The clause combines UNION data in SQL
In SQL, you can combine the same structured data from multiple tables into one query using the UNION and UNION ALL operators. These tables are sometimes in the same database, sometimes in different databases.
- UNION combines but removes the same.
- UNION ALL combines but does not remove the same.
In this article, Quantum will guide in detail how to use the UNION clause in SQL with syntax and specific examples to make it easier to visualize and capture statements.
UNION in SQL
The UNION clause / SQL operator is used to combine the results of two or more SELECT statements without returning any duplicate records.
To use UNION, each SELECT statement must have the same number of columns, the same number of expressions of columns, the same data type, and the corresponding column must be in the correct order but not the same length.
UNION syntax in SQL
The basic syntax of the UNION clause is as follows:
SELECT cot1 [, cot2 ]
FROM bang1 [, bang2 ]
[WHERE dieu_kien]
UNION
SELECT cot1 [, cot2 ]
FROM bang1 [, bang2 ]
[WHERE dieu_kien]
Here, given dieu_kien can be any expression based on your requirements.
Example of UNION in SQL
Suppose the two tables are NHANVIEN and TIENTHUONG with the following records:
Table 1: NHANVIEN
+----+----------+-----+-----------+----------+ | ID | TEN |TUOI | DIACHI | LUONG | +----+----------+-----+-----------+----------+ | 1 | Thanh | 32 | Haiphong | 2000.00 | | 2 | Loan | 25 | Hanoi | 1500.00 | | 3 | Nga | 23 | Hanam | 2000.00 | | 4 | Manh | 25 | Hue | 6500.00 | | 5 | Huy | 27 | Hatinh | 8500.00 | | 6 | Cao | 22 | HCM | 4500.00 | | 7 | Lam | 24 | Hanoi | 10000.00 | +----+----------+-----+-----------+----------+
Table 2: TIENTHUONG
+-----+---------------------+-------------+--------+ |TT_ID| NGAY | NHANVIEN_ID | SOTIEN | +-----+---------------------+-------------+--------+ | 102 | 2019-01-08 00:00:00 | 3 | 3000 | | 100 | 2019-01-08 00:00:00 | 3 | 1500 | | 101 | 2019-02-20 00:00:00 | 2 | 1560 | | 103 | 2018-12-20 00:00:00 | 4 | 2060 | +-----+---------------------+-------------+--------+
Now we combine these two tables in the SELECT statement as follows:
SQL> SELECT ID, TEN, SOTIEN, NGAY
FROM NHANVIEN
LEFT JOIN TIENTHUONG
ON NHANVIEN.ID = TIENTHUONG.NHANVIEN_ID
UNION
SELECT ID, TEN, SOTIEN, NGAY
FROM NHANVIEN
RIGHT JOIN TIENTHUONG
ON NHANVIEN.ID = TIENTHUONG.NHANVIEN_ID;
The result is:
+------+----------+--------+---------------------+ | ID | TEN | SOTIEN | NGAY | +------+----------+--------+---------------------+ | 1 | Thanh | NULL | NULL | | 2 | Loan | 1560 | 2019-02-20 00:00:00 | | 3 | Nga | 3000 | 2019-01-08 00:00:00 | | 3 | Nga | 1500 | 2019-01-08 00:00:00 | | 4 | Manh | 2060 | 2018-12-20 00:00:00 | | 5 | Huy | NULL | NULL | | 6 | Cao | NULL | NULL | | 7 | Lam | NULL | NULL | +------+----------+--------+---------------------+
UNION ALL in SQL
The clause / UNION ALL operator in SQL is used to combine the results of two or more SELECT statements including duplicate records.
The rules applicable to UNION also apply to the UNION ALL operator.
The UNION ALL syntax in SQL
The basic syntax of UNION ALL clause is as follows:
SELECT cot1 [, cot2 ]
FROM bang1 [, bang2 ]
[WHERE dieu_kien]
UNION ALL
SELECT cot1 [, cot2 ]
FROM bang1 [, bang2 ]
[WHERE dieu_kien]
Here, given dieu_kien can be any expression based on your requirements.
Example of UNION ALL in SQL
Suppose the two tables are NHANVIEN and TIENTHUONG with the following records:
Table 1: NHANVIEN
+----+----------+-----+-----------+----------+ | ID | TEN |TUOI | DIACHI | LUONG | +----+----------+-----+-----------+----------+ | 1 | Thanh | 32 | Haiphong | 2000.00 | | 2 | Loan | 25 | Hanoi | 1500.00 | | 3 | Nga | 23 | Hanam | 2000.00 | | 4 | Manh | 25 | Hue | 6500.00 | | 5 | Huy | 27 | Hatinh | 8500.00 | | 6 | Cao | 22 | HCM | 4500.00 | | 7 | Lam | 24 | Hanoi | 10000.00 | +----+----------+-----+-----------+----------+
Table 2: TIENTHUONG
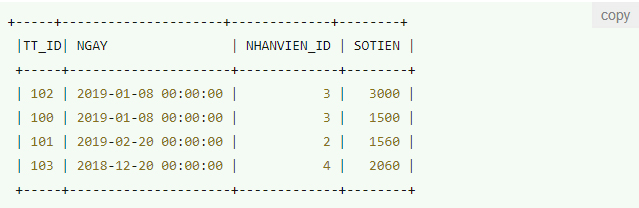
Now we combine these two tables in the SELECT statement as follows:
SQL> SELECT ID, TEN, SOTIEN, NOW
FROM NHANVIEN
LEFT JOIN TIENTHUONG
ON NHANVIEN.ID = TIENTHUONG.NHANVIEN_ID
UNION ALL
SELECT ID, TEN, SOTIEN, NOW
FROM NHANVIEN
RIGHT JOIN TIENTHUONG
ON NHANVIEN.ID = TIENTHUONG.NHANVIEN_ID;
The result is:
+------+----------+--------+---------------------+ | ID | TEN | SOTIEN | NGAY | +------+----------+--------+---------------------+ | 1 | Thanh | NULL | NULL | | 2 | Loan | 1560 | 2019-02-20 00:00:00 | | 3 | Nga | 3000 | 2019-01-08 00:00:00 | | 3 | Nga | 1500 | 2019-01-08 00:00:00 | | 4 | Manh | 2060 | 2018-12-20 00:00:00 | | 5 | Huy | NULL | NULL | | 6 | Cao | NULL | NULL | | 7 | Lam | NULL | NULL | | 3 | Nga | 3000 | 2019-01-08 00:00:00 | | 3 | Nga | 1500 | 2019-01-08 00:00:00 | | 2 | Loan | 1560 | 2019-02-20 00:00:00 | | 4 | Manh | 2060 | 2018-12-20 00:00:00 | +------+----------+--------+---------------------+
In addition, there are two other clauses / operators similar to the UNION clause:
- The INTERSECT clause in SQL : is used to combine two SELECT statements, but returns rows only from the first SELECT statement that is the same as the one in the second SELECT statement.
- The EXCEPT clause in SQL : is used to combine two SELECT statements and return rows from the first SELECT statement that are not returned by the second SELECT statement.
In the next articles, Quantrimang will discuss with you the NULL value in SQL. Have you remembered to it!
Previous lesson: The JOIN data clause in SQL
Next lesson: NULL value in SQL