What is the Project Manager, Product Owner or Software Architect ...?
One of the key factors that help successful candidates find their job is to understand the job description and the list of employers' requirements for the position they have applied. However, the reality is that many people, especially new graduates, are often vague about the positions at the companies that make them fall into a situation where they can never get a job. Because, no one recruits a person who does not understand what he will do if he is applied or the application has no connection to what the employer is looking for.
Here are 5 IT professions that are attracting the attention of many people in the labor market. Know the difference between these positions to choose a suitable job and be more confident in the job search process.
1. Project Manager
Project Manager (Project Manager) is a popular position in Outsourcing companies (outsourced), paid quite high and has great potential for development.

Project Manager's work includes:
- Planning, monitoring and evaluating work results; train, guide and practice discipline for employees; make initiatives, coordinate, improve systems, policies and rules.
- Building human resources through recruitment, selection, transfer and training of employees; maintain a safe and secure working environment, and develop growth opportunities for each individual in the organization.
- Develop plans and processes for making products and software as required or demanded by customers.
- Arrange the process, working schedule of Developer, Tester and related positions, closely monitor to ensure quality and deliver products on time.
- Communicating with customers, including progress reports, the status of completed tasks, and errors that are being encountered for resolution.
- Propose information technology strategies, policies and procedures by assessing the results of the organization, identifying problems, evaluating trends and discussing the requirements set forth.
- Cultivate technical knowledge and maintain a professional working style by attending educational seminars, building a relationship network .
Required skills of a Project Manager:
1. Project management skills, including setting up detailed work processes, time to complete the phases to deliver products with the correct deadlines, such as arranging jobs in order of importance, level Priority of each part, who is responsible for each part to ensure no duplication and complete the task on time.
2. Planning skills to ensure everything happens in the right order, professionally, fairly in assigning tasks and science.
3. Communication skills with customers, including listening carefully to customers and reviewing their feedback to correct the product in the right way.
4. Skills to solve problems in trouble, including analyzing causes and finding appropriate solutions through case studies, experiences from colleagues.
There are also a number of skills requirements: skills in information analysis, problem presentation, data center management, budget development, association, quality management, and technical management. .
2. Product Owner
Product Owner - as its name implies - is the owner of the product, fully understands the product and related requirements. Typically, at businesses, the Product Owner is usually handled by the customer. If the customer is not available, this position can be assigned to Business Analyst of the software company or consulting firm. In addition, Product Owner is also responsible for the output requirements of the product and is the one who accepts the product.
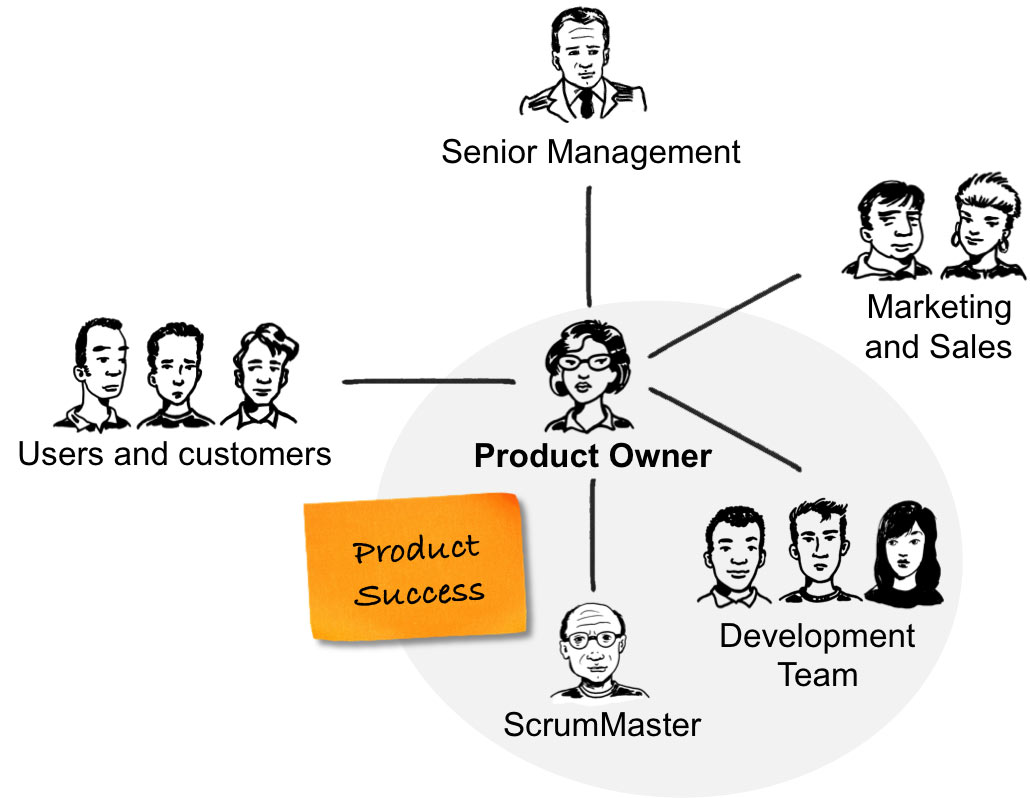
Product Owner's work includes:
