Intel challenged IBM and Google with supercomputers with 250 times cooler temperatures than the universe
On Tuesday, Intel introduced a 17-bit superconducting chip, similar to the largest quantum computer chip ever produced by IBM.
So far, quantum computing has become a race between IBM and Google. In April, Google introduced a 9qubit chip study and another study could break the record of quantum computing by the end of the year. In May, IBM introduced the first 17qubit chip.
IBM products are based on research conducted by Professor Robert Schoelkopf at Yale University (IBM group consists of PhD PhDs, students studying PhDs). Google products are based on research by California University Professor John Martinis, supported by Google in 2014.
All researchers from IBM, Intel, Google or anywhere else, such as Microsoft, are in the race for a 50qubit chip. That's the level of need to create a supercomputer stronger than any supercomputer. No one knows what fast and smart computers can solve these problems.
Quantum entanglement
Quantum computers are different from digital computers today. Digital computers think in two states: 1 and 0 (turn on and off), but quantum computers use combinations 1 and 0 to create more complex states, which can be 1, 0, both 2 at the same time or (strangely) some in the middle, a mysteriously difficult state to describe.
This confusing state is called 'quantum entanglement', and there are also some mathematical formulas (or algorithms) that use this state to calculate things that traditional computers aren't powerful enough to calculate. For example, quantum computers can work with billions of variables at the same time.
They are also used for machine learning. These computers are expected to find new remedies, how to secure new computers. This form of calculation is also expected to create a computer that can be thought of to create a human-like robot or a personalized medicine for each person.

Intel's Quantum Hardware Manager, Jim Clarke with 17-bit superconducting test chip in hand
This may sound difficult but the journey is not alone. Microsoft also bet on quantum computation even though Bill Gates himself admitted that he did not really understand how it worked.
Temperatures are colder than the universe
Until now, the challenge was simply to create a larger quantum computer. As Intel explains, qubits are very fragile. Any small sound or dispersion can cause data loss. They depend and superconducting metals need to be kept at a very cold temperature of 20 milligrams - or 250 times cooler than outer space. This condition is difficult to create and maintain.
Temperature is not the only problem. Quantum computers are larger in size when adding multiple qubits and can also cause many errors.
But the speed of development is still very fast. In May 2016, IBM introduced the world's first 5qubit machine and cloud service. After only one year, these chips were three times larger.
Google expects to create a large and powerful test computer by the end of the year, which can perform calculations that traditional supercomputers can't do, called the supreme quantum world or the quantum throne.
At the same time, Intel also threw himself into the game. Below is more detailed information about Intel's chip.
The 17qubit chip has a square with connect gold that allows the chip to connect to the world outside the quantum computer.
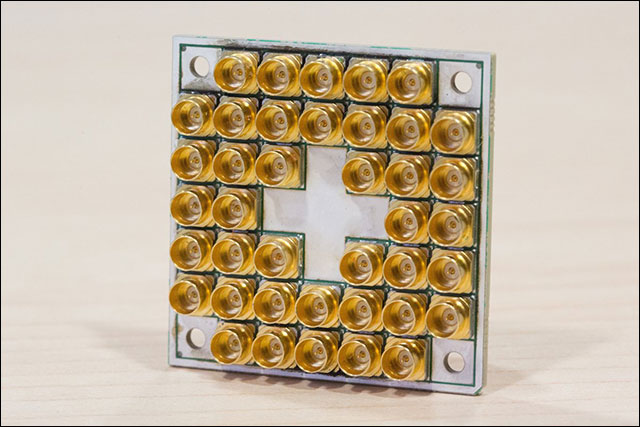
Intel's 17qubit square chip
This is a picture of the other side of the chip when packaged in a box. One of the things Intel is aiming for is mass production of this chip. That would be much more difficult to create a test chip.
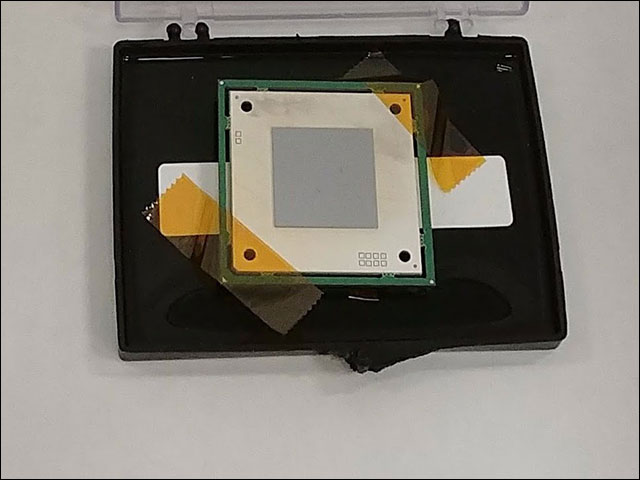
Quantum chip testing package in box
There is much to be done before this technology is ready for production. Researchers at QuTech's quantum computing lab are focusing on that.
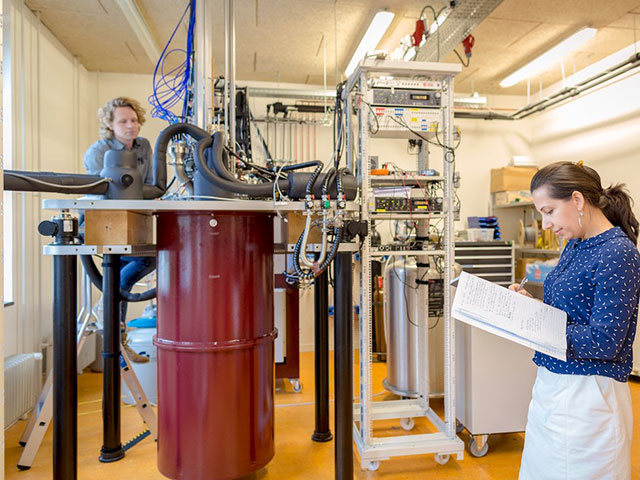

There are many things to improve before producing large quantities of quantum chips
IBM's quantum computer lives in this white tube. It is a special refrigerator to keep temperature 0 completely.
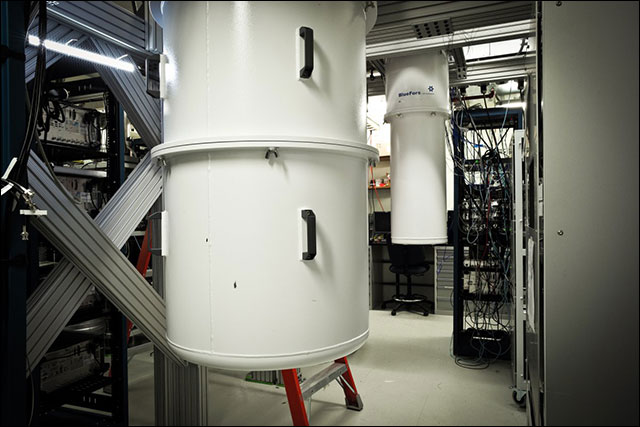

Need to keep the temperature very low for quantum computers
QuTech Leo DiCarlo and Intel scientist Dave Michalak are very interested in the new chip, have made this video, in which they explain in more detail how the chip was created.
You should read it
- ★ For the first time scientists photographed the phenomenon of quantum entanglement, which Einstein once called 'spooky impact'.
- ★ For the first time, scientists have successfully implemented quantum shifts between two chips
- ★ New chip technology can enhance quantum computing
- ★ Insert the photon into the empty space inside the diamond
- ★ Google achieves new achievements in quantum computing with the 53-qubit Sycamore chip