Multiple Inheritance in Python
In the previous lesson, we learned about Inheritance in object-oriented programming of Python language. Inheritance allows us to declare the new class to re-use the parent class's functions and attributes and extra functions. In this article, Quantrimang will continue the lesson with the theme Inheritance but at a deeper level, which is the Inheritance and the order of method access of the parent classes (Method Resolution Order).
Multiple Inheritance
Like C ++, in Python a class can be defined from multiple parent classes. This is called multiple inheritance.
Syntax:
class LopCha1:
pass
class LopCha2:
pass
class LopCon(LopCha1, LopCha2):
pass

Subclasses are defined from multiple parent classes and inherit the characteristics of both classes.
Parent classes can have the same properties or methods. The subclass will prioritize inheriting the attribute, the class method is first in the inheritance list.
Multi-level inheritance (Multilevel Inheritance)
In addition to being able to inherit from parent classes, you can also create new subclasses that inherit previous subclasses. This is called multi-level inheritance (Multilevel Inheritance).
In this case, the properties of the parent class and the previous subclass will be inherited by the new subclass.
Syntax:
class LopCha:
pass
class LopCon1(LopCha):
pass
class LopCon2(LopCon1):
pass

LopCon1 inherits LopCha, LopCon2 inherits LopCon1.
Method Resolution Order (Method Resolution Order)
Class is derived from object. In a multiple inheritance scenario, any attributes that need to be retrieved will first be searched in the current class. If not found, search continues to the first parent class and left to right.
So the order of access will be [LopCon, LopCha1, LopCha2, object].
This order is also called linearization of LopCon and the set of rules used to find this order is called the Method Access Order (MRO).
In simple terms, MRO is used to display lists / tuples of parent classes of a particular class.
MRO is used in two ways:
- __mro__: returns a tuple
- mro (): returns a list.
>>> LopCon.__mro__
( ,( ,
,
,
)
>>> LopCon.mro()
[ ,[ ,
,
,
]
Here is a complex inheritance example and its visual display along with the MRO.
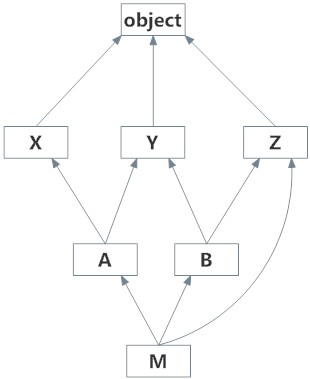
class X: pass
class Y: pass
class Z: pass
class A(X,Y): pass
class B(Y,Z): pass
class M(B,A,Z): pass
# Output:
# [ , ,# [ , ,# [ , ,
# , ,# , ,# , ,
# , ,# , ,# , ,
# ]# ]
See more:
- More than 100 Python exercises have solutions (sample code)
- Free online Python interpreter
- Some tools run Python on Android
Last lesson: Inheritance (Inheritance) in Python
Next lesson: Overload operator in Python