- The Product Owner is the one who must answer the question: "Why is this product required?" What should the product contain? "" When should it be released? ". . before Developer and Enginer started work.
- Detailed planning for product development, including code, design, content orientation as well as related tasks.
- Manage and assign jobs to other Teams (usually Development and Design), and coordinate with Marketing and Sale . to implement the plan.
- Research user needs to strategically change, upgrade, repair products so that they love and continue to use.
Product Owner's required skills:
1. Broad understanding of markets, products, customers, rivals .
2. Always ready to serve customers and support colleagues.
3. Be responsible, make decisions and solve problems yourself.
4. General knowledge of all aspects of the product, mostly design, user experience, code, software, data structure, user interaction data with the product.
5. Being able to lead and motivate the project team to work so that they strive to complete the project according to the set target.
3. Software Architect
Software Architect is the "right-hand man" of a product-making company, seen as an "architect" to build the overall architecture of software and how it works for those parts. Depending on the task, Software Architect will be in charge of different areas of work.

- Professional Architect (Enterprise Architect): A bridge between product owner and technical team. They are people with in-depth experience in the field where the product is being built; responsible for building and developing requirements - setting the perspective, the framework of the IT environment in the product.
- Infrastructure Architect (Infrastructure Architect): The person responsible for setting up and building solutions for IT infrastructure (for example: network, security issues, equipment / storage methods, .) in products to meet the needs of businesses.
- Solution Architect: Solution Architect is the person responsible for designing and building solutions for product requirements.
- Technical architect (Technology-specific Architect): The person responsible for one or more specific technical areas.
Required skills of Software Architect:
1. Having experience working with the overall architecture of a product or system to have a panoramic view of it as well as gradually developing the way of thinking of a true Software Architect.
2. Proficient in a certain technology, including programming language syntax, APIs, frameworks, design patterns, principles, tests .
3. Having background knowledge about other related technologies to support the construction of architecture for products.
4. Assertive when making technology and technical decisions for their products.
5. Good communication ability to convey vision into that design.
6. Leadership skills, including the ability to motivate team members to join, motivate the team to work, listen, and lead them.
7. Sensitive to economic movements, with vision.
8. Constantly learning, cultivating ourselves, always studying new technical directions, from IT architecture to application and application development trends.
4. Tester (software testing)
Tester is a software testing staff, responsible for testing software and applications before they are officially released. Depending on the project, stage and type of Testing (manual - Manual or automatic - Automation) the work of each Tester will be different.

In general, Tester will be responsible for finding errors or appraisals, verifying whether the software / application system meets the technical requirements and business requirements, ensuring the product meets the right quality. quantity and requirements that customers want.
The career path of a Tester can start as a software testing specialist => Test Leader => Test Manager => Test Director.
