The truth about recycling e-waste and its effectiveness
Every day, people create a large amount of waste. Every average person now throws away 4.3 pounds of garbage every day, up more than 30% since 1960. Over the years, the total amount of waste has increased by 2.6 trillion pounds worldwide.
And in the digital age that is growing at a dizzying pace, more and more electronic waste will be released into the environment. Unlike 'traditional' waste, in which about two-thirds can be used for composting, e-waste will be more difficult to handle.
As responsible citizens of the planet, we should start taking steps to recycle old utilities. But is that really a worthwhile effort?
The truth about recycling e-waste and its effectiveness
- What is e-waste?
- Why is e-waste becoming a problem?
- Advantages of recycling e-waste
- Process of recycling e-waste
- Be careful with 'fake' recycling companies.
- How can you recycle e-waste sustainably?
- Be part of the solution to solve the problem
What is e-waste?
All types of electronic devices have a limited life. It becomes obsolete when technology changes, or it no longer works when internal components fail.
It is also not limited to smartphones and laptops. Think about how many home electronics you have: microwave ovens, televisions, refrigerators, security systems, printers, DVD players, game consoles, etc. When you throw them away, they will go where?
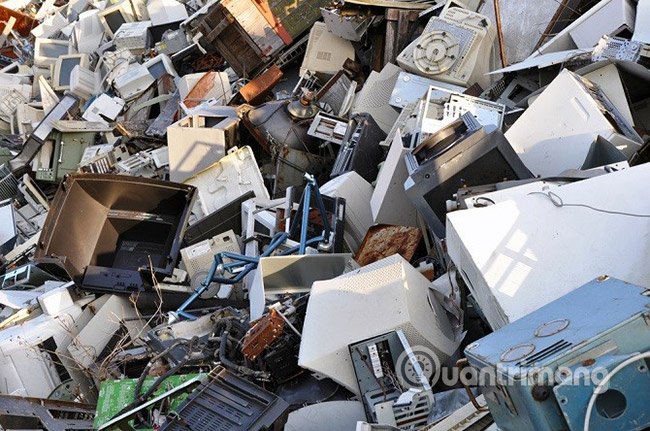

The United Nations estimates that 20-50 million tons of e-waste is discarded each year. That number is equivalent to 800 laptops per second. The United States alone accounted for 9.4 million tons of waste.
Sadly, according to the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), we actually only recycle about 12.5% of e-waste every year.
Why is e-waste becoming a problem?
As you know, plastic and other similar materials may take longer to decompose. Depending on how they are created, the decomposition process can take between 500 and 1,000 years.
- Bioplastic biodegradable in natural environment made from shrimp shells
But the problem is greater than the slow decay rate. Electronic devices also contain toxic chemicals and metals. The amount of chemicals and metals in electronic devices accounts for 70% of the world's total toxic waste.
Metals and elements like mercury, lead, arsenic, cadmium, selenium and chromium are present in everything from laptops to refrigerators. Cathode ray tubes, in TVs and old screens in schools, often use leaded glass on the back of them. Computer chips contain bromine flame retardants. The list of dangers is endless. These toxins will lead to worrying environmental and health problems.
Exposure to lead can affect children's intellectual development. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), brominated dioxins and other heavy metals acidify the river, kill fish and plants. Burning old chips releases fine particles of glass, tin, lead, beryllium cadmium and mercury into the atmosphere. Heavy metals penetrate the soil to release toxic phosphorus, affecting agriculture and food chains.
No need to be a chemist, you know all this is bad news. And even if you want to recycle in an environmentally friendly way, this is also very difficult, because don't forget there are also security issues to consider.
Advantages of recycling e-waste
In theory, there are many benefits from recycling discarded electronic devices.
Clearly the goal is to minimize the environmental issues listed above. Besides, there is a fact that many people may not know: A ton of circuit boards extract 800 times more gold than a ton of ore. Similarly, the same ton of board contains at least 30 times more copper than a ton of ore.
