Replica Set in MongoDB
Replication is the process of synchronizing data from multiple servers. Replication provides redundancy and increased data availability for multiple data copies on many different Database Servers. Replication protects a database from the loss of a particular Server. Replication also allows you to recover data from hardware errors or service disconnections. With additional data copies, you can use it for recovery, reporting, or backup.
Why use Replication?
To make your data safe.
High availability of data (24 * 7).
Recover data due to an error.
It doesn't take time to maintain (like backup, rebuild the index).
Expand readability (read from additional copies).
Replica Set is transparent for the application.
How Replication works in MongoDB
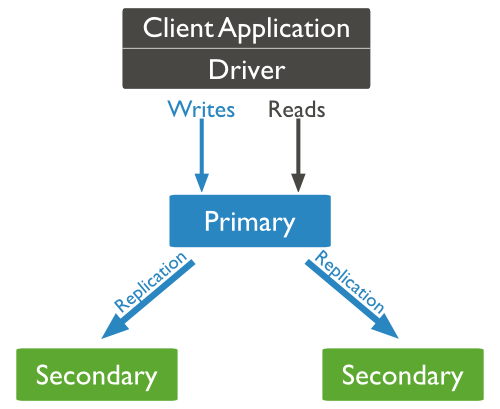
MongoDB uses Replica Set to implement Replication. A Replica Set is a group of mongodb instances that host the same data. In a Replica, a node that is Primary node (can be called a secondary node) will receive all write operations. All other, secondary instances, apply operations from the secondary node so that they have the same data set. Replica Set can have only one secondary node.
- Replica Set is a group of two or more nodes (generally, need at least 3 nodes).
- In a Replica Set, a node is a secondary node and the other nodes are primary.
- All data replicated from primary node to secondary node.
- At the time of automatic maintenance, the selection for the primary and a primary node is selected.
- After the node recovery has failed, it again combines Replica Set and works as a secondary node.
Below is a Replication-specific diagram in MongoDB, in which the Client application always interacts with the primary node and this primary node then recreates the data for the secondary node.
Features of Replica Set
A Cluster consists of N nodes
Any node can be primary
All activities are recorded in elementary level
Automatically maintained
Auto recovery
Install a Replica Set
In this chapter, we will convert the instance to a Replica Set. To convert to Replica Set, follow these steps:
Turn off MongoDB Server running.
Now, start MongoDB Server with the --replSet option specified . --ReplSet 's basic syntax is as follows:
mongod -- port "PORT" -- dbpath "YOUR_DB_DATA_PATH" -- replSet "REPLICA_SET_INSTANCE_NAME"
For example
mongod -- port 27017 -- dbpath "D:set upmongodbdata" -- replSet rs0
It will start an instance with the name rs0, on port 27017. Now, start the command line and connect to this instance. In the Mongo Client notice the rs.initiate () command to initialize a new Replica Set. To check the Replica Set configuration, you notice the command rs.conf () . To check the status of Replica Set, you notice the command rs.status () .
Add members to Replica Set
To add members to Replica Set, start instance descriptions on multiple devices. Now, start a Mongo Client and notice a command rs.add ().
Syntax
The basic syntax of rs.add () is as follows:
> rs . add ( HOST_NAME : PORT )
For example
Suppose the name of your mongod instance is mongod1.net and is running on port 27017 . To add this instance to Replica Set, you tell rs.add () in Mongo Client:
> rs . add ( "mongod1.net:27017" ) >
You can add an instance to Replica Set only if you are connected to the primary node. To check if you have connected to this primary node, you report the db.isMaster () command in Mongo Client.
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Aggregation in MongoDB
Next article: Shard in MongoDB