no size limit for variables in PHP.
Follow tutorialspoint
Previous article: PHP syntax
Next lesson: What is PHP?
 What is PHP?
What is PHP? Constants in PHP
Constants in PHP Operator in PHP
Operator in PHP If, else, switch commands in PHP
If, else, switch commands in PHP Loop in PHP
Loop in PHP