The environmental costs for extracting precious metals from ore are huge. The exploitation, processing and distribution of metals requires a lot of energy. Everything from machines to manpower has a negative impact on the planet.
Recycling can also reduce your energy bill. EPA claims to recycle one million laptops can save the total amount of energy used by 3,657 families in the United States in a year.
And about 65% of people in the world do not have a computer or smartphone? There have been programs to refurbish and re-use discarded devices, to bring the digital revolution to every corner of the Earth.
Process of recycling e-waste
Obviously you should recycle your old electronic devices. No matter which country you live in, it is not difficult to find an e-waste recycling company.
Theoretically, recycling companies will throw away your device in a moral code:
- Reuse all devices by donating to those who can still use them.
- Repair and refurbish all equipment.
- Restore and reuse any components or peripherals that are still active.
- Recycle constituent materials that cannot be used.
- Responsible hazardous waste disposal, in licensed landfills. Each toxic material has a strict treatment process.
Be careful with 'fake' recycling companies.
Everything seems simple? Not quite so.
Recycling waste is a big problem and there is a fact: Old components in e-waste are less than the cost of recycling them, at least in the United States.
Vice.com's Jason Koebler wrote about a great discovery of the situation and found that there is a secondary industry developing: Fake recycler - 'fake recycling companies', making photos enjoy the work of sustainable legal recycling companies.
These "fake" companies sell e-waste to scrap yards in developing countries, often in Southeast Asia. In return, the junkyards use cheap local labor (and often underage) to find and select anything worth keeping, and throw away what is no longer valuable. These companies are not concerned with the environmental issues listed earlier.
Surprisingly, an industry watchdog has used a GPS tracker and found that up to 40% of US e-waste recycling companies fall into this 'scam' list.
How can you recycle e-waste sustainably?
There are many companies that will recycle your waste, in the most efficient and environmentally friendly way possible, but you will have to spend some time learning it. To make a wise choice, you need some basic information.
Back in 1989, 185 countries signed an international treaty called the "Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal", referred to as "the Convention. Basel ". It is the world's first remarkable effort to control the export of hazardous waste from developed countries to underdeveloped countries. In 1995, a revised proposal was introduced, aimed at completely banning the transport of hazardous waste from OECD Economic Cooperation and Development countries to developing countries, but not yet. ratify.
As a consequence of the treaty, the Basel Action Network (BAN) was established. Based in Seattle, the organization's non-governmental charity campaigns aim to prevent underdeveloped countries from becoming e-waste dumps.
Several initiatives have been launched. For a conscientious consumer e-waste recycling company, 'e-Stewards' is probably the most important factor.
e-Stewards has introduced a standard for responsible recycling and reuse of electronic devices. Companies that meet the requirements are awarded the Certified e-Stewards Recycler certification . To obtain this certification, recyclers must have the registered ISO 14001 environmental management system and pass two initial checks. After that, they have to go through annual tests and meet the performance requirements.
These are the companies you should look for. The e-Stewards website lists all eligible recycling companies there.
Be part of the solution to solve the problem
We all love technology. But be responsible technology lovers.
Do not harm the environment. Do not help propagate unethical companies, want to make profits quickly and do not care about environmental issues.
Study yourself and become part of the solution to solve the problem.
Do you know about e-waste related issues? Let us know your thoughts on this issue in the comment section below!
See more:
- Gold mine in landfill electronic components
- Examine the process of turning garbage into street bricks and clothes in Japan
- Incidentally: Used toilet paper can be recycled into electricity
You should read it
- ★ While many countries are 'flooded with garbage', the country is importing waste to use
- ★ Chemical recycling can be a solution to the problem of plastic waste pollution
- ★ The world's first biologist was built from agricultural waste
- ★ Dubai builds the world's largest waste-to-electricity recycling plant
- ★ How are people using plastic to destroy nature?