The skills required of a Tester:
1. Skill in designing, programming, analyzing and understanding various applications of the software.
2. Foreign language ability to read, understand and write specialized documents.
3. Be careful, meticulous, sharp, can see the problems that the Developer is missing in the product.
4. Know the specific test method for each case corresponding to each domain, process, product, customer, type of error, requires Tester to master basic knowledge about software and product testing experience Products.
5. Critical thinking and logical thinking from many angles to find hidden bugs in the product.
6. Skillful communication skills to convey the meaning of testing to relevant teams.
Distinguish Tester, QC and QA:
♦ Tester is a software testing staff, only responsible for testing software, searching for errors and shortcomings in the product during the process of implementing the system for Developer to revise and work independently with team QC and QA .
♦ Quality Assurance (QA) is a quality assurance engineer, establishing and developing manuals and procedures for quality management systems where applicable; internal assessment of the company's annual quality management system; participating in production improvement activities, coordinating with producers when evaluating customers, participating in training for relevant departments on the application of systems, standards and processes as well as those system changes and processes to suit actual requirements.
♦ Quality Control (QC) is a quality management engineer. These are the people who directly do, check the actual products for each stage of the production process. QC engineers require knowledge of the product being made, understand the content of the drawing, the order of production stages, regular and direct monitoring at the production site .
5. DevOps Engineer
DevOps Engineer is an engineer working with DevOps model. Anyone, whether Developer, Tester, QA . can do DevOps Engineer because this is an extremely versatile position and works primarily with systems.
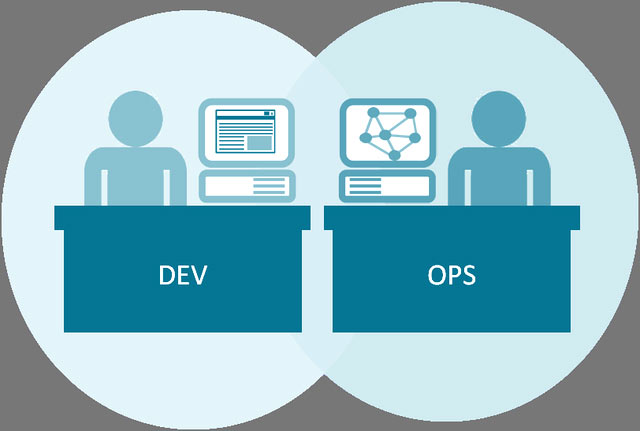
DevOps Engineer's work includes:
- Construction and system design for Team Development, Testing and Operation teams work smoothly, smoothly, optimize the software development life cycle (SDLC - Software Development Life Cycle), saving product completion time.
- Coordinate with these teams in different stages of product release, including: Build (build), Deploy (deployment), Test (test) and Continuous Improvement.
- Create, deploy, troubleshoot and maintain software systems daily.
- Continuously research, evaluate and work with new technologies to maximize the effectiveness of the software.
- Use DevOps, cloud computing, infrastructure tools . to increase product output.
DevOps Engineer required skills:
1. Ability to work with a variety of technologies and proficiently use all tools to cater to many processes.
2. Ability to code, script, deploy and test because it has to coordinate with all teams in the product making process.
3. Keep an eye on the system to ensure the connection throughout the implementation process.
4. The ability to manage data with extremely large amounts of data, involving many different teams and jobs.
5. Cross-team skills, human skills. This is the most important skill of a DevOps Engineer because this job requires very high teamwork.
What any DevOps Engineer must keep in mind is that technical expertise does not make this position, but it must have DevOps thinking with close and harmonious coordination between teams and product creation stages.
You should read it
- ★ Top 10 predictions about DevOps in 2019
- ★ Learn about information security engineers
- ★ Journey to change jobs from fashion models to software engineers within 1 year
- ★ This is the amount of money you can earn when doing one of the 9 hottest jobs in software technology
- ★ Types of errors (bugs) in the testing process