Function freopen () in C
Function FILE * freopen (const char * filename, const char * mode, FILE * stream) in Library C attaches a new filename with the given Stream and at the same time closes the old FILE in Stream.
Declaring the function freopen () in C
Below is the declaration for freopen () function in C:
FILE * freopen ( const char * filename , const char * mode , FILE * stream )
Parameters
filename - This is the string containing the file name to be opened.
mode - This is the string containing the file access mode. Include:
mode Description "r" Open a file to read. File must exist "w" Create an empty file to write. If a file with the same name already exists, its content is removed and the file is treated as a new blank file "a" Append to a file. With write operations, append data at the end of the file. The file is created if it does not already exist "r +" Open a file to write and read. File must exist "w +" Create an empty file to write and read "a +" Open a file to read and appendstream - This is the pointer to a FILE object that identifies the Stream to be reopened.
Returns the value
If the file is successfully reopened, the function returns a pointer to an object that identifies the Stream, otherwise the null pointer is returned.
For example
The following C program illustrates the usage of freopen () function in C:
#include int main () { FILE * fp ; printf ( "Dong text nay hien thi tren stdoutn" ); fp = freopen ( "baitapc.txt" , "w+" , stdout ); printf ( "Dong text nay duoc ghi vao baitapc.txtn" ); fclose ( fp ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above program will send the following line at STDOUT first:
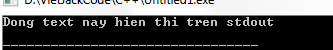
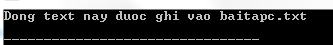
After the call to freopen (), it binds STDOUT to baitp.txt, so whatever we write at STDOUT will go into baitapc.txt. Therefore, the baitapc.txt will have the following content:

Now you follow the contents of the above file by using the following C program:
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous lesson: Function fread () in C
Next lesson: Function fseek () in C