The function memcpy () in C
Function void * memcpy (void * str1, const void * str2, size_t n) copies n characters from str2 to str1 .
Declare the function memcpy () in C
Below is the declaration for memcpy () in C:
void * memcpy ( void * str1 , const void * str2 , size_t n )
Parameters
str1 - This is the pointer to the destination array, where the content to be copied, cast into a pointer of type void *.
str2 - This is the pointer to the data source to copy, cast into a pointer of type void *.
n - This is the number of bytes to be copied.
Returns the value
This function returns a pointer to the destination string, str1.
For example
The following program C illustrates the usage of memcpy () in C:
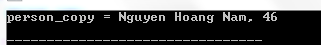
#include #include struct { char name [ 40 ]; int age ; } person , person_copy ; int main () { char myname [] = "Nguyen Hoang Nam" ; /* su dung ham memcpy de sao chep chuoi: */ memcpy ( person . name , myname , strlen ( myname )+ 1 ); person . age = 46 ; /* su dung ham memcpy de sao chep struct: */ memcpy ( & person_copy , & person , sizeof ( person ) ); printf ( "person_copy = %s, %d n" , person_copy . name , person_copy . age ); return 0 ; } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Function memcmp () in C
Next lesson: memmove function in C
Share by
Micah Soto
Update 25 May 2019